ISSN
2307–3489 (Print), ІSSN
2307–6666
(Online)
Наука
та прогрес транспорту. Вісник
Дніпропетровського
національного університету залізничного
транспорту, 2018,
№ 4 (76)
МОДЕЛЮВАННЯ
ЗАДАЧ ТРАНСПОРТУ ТА ЕКОНОМІКИ
МОДЕЛЮВАННЯ
ЗАДАЧ ТРАНСПОРТУ ТА ЕКОНОМІки
UDC
624.953.014.2.004.15
s. n. semenets1*,
s. s. nasonova2*,
G. I. semenets3*
1*Dep.
«Applied Mathematics and
Information Technologies»,
Pridneprovsk State Academy of Civil Engineering and Architecture,
Chernishevskiy St., 24-A, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49600, tel. +38 (067) 639
60 64,
e-mail Ssemenets28@gmail.com,ORCID
0000-0002-6359-1069
2*Dep.
«Higher Mathematics», Ukrainian State Chemical-Technological
University, Gagarin Av., 8, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49005, tel. +38
(097) 940 98 56,
e-mail ms.nasonova.s@gmail.com, ORCID
0000-0002-0920-7417
3*Dep. «Higher Mathematics»,
Dnipropetrovsk National University of Railway Transport named after
Academician V. Lazaryan, Lazaryan St., 2, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49010,
tel. +38 (096) 879 48 19,
e-mail semga1952@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0003-2693-3282
OPTIMAL STRUCTURAL RESERVATION OF
TECHNICAL SYSTEMS
Purpose.
The purpose of the article is to give designers of highly
reliable technical systems that do not have special knowledge in the
field of optimization and programming skills, a simple and accessible
mathematical tool for choosing the optimal solution for structural
redundancy of systems. Methodology. The article poses the
problem of optimal structural redundancy of technical systems. Two
typical redundancy schemes are considered: a) a separate «hot»
backup scheme; b) a separate «cold» backup scheme. The
computational models for estimating the reliability of redundant
systems are formulated. We offer optimization models that allow us to
find a rational option for reserving a system that is being designed,
taking into account conflicting requirements for its reliability and
cost. These models are numerically implemented in the operating
environment of the Excel spreadsheet as applied to the main object,
consisting of 7 elements. The optimal variants of reserving this
object according to the «hot» and «cold» separate reservation
schemes are given. Findings. Calculated models for estimating
reliability, as well as models for optimizing the systems reserved
for the «hot» and «cold» separate backup schemes, have been
developed. With the use of the Excel spreadsheet, the optimal options
for reserving 7 element objects are found for separate «hot» and
«cold» backups. Originality. New computational models for
estimating the reliability of redundant systems are proposed, as well
as optimization models developed on the basis of these, which are
formulated using the decomposition of unknown initial problem of
structural redundancy into binary components. In this case, the
obtained optimization models belong to the class of problems of
non-linear mathematical programming with binary variables, for the
numerical solution of which (even for a sufficiently large dimension)
well-known packages of applied computer programs, in particular, the
MS Excel spreadsheet, are well adapted. Thus, the process of solving
the initially very complicated problem of optimal structural
redundancy is much simpler and reduced to performing elementary
actions in the corresponding software interfaces.
Practical
value. The proposed calculation models for estimating the
reliability of redundant systems, models for optimal structural
redundancy, and the methodology for their formation, in order to
simplify further numerical implementation, can be useful in solving
problems of ensuring the reliability of technical systems in the
early stages of their design.
Keywords: system; design; reliability; structural
reservation; model; optimization; binary variables
Introduction
Inadequate design reliability
of technical systems leads to a significant increase in the share of
operating costs in total expenditures for their design, fabrication
and application. At the same time, the cost of operation can many
times exceed the cost of designing and manufacturing the system [1,
3, 10]. Therefore, the reliability of technical systems should be
ensured, first of all, at the design stage [2, 12, 13].
One of the main methods for
ensuring the reliability of the technical systems being designed is
the method of structural redundancy [6-8], which involves the use of
redundant elements in the system. The essence of structural
redundancy lies in the fact that in addition to the main (reserved)
object containing the minimum required number of elements for the
normal performance of the system's functions, in the system
structure the additional identical (in terms of performed
operational functions and reliability) elements are introduced.
These redundant elements are designed to perform the work functions
of the main elements. Thus, a system with redundancy is a system
containing redundant structural components with respect to being
reserved object that perform the same work functions as the
corresponding components of the main object. The redundant system
remains operable after subsequent failure of any element if the
number of operable elements does not become less than the minimum
required number provided for by regulatory requirements for the main
object.
The problem of rational choice
of one of the several variants of the system composition always
arises during the structural redundancy. On the one hand, to
increase reliability it is desirable to provide each of the system
elements with maximum possible number of redundant elements, and, on
the other hand, it is impossible to design a system with too large
cost, weight or dimensions. Therefore, the actual task is how to
reserve the system in such a way as to provide the required level of
system reliability at acceptable costs. The choice of the cost
characteristic is determined by the type of the system and its
purpose. For example, for aircrafts the essential factor is weight,
and for the ground system – the cost. Regardless of the physical
essence, the selected cost characteristic for brevity below will be
referred to as cost. Usually, the problems of optimal structural
redundancy of technical systems are formulated as non-linear
programming problems, and to solve them, depending on the complexity
and required accuracy, the special algorithms are used. They are
based primarily on the dynamic programming method [6]. In this
article, the initial optimization model is represented in terms of
the problem of non-linear integer programming with binary variables,
which greatly simplifies its numerical implementation.
Purpose
The purpose of the article is
to give the designers of highly reliable technical systems that do
not know modern optimization methods and programming skills, a
simple mathematical tool for choosing the optimal structure of a
redundant system.
Methodology
During
problem definition of the optimal structural redundancy, the main
object is considered as a system consisting of
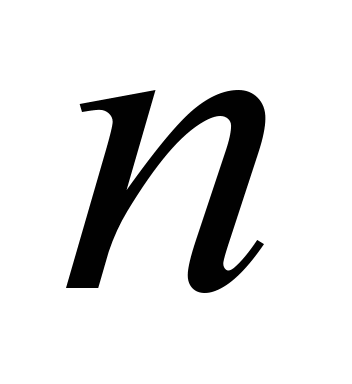 of various elements that have a coherent connection [4] (see Fig.
1).
of various elements that have a coherent connection [4] (see Fig.
1).
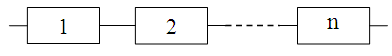
Fig.
1. Structural diagram of reliability
of the main object
As the main indicator of
reliability of the redundant system, the probability of its
fail-safe operation is assumed. It is believed that the failure flow
of elements put into operation is described by the Poisson arrival
[5]. Possible variants of the main object redundancy are limited to
the consideration of typical schemes of separate «cold» backup
with an integer multiplicity with an ideal switch (see Fig. 2) and
«hot» backup with parallel connection of elements (see Fig.3) [7].
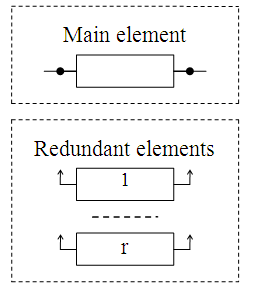
Fig.
2. Structural scheme of
reliability at «cold» backup
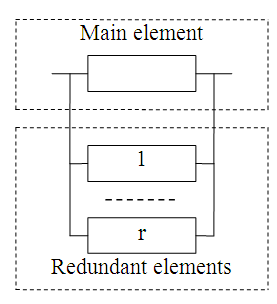
Fig.
