ISSN 2307–3489 (Print), ІSSN
2307–6666 (Online)
Наука та прогрес
транспорту. Вісник Дніпропетровського
національного університету залізничного
транспорту, 2017, № 4 (70)
ЕКОЛОГІЯ
НА ТРАНСПОРТІ
UDC 502.3:504.5:629.33
M. M. BILIAIEV1*,
O. S. SLAVINSKA2*,
R. V. KYRYCHENKO3*
1*Dep. «Hydraulics
and Water Supply», Dnipropetrovsk National University of Railway
Transport named after Academician
V.
Lazaryan, Lazaryan St., 2, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49010, tel. +38 (056)
273 15 09, e-mail water.supply.treatment@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0002-1531-7882
2*Dep.
«Manufacturing and Property Management», National Transport
University of Ukraine, Suvorov St., 1, Kyiv,
Ukraine, 01010, tel. +38 (044) 280 82
03, e-mail water.supply.treatment@gmail.com, ORCID
0000-0001-5163-5645
3*Dep.
«Manufacturing and Property Management», National Transport
University of Ukraine, Suvorov St., 1, Kyiv,
Ukraine, 01010, tel. +38 (044) 280 82
03, e-mail water.supply.treatment@gmail.com, ORCID
0000-0001-9918-3895
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF POLLUTION DISPERSION
IN URBAN
STREET
Purpose.
The scientific paper solves the question of 2D numerical model
development, which allows quick computation of air pollution in
streets from vehicles. The aim of the work is numerical model
development that would enable to predict the level of air pollution
by using protective barriers along the road. Methodology. The
developed model is based on the equation of inviscid flow and
equation of pollutant transfer. Potential equation is used to compute
velocity field of air flow near road in the case of protection
barriers application. To solve equation for potential flow implicit
difference scheme of «conditional approximation« is used. The
implicit change – triangle difference scheme is used to solve
equation of convective – diffusive dispersion. Numerical
integration is carried out using the rectangular difference grid.
Method of porosity technique («markers
method») is used to create the form of comprehensive computational
region. Emission of toxic gases from vehicle is modeled using Delta
function for point source. Findings. Authors developed
2D numerical model. It takes into account the main physical factors
affecting the process of dispersion of pollutants in the atmosphere
when emissions of vehicle including protection barriers near the
road. On the basis of the developed numerical models a computational
experiment was performed to estimate the level of air pollution in
the street. Originality. A numerical model has been created.
It makes it possible to calculate 2D aerodynamics of the wind flow in
the presence of noises and the process of mass transfer of toxic gas
emissions from the motorway. The model allows taking into account the
presence of the car on the road, the form of a protective barrier,
the presence of a curb. Calculations have been performed to determine
the contamination zone formed at the protective barrier that is
located at the motorway. Practical value. An effective
numerical model that can be applied in the development of
environmental protection measures for the operation of road transport
in the city is considered. The developed model allows estimating
sizes, the form and intensity of a zone of pollution at a motorway.
Keywords:
air pollution; urban streets; pollution
dispersion; numerical simulation
Introduction
Pollution
from vehicles in urban streets is very intensive and can cause harm
to humans. For this purpose, it is necessary to predict the level of
pollution in streets. Physical modeling, in this case, is very
expensive [8]. For quick prediction empirical
models are used [1]. These models are convenient in practice,
especially when we must run many «pilot»
calculations. But these models do not take into account some
important properties of pollutant dispersion process in streets. The
main problem is that the process of air pollution in streets takes
part in the region having comprehensive geometrical form (presence
of buildings, different obstacles, etc). The alternative way is the
numerical simulation of this process. Many authors apply CFD
simulation to solve the problem [1, 3, 6, 8–10]. As a rule, to
obtain flow pattern in streets foreign authors use Navier –
Stokes equations (this is the model of viscous fluid) coupled with
turbulent models. Very often commercial codes are used for this
purpose. Worthy of note, that application of Navier – Stokes
equations needs application of very fine computational grid during
the computational experiment to simulate in detail the process of
vortexes formation and their dispersion and interaction in the
region. Using the model of viscous fluid, we must use very fine grid
inside the boundary layers. This is a real problem if we have big
dimensions of the buildings, obstacles in streets. So, in case of
Navier – Stokes equations application it is necessary to use
powerful PC and every computational experiment consumes much time.