3. Structural scheme of
reliability at «hot» backup
Note that, taking into account
the assumptions made, the probability of failure-free operation of
the redundant group of elements, the scheme of structural
reliability of which is shown in Fig. 2, is determined by the
Erlangian formula [5, 9]
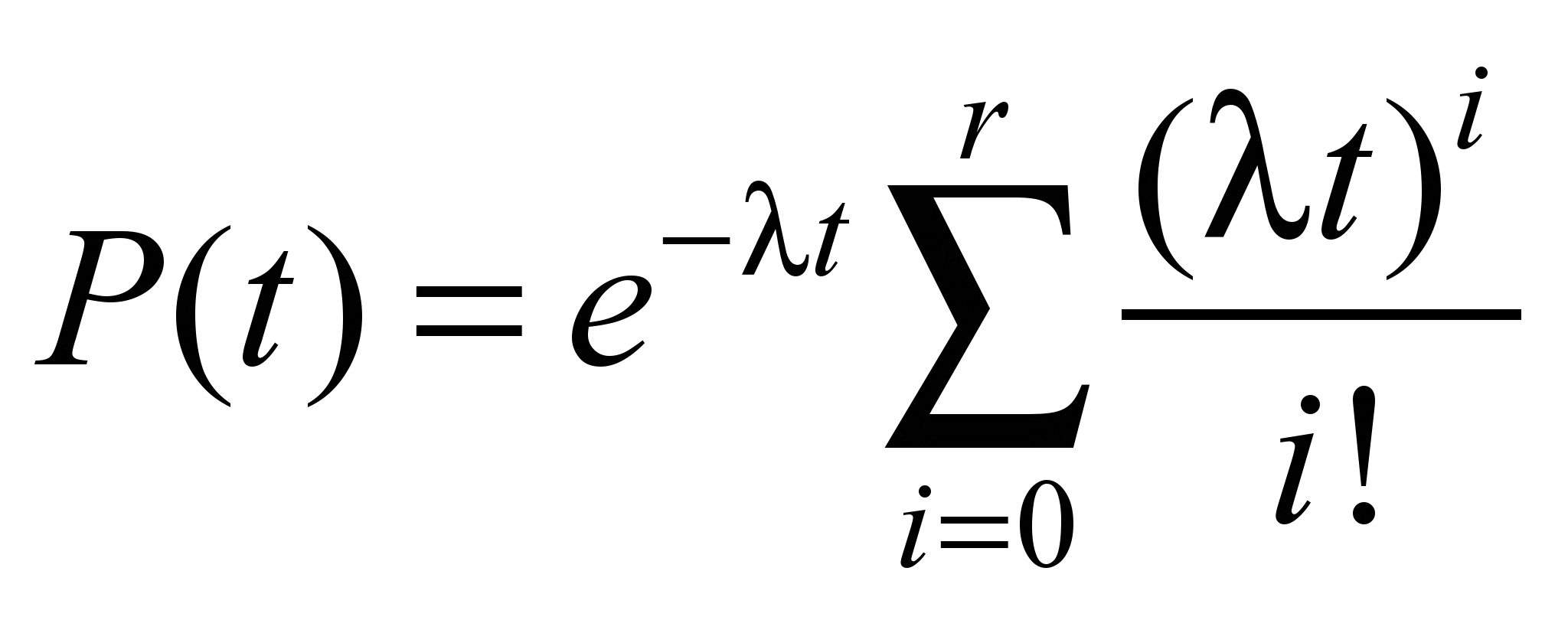 , (1)
, (1)
and the
formula for calculating the probability of failure-free operation of
a redundant group of elements, the structural scheme of reliability
of which is shown in Fig. 3, has the form
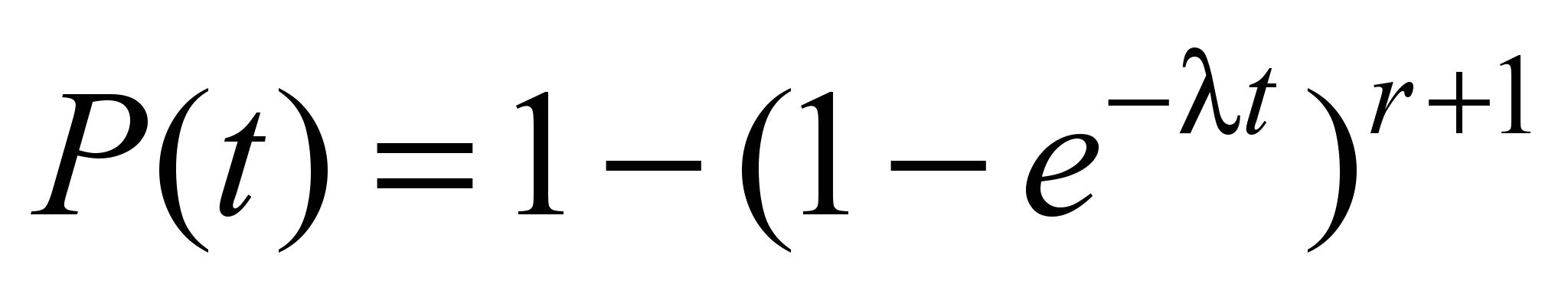 , (2)
, (2)
where
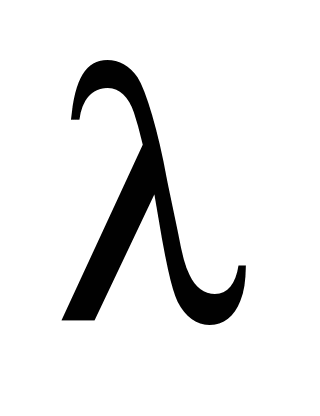 – is the failure rate of the element put into operation;
– is the failure rate of the element put into operation;
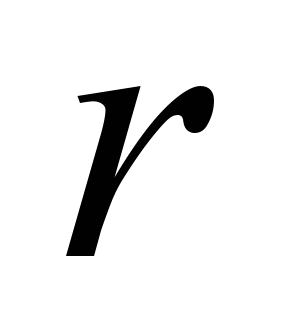 – is the redundancy rate.
– is the redundancy rate.
Let us
introduce the following designations:
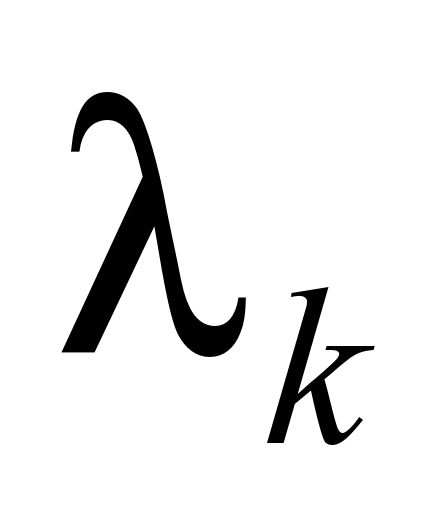 – is the failure rate of the element of the
– is the failure rate of the element of the
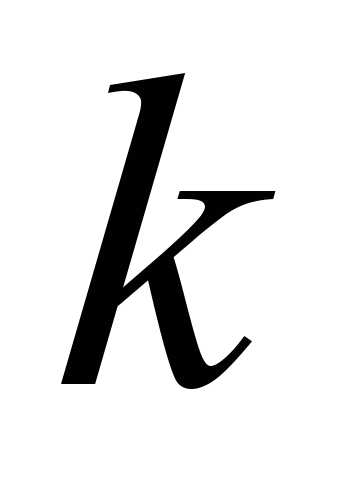 -th
type put into operation;
-th
type put into operation;
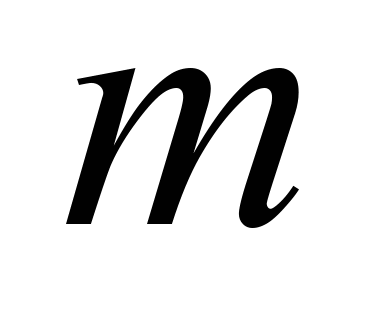 – is the maximum allowable redundancy rate of main elements;
– is the maximum allowable redundancy rate of main elements;
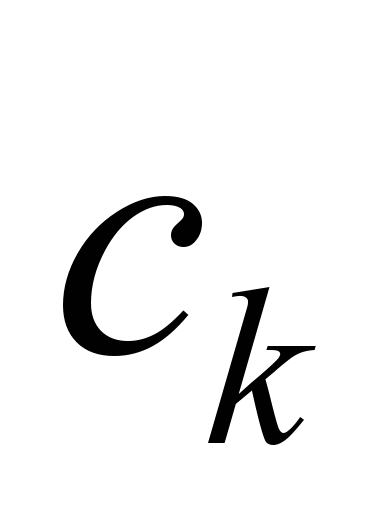 – is the cost of one element of the
– is the cost of one element of the
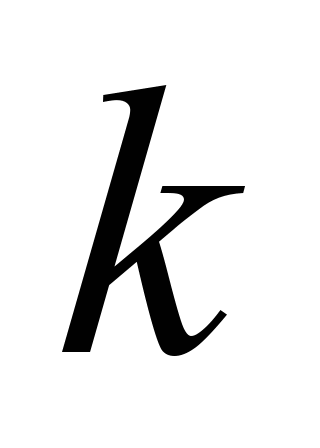 -th
type;
-th
type;
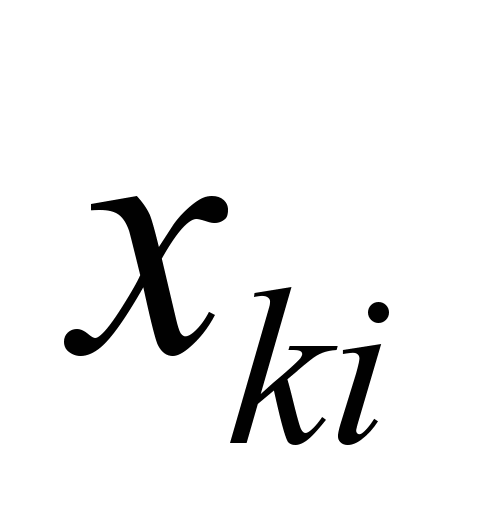 – is the binary variable, equal to 1, if the number of redundant
elements of the
– is the binary variable, equal to 1, if the number of redundant
elements of the
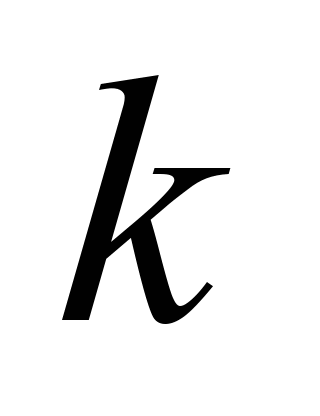 -th
is equal to
-th
is equal to
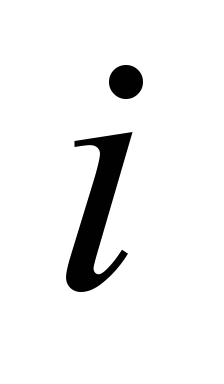 ,
and
,
and
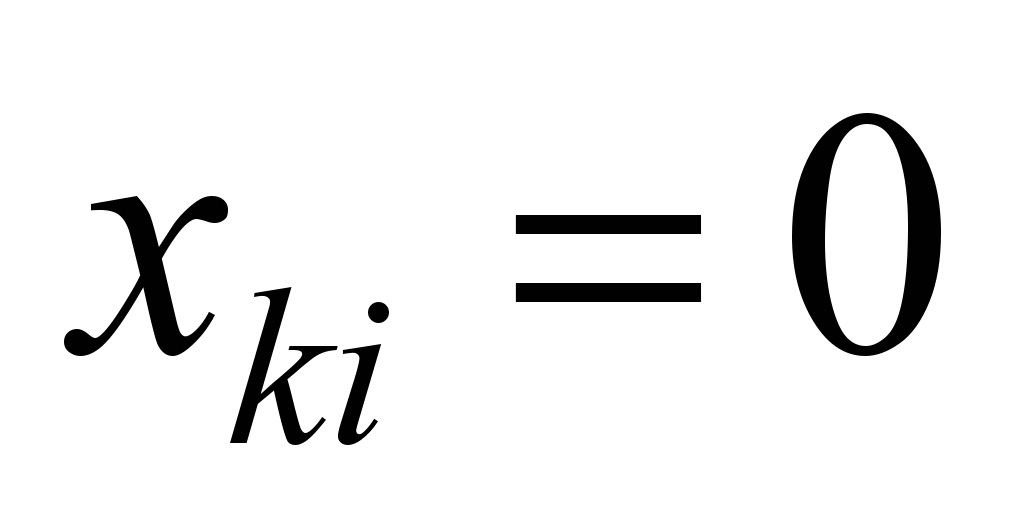 ,
f the number of redundant elements of the
,
f the number of redundant elements of the
 -th
type is not equal to
-th
type is not equal to
 ;
;
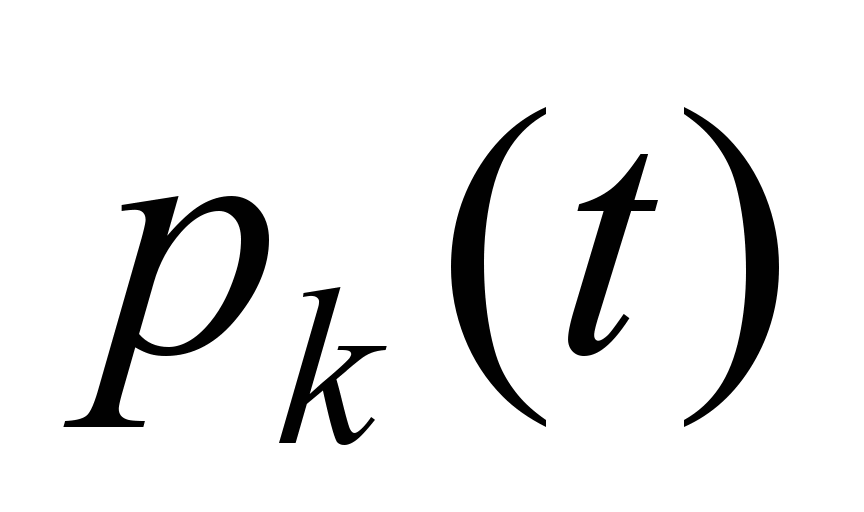 – is the probability of fail-safe operation of the main element of
the
– is the probability of fail-safe operation of the main element of
the
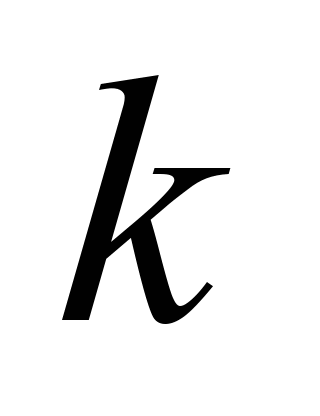 -th
type, over the time
-th
type, over the time
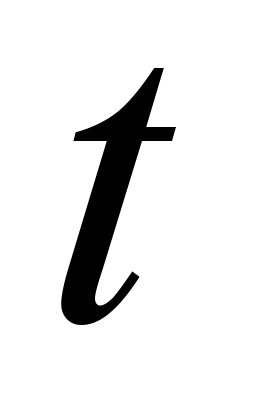