This is not convenient when we must run a lot of practical
calculations considering different scenario of air pollution in
streets and, especially, when we try to find the effective
protection measures because in this case we must consider many
alternative variants of protection. In this case it would be better
to split the study in two steps. At the first step we may find the
«satisfying»
variant using numerical model which does not consume much time and
not take into account some physical features of the process. After
that, at the second step, we may use more powerful model to compute
in detail the variant of protection which has been chosen. So, for
quick calculations at the first step it is important to have CFD
models which consume not much computational time but they allow to
take into account such important features as obstacles, emission
rate, etc.
Purpose
The
purpose of this paper is development a numerical model for quick
computing of the local air quality near roads.
Aerodynamic equation
To
simulate the wind pattern near the road we use model of potential
flow. In this case the governing
equation is [5]:
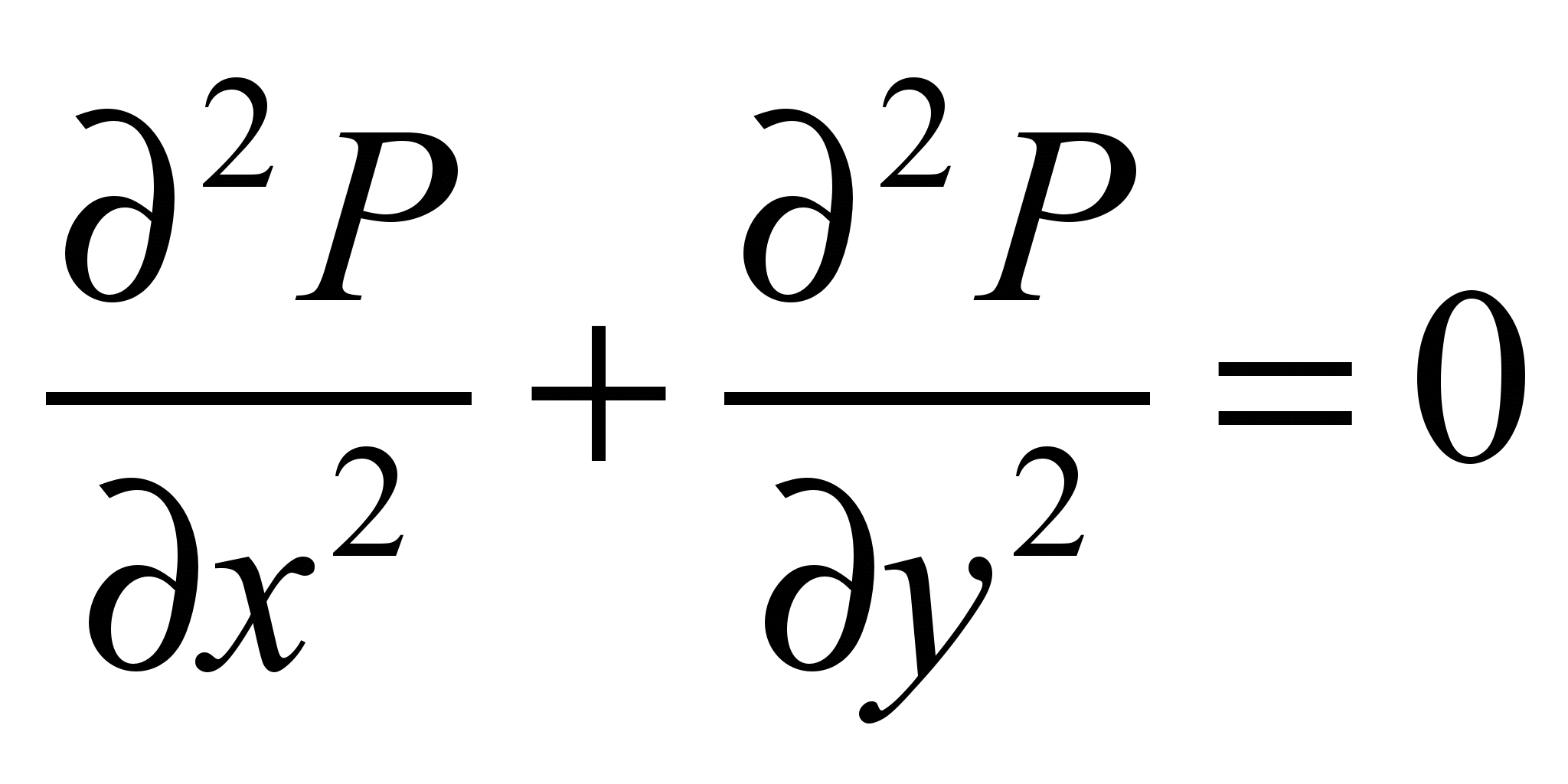 , (1)
, (1)
where Р
is the potential of speed.