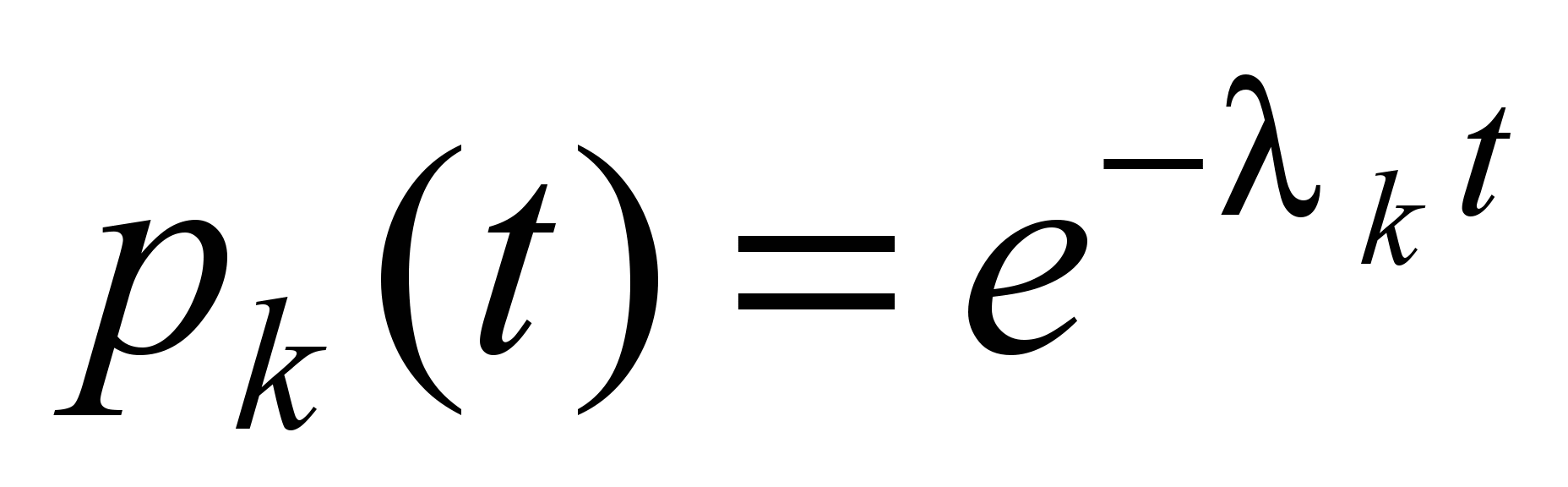 .
.
Let us
consider a redundant group of elements, consisting of the elements
of the
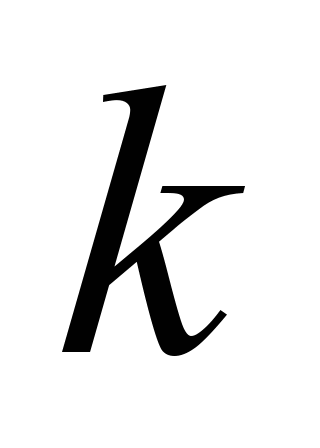 -th
type. Taking into account the introduced designations, the
probability of failure-free operation of a redundant group at «cold»
backup is estimated by formula
-th
type. Taking into account the introduced designations, the
probability of failure-free operation of a redundant group at «cold»
backup is estimated by formula
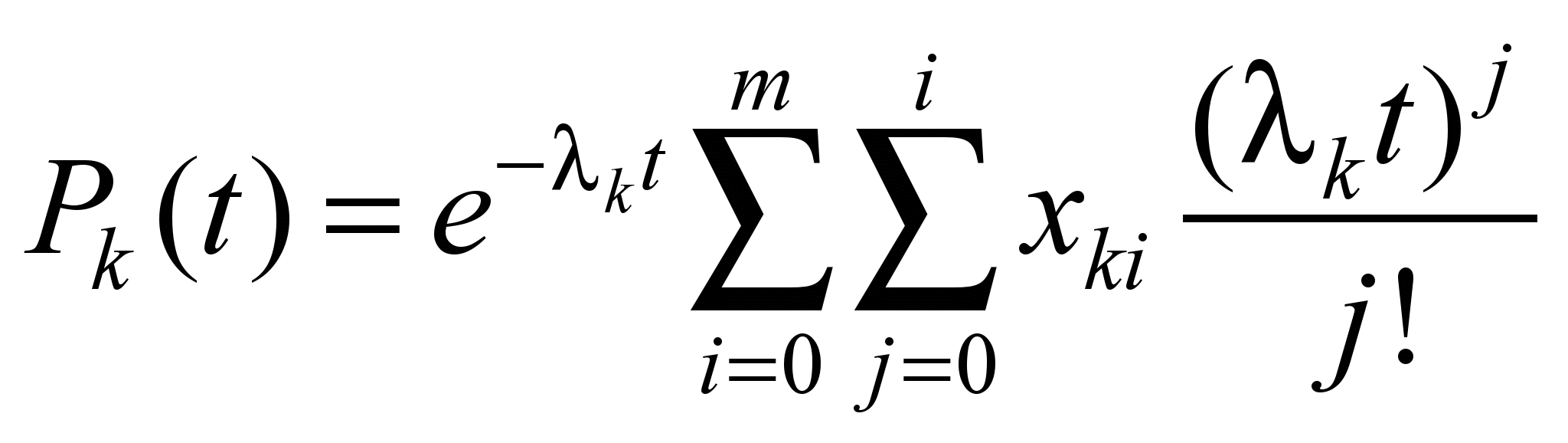 , (3)
, (3)
and
when using the «hot» backup scheme, this probability is
represented as follows
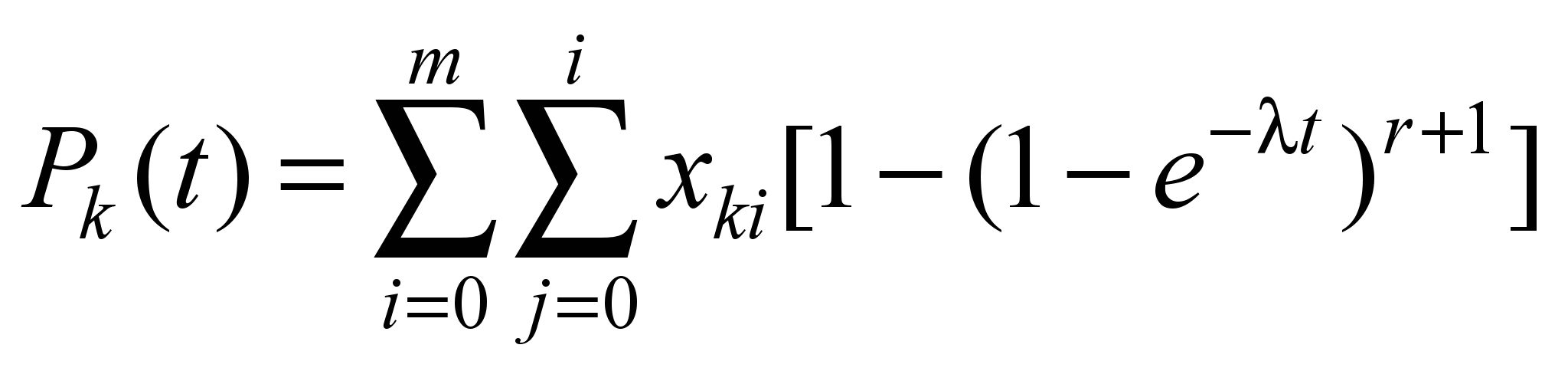 . (4)
. (4)
With neglect
of the cost of switching equipment in case of «cold» backup, the
cost of the redundant group consisting of the elements of the
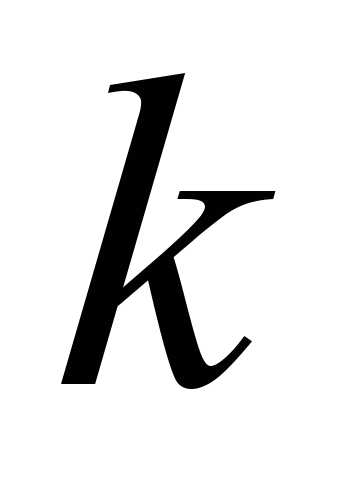 -th
type in both backup schemes can be found using formula
-th
type in both backup schemes can be found using formula
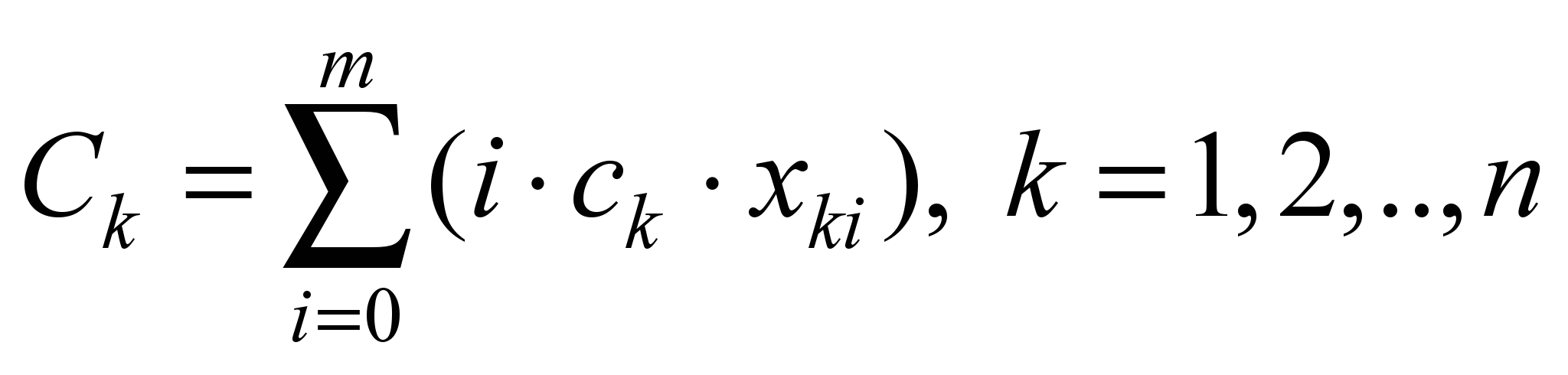 . (5)
. (5)
Taking into account the
coherent connection of the main elements and the product rule, the
probability of failure-free operation and the cost of the entire
redundant system are determined as follows:
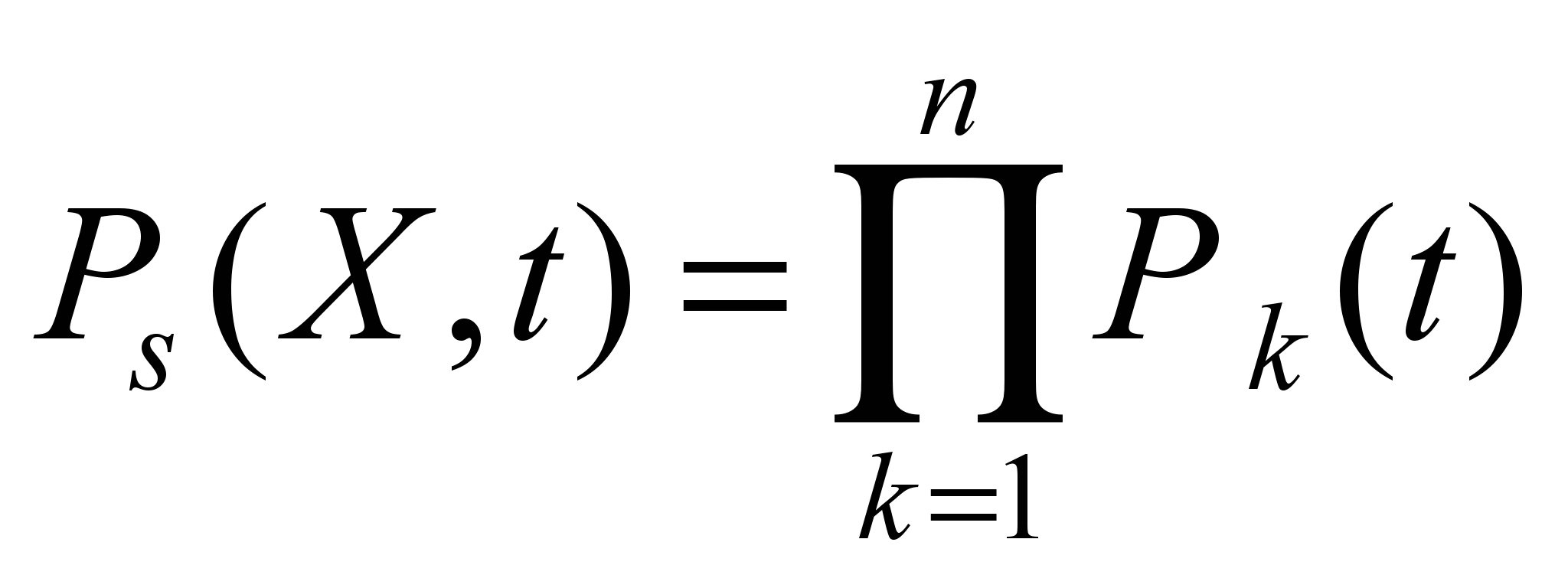 ; (6)
; (6)
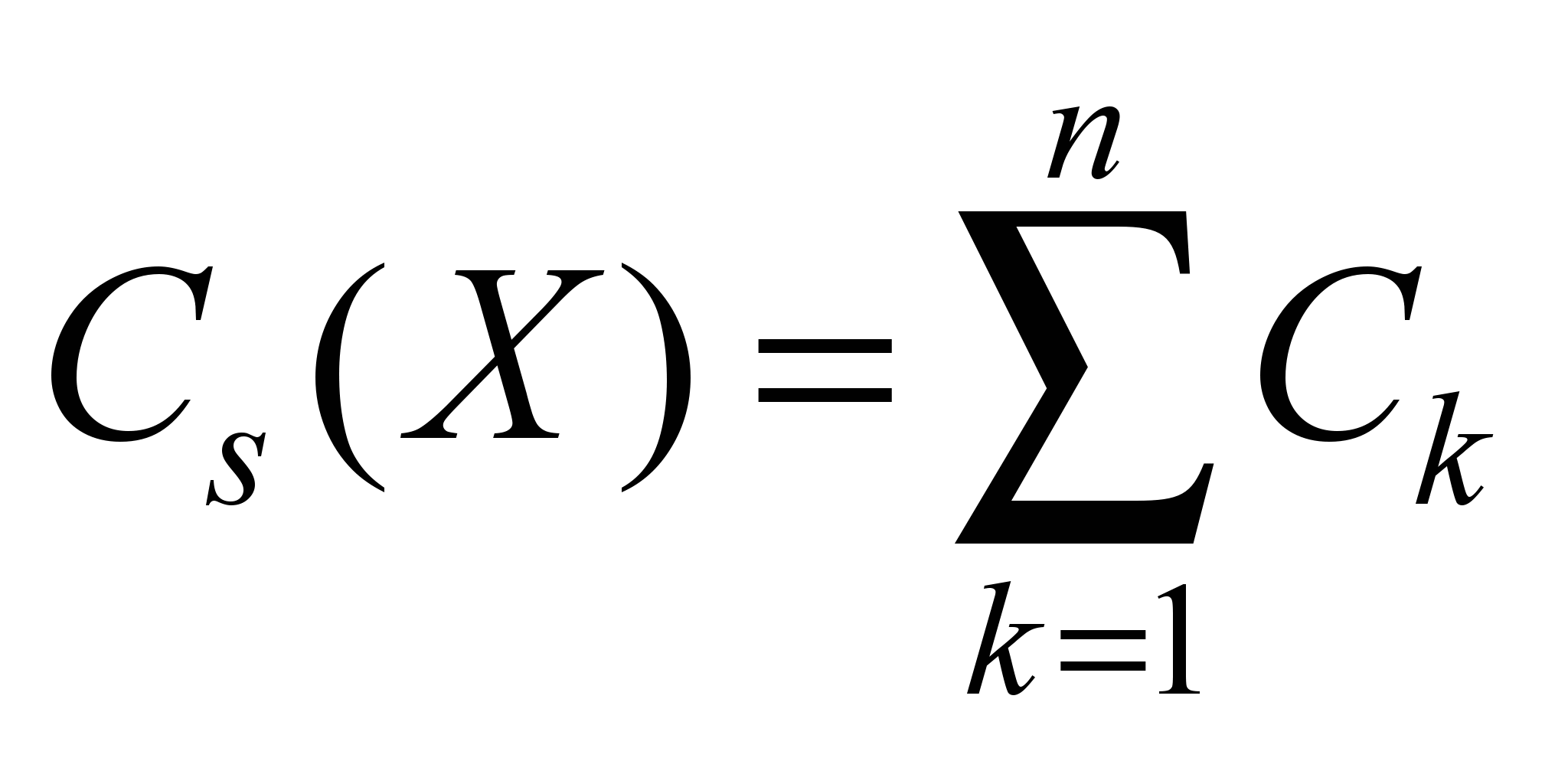 , (7)
, (7)
where
 – is the matrix describing composition of the elements
of the redundant system
– is the matrix describing composition of the elements
of the redundant system
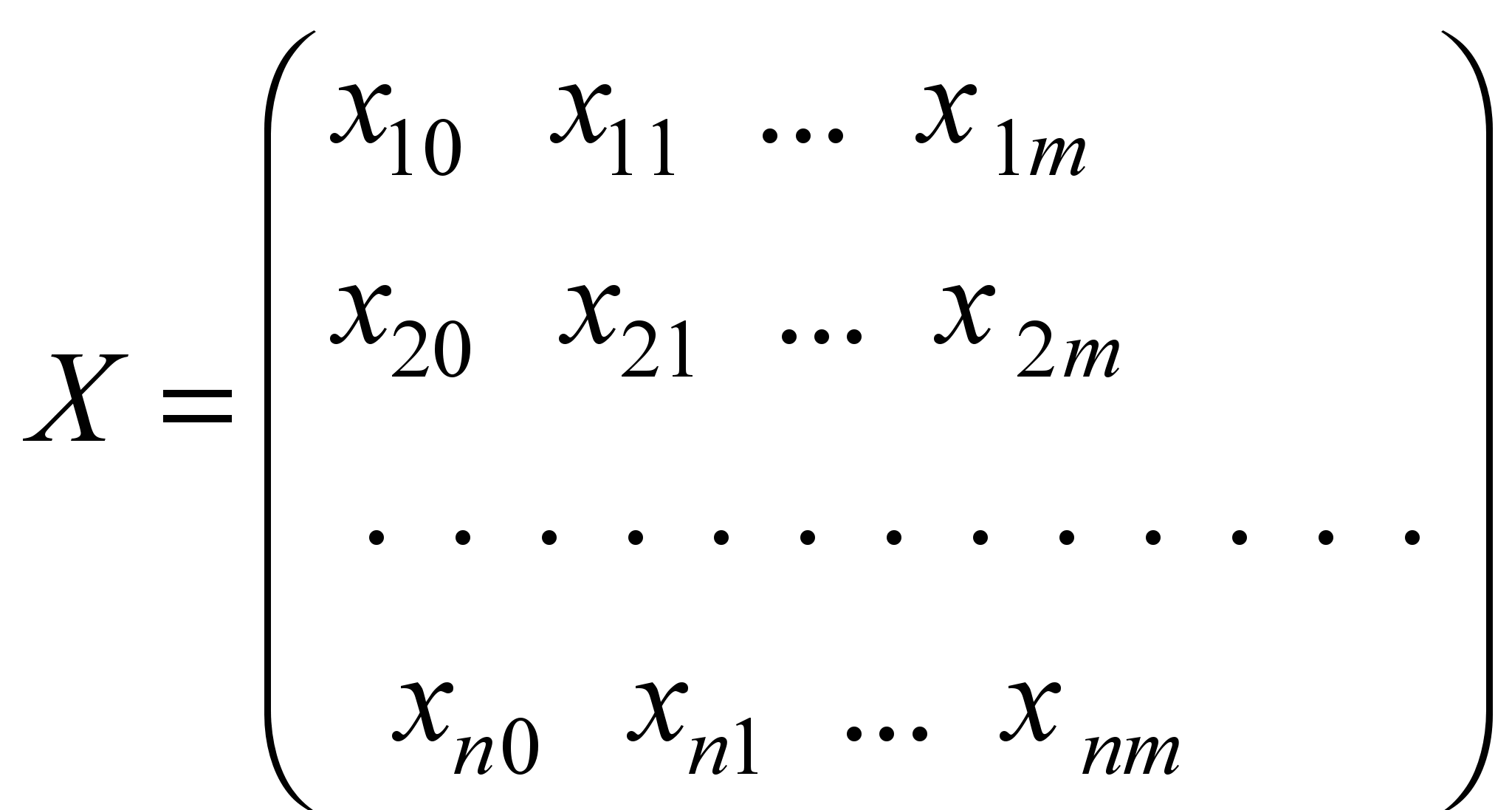 ,
,
and the
probabilities
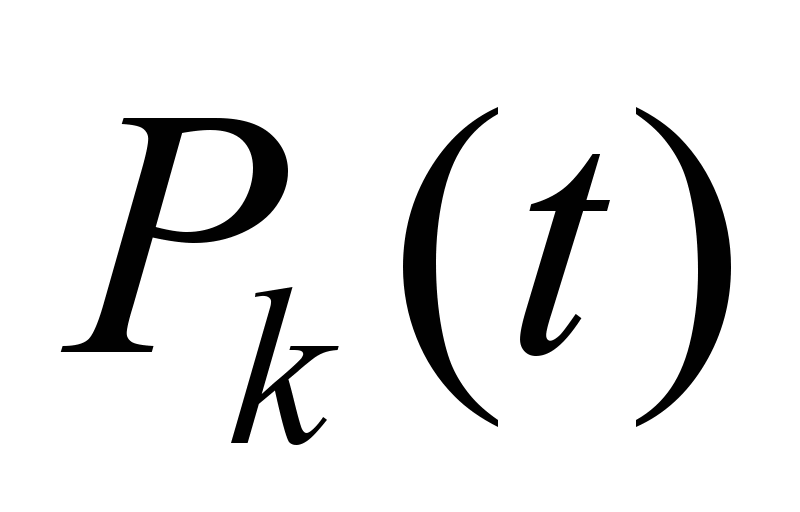 are
determined using formulas (3) and (4) depending on the backup scheme
used.
are
determined using formulas (3) and (4) depending on the backup scheme
used.
In terms of
the mathematical programming problem, the following two typical
statements of the task of optimal structural redundancy are
possible.
The problem
1: it is required to find the composition of redundant elements
(matrix elements
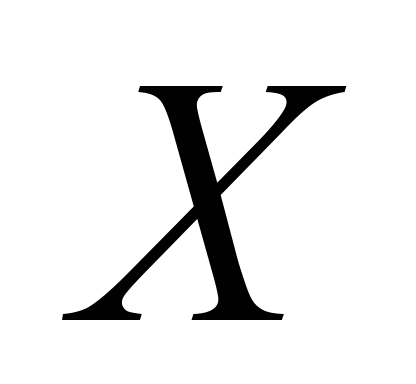 )
that provides the required level of system reliability for a given
time at the lowest possible cost
)
that provides the required level of system reliability for a given
time at the lowest possible cost