The
wind velocity components are calculated as follows:
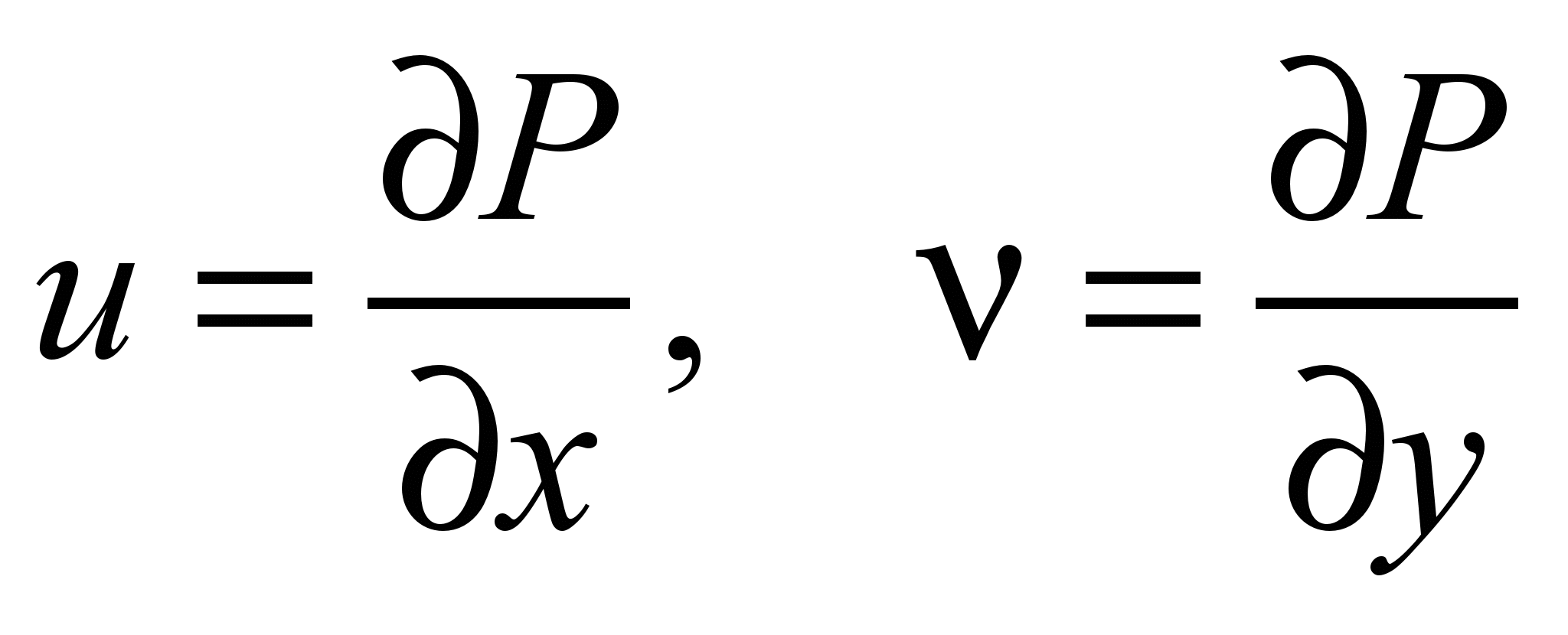 .