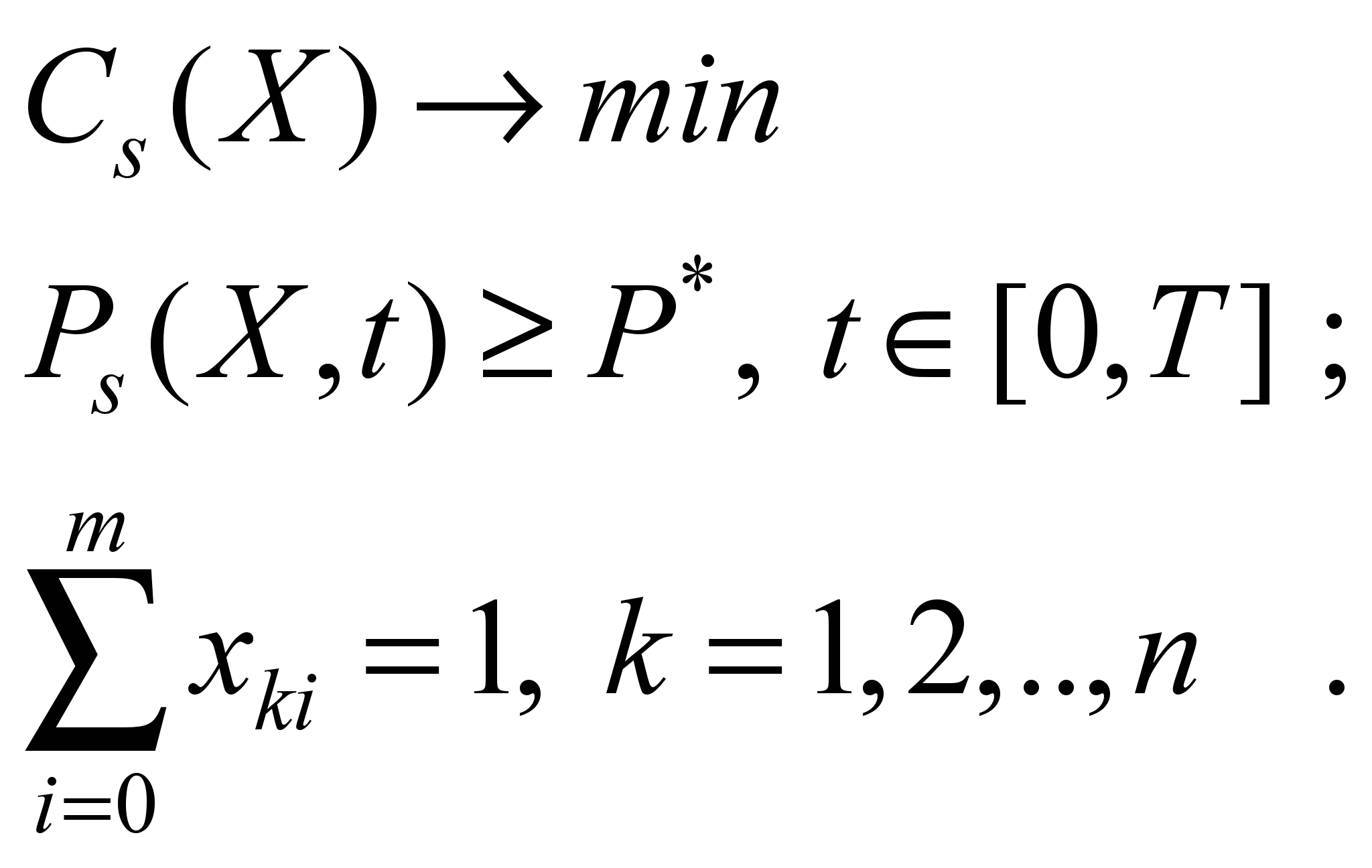 (8)
(8)
The problem
2: it is required to find the composition of redundant elements,
which provides the highest possible level of system reliability for
a given time
 ,
with a restriction on its cost
,
with a restriction on its cost
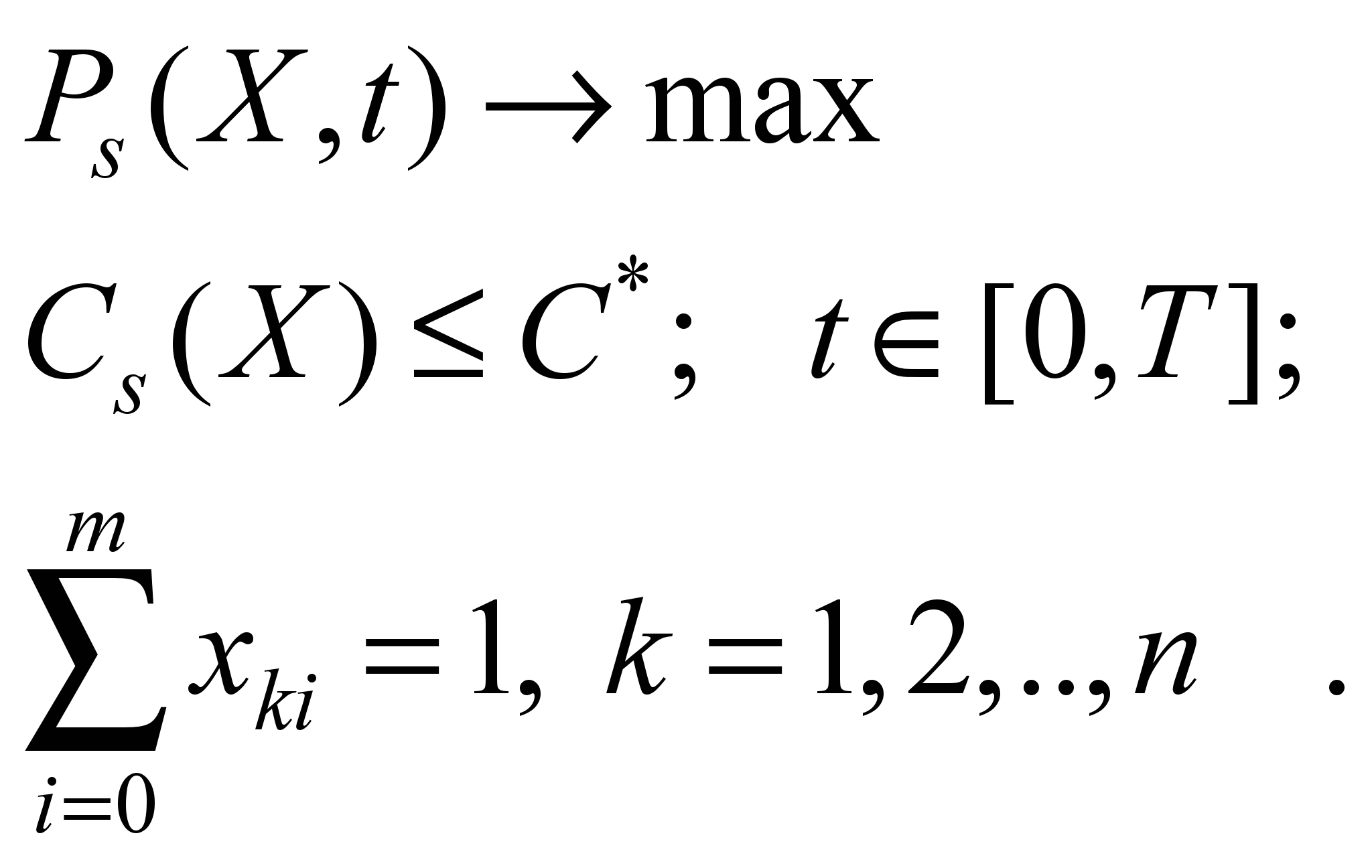 (9)
(9)
The
optimization models (8) and (9) have dimensions
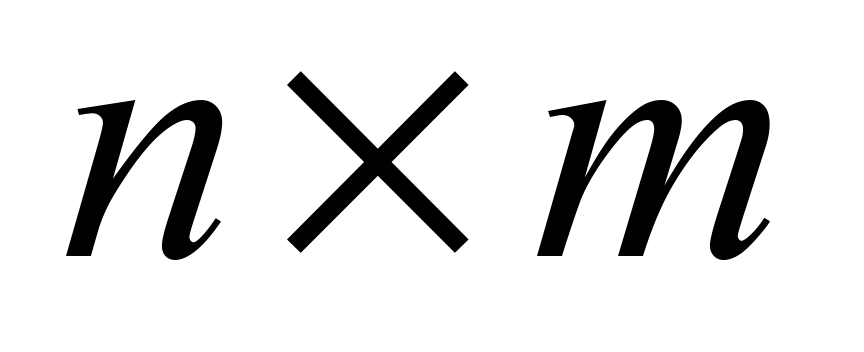 and belong to the class of problems of integer nonlinear programming
with binary variables. The model (8) was numerically realized for
cases of «cold» and «hot» separate backup using the MS Excel
Solver add-in. The problem was solved with the following initial
data:
and belong to the class of problems of integer nonlinear programming
with binary variables. The model (8) was numerically realized for
cases of «cold» and «hot» separate backup using the MS Excel
Solver add-in. The problem was solved with the following initial
data:
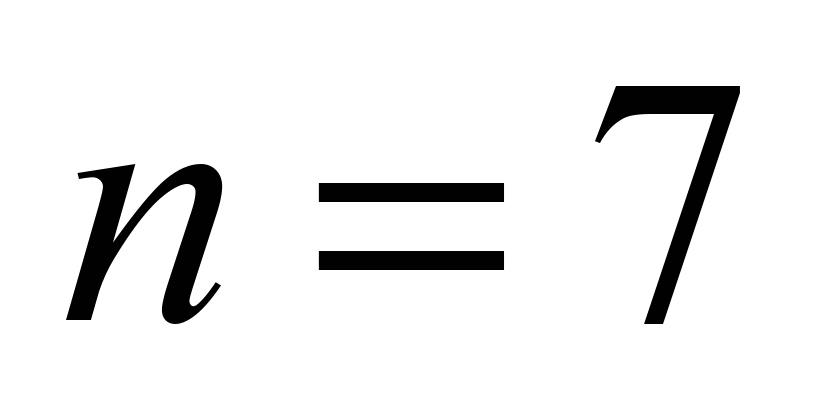 ;
;
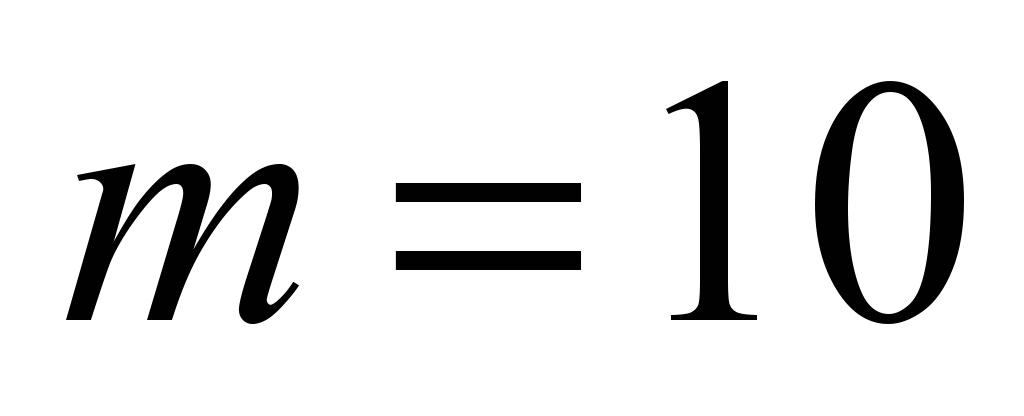 ;
;
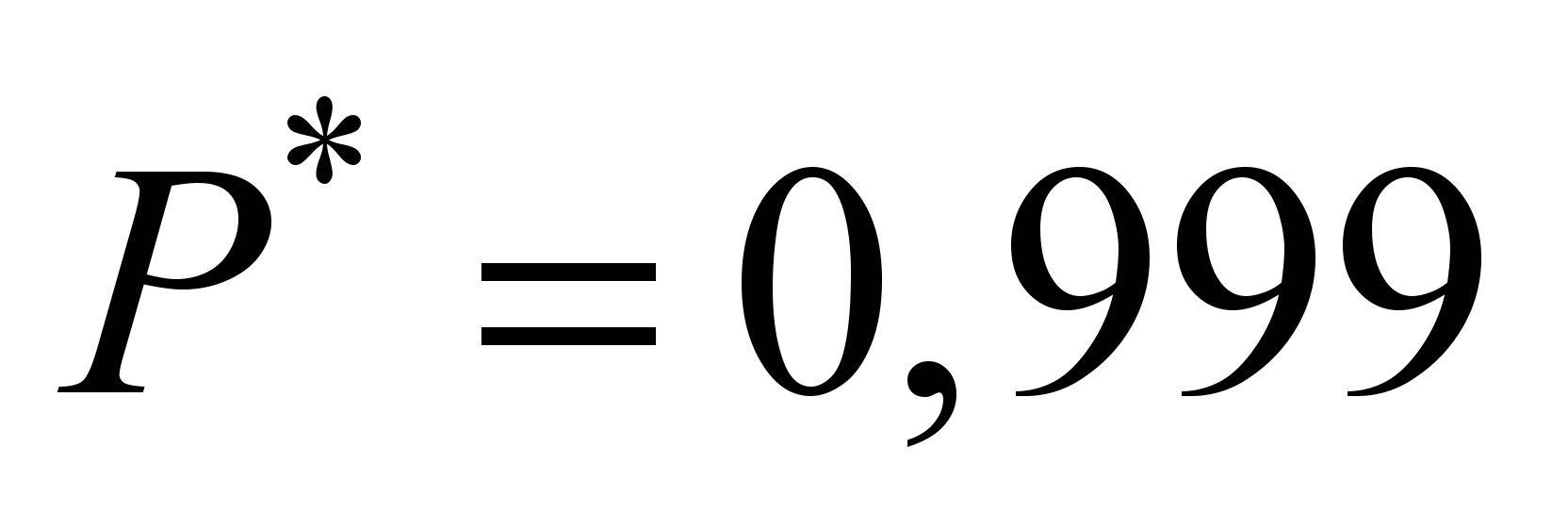 ;
;
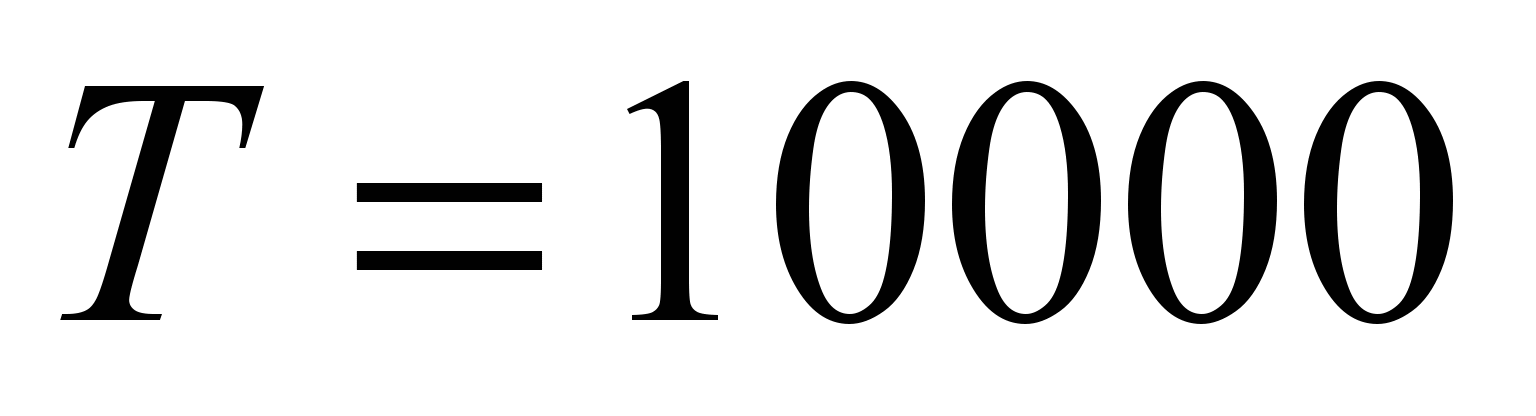 h.
The failure rates and cost of elements were taken using Table 1.
h.
The failure rates and cost of elements were taken using Table 1.
Table 1
Initial
data
|
Number
of element
|
Failure
rate
(hour-1)
|
Cost
(thous.
UAH)
|
|
1
|
0.02·10-4
|
25
|
|
2
|
0.014·10-4
|
52
|
|
3
|
0.09·10-4
|
12
|
|
4
|
0.30·10-4
|
17
|
|
5
|
0.11·10-4
|
29
|
|
6
|
0.01·10-4
|
43
|
|
7
|
0.07·10-4
|
34
|
The optimal
values of the unknowns
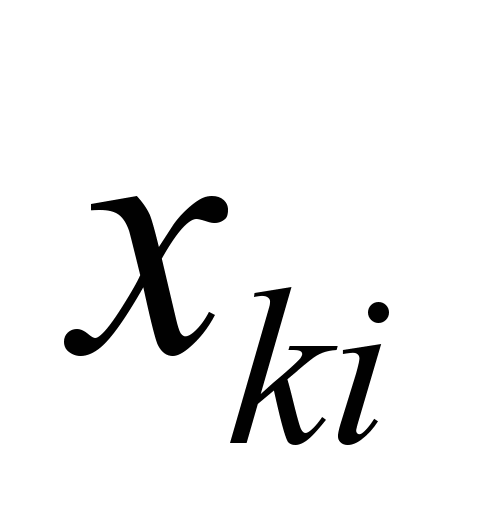 in cases of «cold» and «hot» backup are found in Tables,
respectively, 2 and 3, and the corresponding structural diagrams of
the system reliability are shown in Figures 4 and 5. The calculated
reliability estimates and the cost of the optimal system for «cold»
and «hot» backup are listed in Table 4.
in cases of «cold» and «hot» backup are found in Tables,
respectively, 2 and 3, and the corresponding structural diagrams of
the system reliability are shown in Figures 4 and 5. The calculated
reliability estimates and the cost of the optimal system for «cold»
and «hot» backup are listed in Table 4.
Table
2
Optimal
parameters of the «cold» backup
|
k\i
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
2
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
3
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
4
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
5
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
6
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
7
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
Table
3
Optimal
parameters of the «hot» backup
|
k\i
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
2
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
3
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
4
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
|
5
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
6
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
7
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
Table
4
The
reliability parameters and the cost of optimal system
|
Backup
type
|
P1
|
P2
|
P3
|
P4
|
P5
|
P6
|
P7
|
Ps
|
Cs
|
|
cold
|
0.99982
|
0.99995
|
0.99982
|
0.99983
|
0.99981
|
0.99992
|
0.99993
|
0.99908
|
533
|
|
hot
|
0.99999
|
0.99999
|
0.99994
|
0.99992
|
0.99988
|
0.99999
|
0.99997
|
0.99971
|
718
|
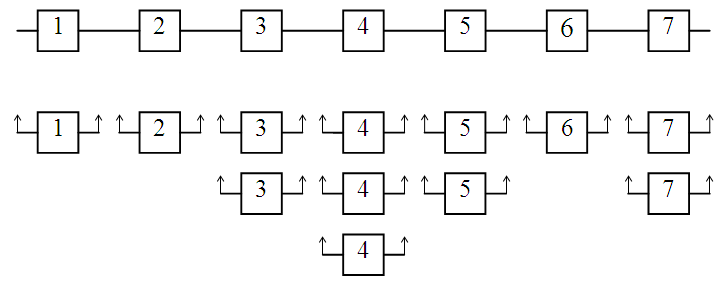
Fig.
4. Optimal
structural scheme of the
system reliability with «cold» redundancy
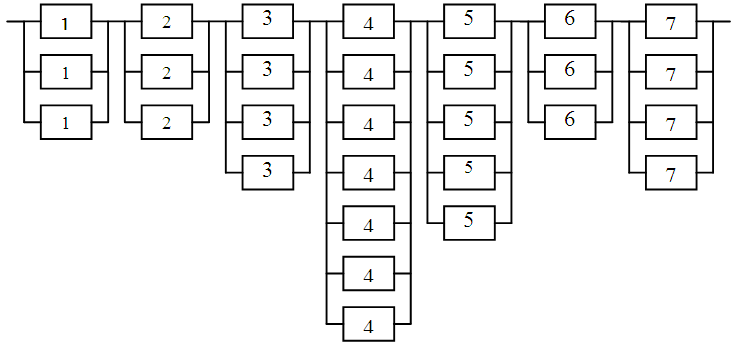
Fig.
5. Optimal
structural scheme of the
system reliability with «hot» redundancy
Findings
The calculated models for
estimating reliability, as well as the optimization models for the
redundant systems according to the «hot» and «cold» separate
backup schemes, have been developed. The optimal options for
reserving the 7 element object at separate «cold» and «hot»
backup using the Excel spreadsheet were found.
Originality
and practical value
New calculation models for
estimating the reliability of redundant systems are proposed, as
well as the optimization models developed on their basis, which are
formulated using the unknown decomposition of initial problem of
structural redundancy into binary components. The obtained
optimization models belong to the class of problems of non-linear
mathematical programming with binary variables, for the numerical
solution of which (even for a sufficiently large dimensions) the
well-known packages of applied computer programs, in particular, the
MS Excel spreadsheet, are well adapted. Thus, the process of solving
the initially very complicated problem of optimal structural
redundancy is greatly simplified and reduced to performing
elementary actions in the corresponding programming interfaces. The
proposed calculation models for estimating the reliability of
redundant systems, the models of optimal structural redundancy, and
the methodology for their formation in order to simplify further
numerical implementation can be useful in solving the problems of
ensuring the reliability of technical systems at the early stages of
their design.
Conclusions
The results
obtained in the article using the specific examples show the
efficiency and sufficient generality of the considered approach to
solving the problems of optimal structural redundancy. The
optimization models (8) and (9) belong to the class of non-linear
programming problems with binary variables and are easily
implemented numerically in the operating
environment of the Excel spreadsheet. The
obtained calculation models for estimating the reliability of
redundant systems (3) – (6), the models for optimal structural
redundancy (8) and (9), and the methodology for their formation can
be used in practical problems of ensuring the reliability of
technical systems at the early stages of their design.
LIST
OF REFERENCE LINKS
Афанасьев,
В. П. Надежность тонкостенной оболочки
в условиях коррозионного износа
/ В.
П. Афанасьев,
Г. И.
Семенец // Вісн. Дніпропетр.
нац. ун-ту залізн. трансп.
ім. акад. В. Лазаряна. –
Дніпропетровськ, 2006. – Вип. 11. – С.
171–174.
Безопасность
и надежность сложных систем
:
учеб.
пособие / Л. Н. Александровская, И. З.
Аронов, В. И. Круглов [и др.]. –
Москва : Логос,
2017. – 376 с.
Бородин,
А. В. Технико-экономическое обоснование
варианта резервирования сетевой
компоненты отказоустойчивой
масштабируемой вычислительной системы
специального назначения / А. В. Бородин
// Кибернетика и программирование. –
2015. – № 6. – С. 55–70.
Капур,
К. Надежность и проектирование систем
: [пер. с англ.] /
К. Капур, Л. Ламберсон. – Москва :
Мир, 1980. – 604 с.
Каштанов,
В. А. Теория надежности сложных систем
/ В. А. Каштанов, А. И. Медведев. – Москва
: Физматлит, 2010. – 606 с.
Насонова,
С. С. Оптимизация риска отказа в задачах
управления надежностью стальных
резервуаров для нефтепродуктов / С. С.
Насонова // Вісн. Дніпропетр.
нац. ун-ту залізн. трансп.
ім. акад. В. Лазаряна. –
Дніпропетровськ, 2008. – Вип. 20. – С.
126–130.
Обеспечение
надежности сложных технических систем
/ А. Н. Дорохов, В. А. Керножицкий, А.
Н. Миронов, О. Л. Шестопалова. –
Санкт-Петербург : Лань, 2011. – 352 с.
Половко,
А. М. Основы теории надежности / А. М.
Половко, С. В. Гуров. – Санкт-Петербург
: БХВ, 2006. – 704 с.
Рябинин,
И. А. Надежность и безопасность
структурно-сложных систем
/ И. А. Рябинин. – Санкт-Петербург
: Политехника, 2000. – 248
с.
Трошин,
А. В. Оптимизация резервирования в
коммутируемых пакетных сетях / А. В.
Трошин // Инфокоммуникационные
технологии. – 2017. – Т. 15, № 4. – С. 354–360.
Шишмарев,
В. Ю. Надёжность технических систем :
учебник / В. Ю. Шишмарев. – Москва :
Юрайт, 2018. – 306 с.
Chanda,
N. Redundant Transmitting System in Aircraft (RTSA) / N. Chanda //
SAE
Technical Paper Series
2015-01-2443.
– 2015. doi: 10.4271/2015-01-2443
Jaberipur,
G. Redundant Number System-Based Arithmetic Circuits / G. Jaberipur
// Arithmetic
Circuits for DSP Applications. – Hoboken
: John
Wiley & Sons,
2017.
– P. 273–312. doi:
10.1002/9781119206804.ch8
с. м.
семенець1*,
с. с.
насонова2*,
Г. І. семенець3*
1*Каф.
«Прикладна математика та інформаційні
технології», Придніпровська державна
академія будівництва та архітектури,
вул. Чернишевського, 24-а, Дніпро, Україна,
49600, тел. +38 (067) 639 60 64, ел. пошта
Ssemenets28@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0002-6359-1069
2*Каф.
«Вища математика», Український державний
хіміко-технологічний університет, пр.
Гагаріна, 8, Дніпро, Україна, 49005, тел.
+38 (097) 940 98 56, ел. пошта ms.nasonova.s@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0002-0920-7417
3*Каф.
«Вища математика», Дніпропетровський
національний університет залізничного
транспорту імені академіка В. Лазаряна,
вул. Лазаряна, 2, Дніпро, Україна, 49010,
тел. +38 (096) 879 48 19, ел. пошта semga1952@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0003-2693-3282
ОПТИМАЛЬНЕ
СТРУКТУРНЕ РЕЗЕРВУВАННЯ
ТЕХНІЧНИХ СИСТЕМ
Мета.