.
Boundary
conditions equation (1) are discussed in [1]. To perform numerical
integration of this equation rectangular grid was used.
To
solve equation of potential flow (1) we used the difference scheme
of «conditional
approximation».
In this case, first of all, we transformed Eq. 1 to equation having
«evolution
type» [5]
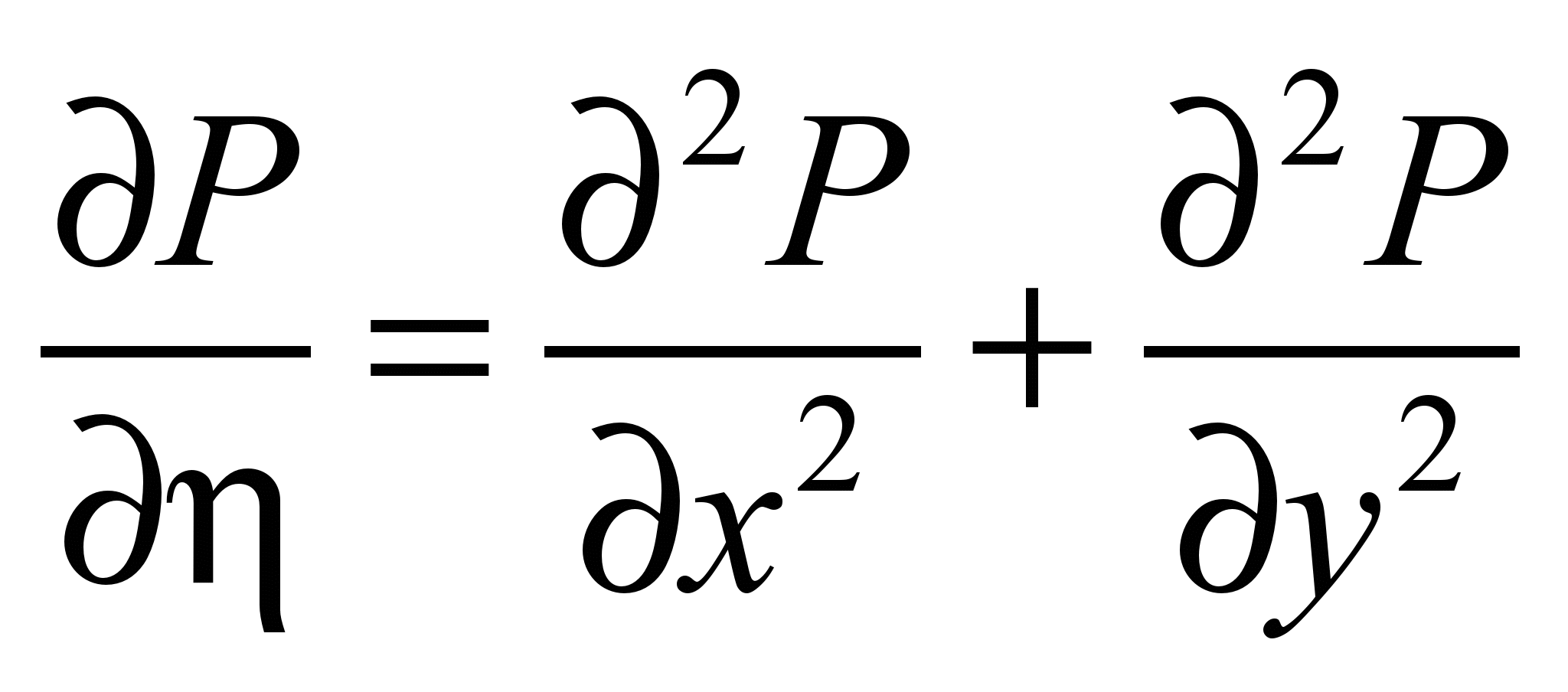 , (2)
, (2)
where
 is «fictitious»
time.
is «fictitious»
time.