Основна мета статті – дати проектувальникам
високонадійних технічних систем, які
не володіють спеціальними знаннями в
галузі оптимізації та навичками
програмування, простий і доступний
математичний інструмент для вибору
оптимального рішення під час структурного
резервуванні систем.
Методика. За головний
показник надійності резервованої
системи прийнята ймовірність її
безвідмовної роботи. Розглянуті дві
типові схеми резервування: 1) схема
роздільного «гарячого» резервування;
2) схема роздільного «холодного»
резервування. Сформульовані розрахункові
моделі оцінки надійності резервованих
систем.
Результати.
У роботі запропоновані оптимізаційні
моделі, що дозволяють знайти раціональний
варіант резервування проектованої
системи з урахуванням суперечливих
вимог до її надійності й вартості. Ці
моделі чисельно реалізуються в
операційному середовищі табличного
процесора Excel стосовно основного
об’єкта, який складається із 7 елементів.
Наведені оптимальні варіанти резервування
цього об’єкта за схемами «гарячого»
й «холодного» роздільного резервування.
Наукова новизна.
Запропоновані нові розрахункові моделі
оцінки надійності резервованих систем,
а також розроблені на їх основі
оптимізаційні моделі, які сформульовані
з використанням розкладання невідомих
вихідної задачі структурного резервування
на бінарні складові. При цьому отримані
оптимізаційні моделі відносяться до
класу задач нелінійного математичного
програмування з двійковими змінними,
для чисельного вирішення яких (навіть
за досить великої розмірності) добре
пристосовані широко відомі пакети
прикладних комп’ютерних програм,
зокрема табличний процесор MS Excel. Таким
чином, процес вирішення спочатку досить
складної задачі оптимального структурного
резервування значно спрощується і
зводиться до виконання елементарних
дій у відповідних програмних інтерфейсах.
Практична значимість.
Запропоновані розрахункові моделі
оцінки надійності резервованих систем,
моделі оптимального структурного
резервування, а також методологія їх
формування з метою спрощення подальшої
чисельної реалізації можуть бути
корисні при вирішенні задач забезпечення
надійності технічних систем на ранніх
стадіях їх проектування.
Ключові слова: система;
проектування; надійність; структурне
резервування; модель; оптимізація;
бінарні змінні
с. н. семенец1*,
с. с.
насонова2*,
Г. И. семенец3*
1*Каф.
«Прикладная математика и информационные
технологии», Приднепровская государственная
академия строительства и архитектуры,
ул. Чернышевского, 24-а, Днипро, Украина,
49600, тел. +38 (067) 639 60 64,
эл. почта
Ssemenets28@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0002-6359-1069
2*Каф.
«Высшая математика», Украинский
государственный химико-технологический
университет, пр. Гагарина, 8, Днипро,
Україна, 49005, тел. +38 (097) 940 98 56, эл. почта
ms.nasonova.s@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0002-7228-7499
3*Каф.
«Высшая математика», Днепропетровский
национальный университет железнодорожного
транспорта имени академика В. Лазаряна,
ул. Лазаряна, 2, Днипро, Украина, 49010, тел.
+38 (096) 879 48 19, эл. почта semga1952@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0003-2693-3282
ОПТИМАЛЬНОЕ СТРУКТУРНОЕ
РЕЗЕРВИРОВАНИЕ ТЕХНИЧЕСКИХ СИСТЕМ
Цель.
Основная цель статьи –
дать проектировщикам высоконадежных
технических систем, не обладающим
специальными знаниями в области
оптимизации и навыками программирования,
простой и доступный математический
инструмент для выбора оптимального
решения при структурном резервировании
систем. Методика. В качестве
главного показателя надежности
резервированной системы принята
вероятность ее безотказной работы.
Рассмотрены две типовые схемы
резервирования: 1) схема раздельного
«горячего» резервирования; 2) схема
раздельного «холодного» резервирования.
Сформулированы расчетные модели оценки
надежности резервированных систем.
Результаты. В работе предложены
оптимизационные модели, позволяющие
найти рациональный вариант резервирования
проектируемой системы с учетом
противоречивых требований к ее надежности
и стоимости. Данные модели
численно реализуются в операционной
среде табличного процессора Excel
применительно к основному объекту,
состоящему из 7 элементов. Приведены
оптимальные варианты резервирования
этого объекта по схемам «горячего» и
«холодного» раздельного резервирования.
Научная новизна. Предложены
новые расчетные модели оценки надежности
резервированных систем, а также
разработанные на их основе оптимизационные
модели, которые сформулированы с
использованием разложения неизвестных
исходной задачи структурного
резервирования на бинарные составляющие.
При этом полученные оптимизационные
модели относятся к классу задач
нелинейного математического
программирования с двоичными переменными,
для численного решения которых (даже
при достаточно большой размерности)
хорошо приспособлены широко известные
пакеты прикладных компьютерных программ,
в частности табличный процессор MS
Excel. Таким образом, процесс
решения изначально весьма сложной
задачи оптимального структурного
резервирования значительно упрощается
и сводится к выполнению элементарных
действий в соответствующих программных
интерфейсах. Практическая
значимость. Предложенные расчетные
модели оценки надежности резервированных
систем, модели оптимального структурного
резервирования, а также методология
их формирования с целью упрощения
дальнейшей численной реализации могут
быть полезны при решении задач обеспечения
надежности технических систем на ранних
стадиях их проектирования.
Ключевые слова:
система; проектирование; надежность;
структурное резервирование; модель;
оптимизация; бинарные переменные
REFERENCES
Afanasev,
V. P., & Semenets, G. I. (2006). Reliability of a thin-walled
shell under conditions of corrosive wear. Bulletin
of Dnipropetrovsk National University of Railway Transport named
after Academician V. La-zaryan, 11,
171-174. (in Russin)
Aleksandrovskaya,
L. N., Aronov,
I. Z., & Kruglov,
V. I. (2017). Bezopasnost i nadezhnost
slozhnykh sistem: uchebnoe posobie.
Moscow: Logos.
(in Russian)
Borodin,
A. V.
(2015). Tekhniko-ekonomicheskoe
obosnovanie
varianta
rezervirovaniya
setevoy
komponenty
ot-kazoustoychivoy
masshtabiruemoy
vychislitelnoy
sistemy
spetsialnogo
naznacheniya.
Kibernetika
i
programmirovanie,
6(6),
55-70. doi:
10.7256/2306-4196.2015.6.17523
(in
Russian)
Kapur,
K., & Lamberson, L. (1980). Reliability
in engineering design.
Moscow: Peace. (in Russian)
Kashtanov,
V. A., & Medvedev, A. I. (2010). Teoriya
nadezhnosti slozhnykh system. Moscow:
Fizmatlit. (in Russian)
Nasonova,
S. S. (2008). The optimization of failure
risk in management tasks reliability of steel storage tanks for
petroleum products. Bulletin of
Dnipropetrovsk National University of Railway Transport named after
Academician V. Lazaryan, 20, 126-130.
(in Russian)
Dorokhov,
A. N., Kernozhitskiy, V. A., Mironov, A. N., & Shestopalova, O.
L. (2011). Obespechenie nadezhnosti
slozhnykh tekhnicheskikh system.
Saint Petersburg: Lan. (in Russian)
Polovko,
A. M., &
Gurov, S.V.
(2006). Fundamentals of the theory of
reliability.
Saint Petersburg: BHV. (in Russian)
Ryabinin,
I. A. (2000).
Reliability and safety of structurally
complicated systems. Saint
Petersburg: Politekhnika. (in Russian)
Troshin,
A. V. (2017). Optimizatsiya rezervirovaniya v kommutiruemykh
paketnykh setyakh.
Infokommunikatsionnye
tekhnologii, 15(4), 354-360. (in
Russian)
Shishmarev,
V. Y. (2018).
Nadezhnost tekhnicheskikh sistem:
uchebnik dlya bakalavriata i magistratury.
Moscow: Yurayt. (in Russian)
Chanda,
N. (2015). Redundant Transmitting System in Aircraft (RTSA). SAE
Technical Paper Series, 2015-01-2443.
doi:
10.4271/2015-01-2443
(in English)
Jaberipur,
G. (2017). Redundant Number System-Based Arithmetic Circuits. In
Arithmetic
Circuits for DSP Applications
(рр.
273-312).
Hoboken:
John
Wiley & Sons.
doi: 10.1002/9781119206804.ch8 (in
English)
Received: April 30, 2018
Accepted: August 02, 2018
d oi
: 10.15802/stp2018/141008 ©
s.
n. semenets,
s. s. nasonova,
G. I. semenets, 2018
oi
: 10.15802/stp2018/141008 ©
s.
n. semenets,
s. s. nasonova,
G. I. semenets, 2018
of various elements that have a coherent connection [4] (see Fig.
1).
, (2)
– is the failure rate of the element put into operation;
– is the redundancy rate.
– is the failure rate of the element of the
-th
type put into operation;
– is the maximum allowable redundancy rate of main elements;
– is the cost of one element of the
-th
type;
– is the binary variable, equal to 1, if the number of redundant
elements of the
-th
is equal to
,
and
,
f the number of redundant elements of the
-th
type is not equal to
;
– is the probability of fail-safe operation of the main element of
the
-th
type, over the time
.
-th
type. Taking into account the introduced designations, the
probability of failure-free operation of a redundant group at «cold»
backup is estimated by formula
, (3)
. (4)
-th
type in both backup schemes can be found using formula
. (5)
; (6)
, (7)
– is the matrix describing composition of the elements
of the redundant system
,
are
determined using formulas (3) and (4) depending on the backup scheme
used.
)
that provides the required level of system reliability for a given
time at the lowest possible cost
(8)
,
with a restriction on its cost
(9)
and belong to the class of problems of integer nonlinear programming
with binary variables. The model (8) was numerically realized for
cases of «cold» and «hot» separate backup using the MS Excel
Solver add-in. The problem was solved with the following initial
data:
;
;
;
h.
The failure rates and cost of elements were taken using Table 1.
in cases of «cold» and «hot» backup are found in Tables,
respectively, 2 and 3, and the corresponding structural diagrams of
the system reliability are shown in Figures 4 and 5. The calculated
reliability estimates and the cost of the optimal system for «cold»
and «hot» backup are listed in Table 4.