For
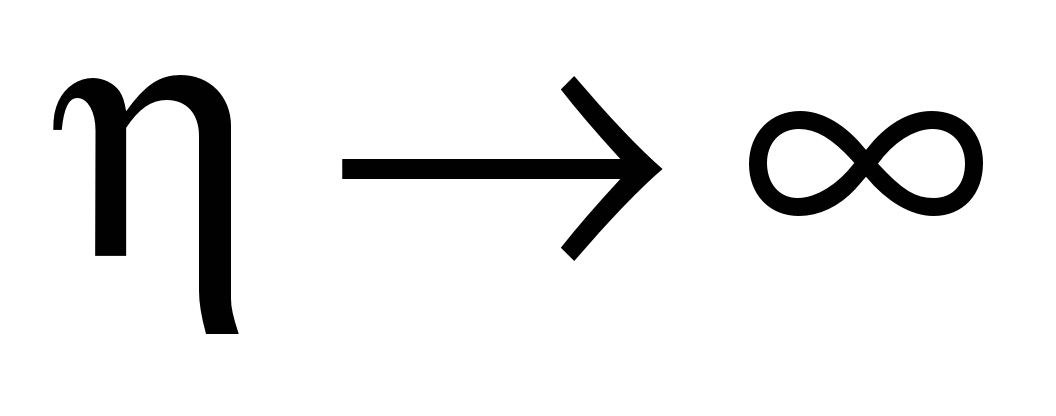 the solution of equation (2) tends to the solution of equation (1).
the solution of equation (2) tends to the solution of equation (1).
After
approximation of Eq. 2, we split it in the sequence of two
difference equations having implicit form [5]
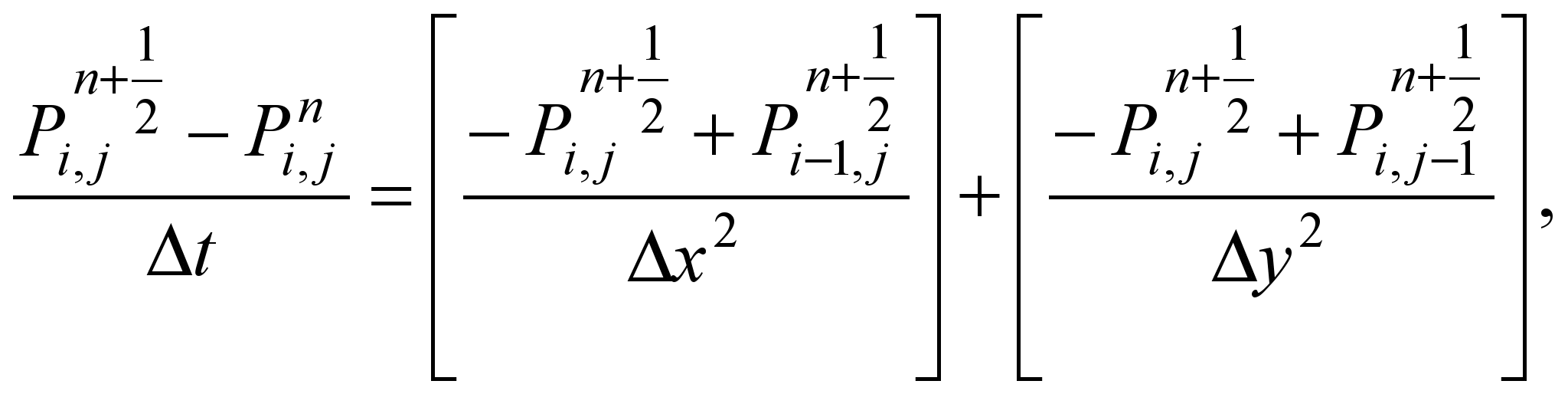
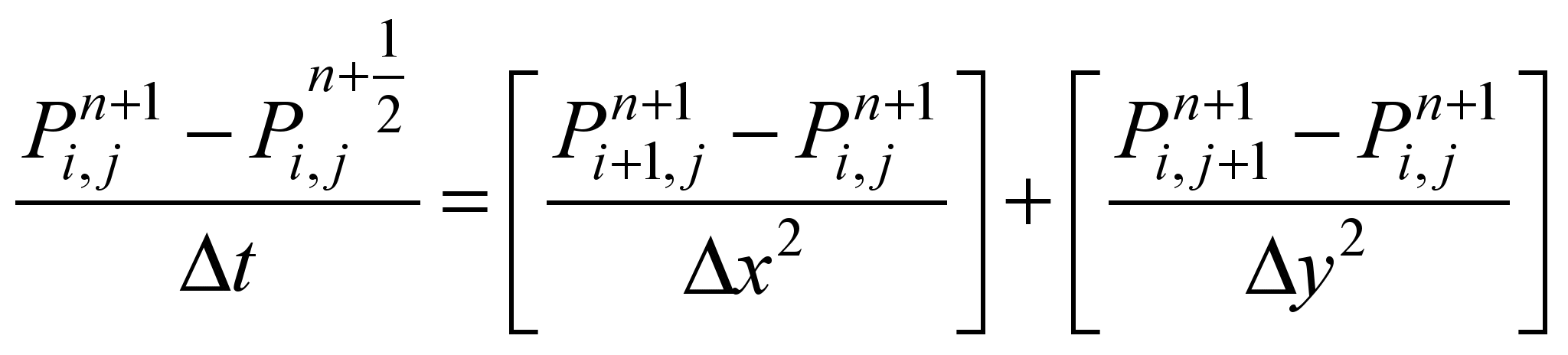 .(3)
.(3)
Unknown
value of
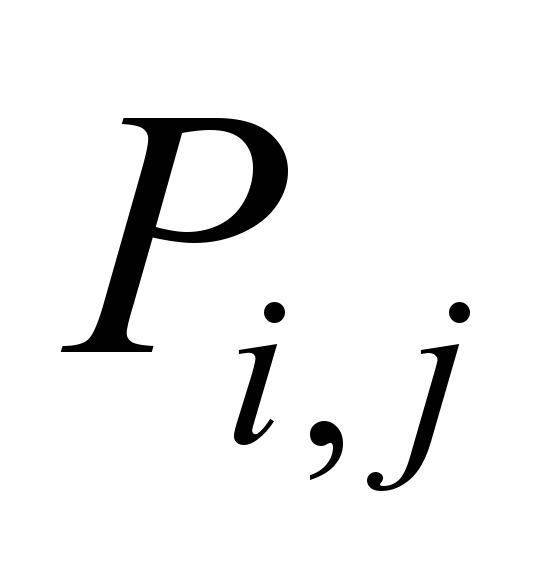 can be easily determined from
each difference equation (3) using explicit formulae of «running
calculation».
As the «initial»
condition for Eq. 2 we may use, for, example, P=0
for
can be easily determined from
each difference equation (3) using explicit formulae of «running
calculation».
As the «initial»
condition for Eq. 2 we may use, for, example, P=0
for
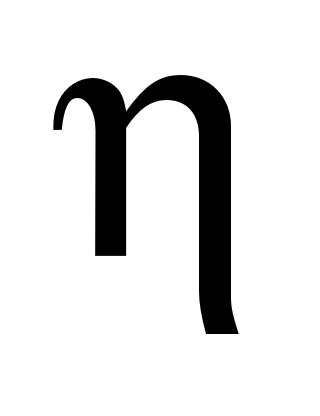 =0.
=0.
Pollutant Transport Equation
To
simulate the pollutant dispersion near road equation of convective –
diffusive transfer is used [1, 4, 7]
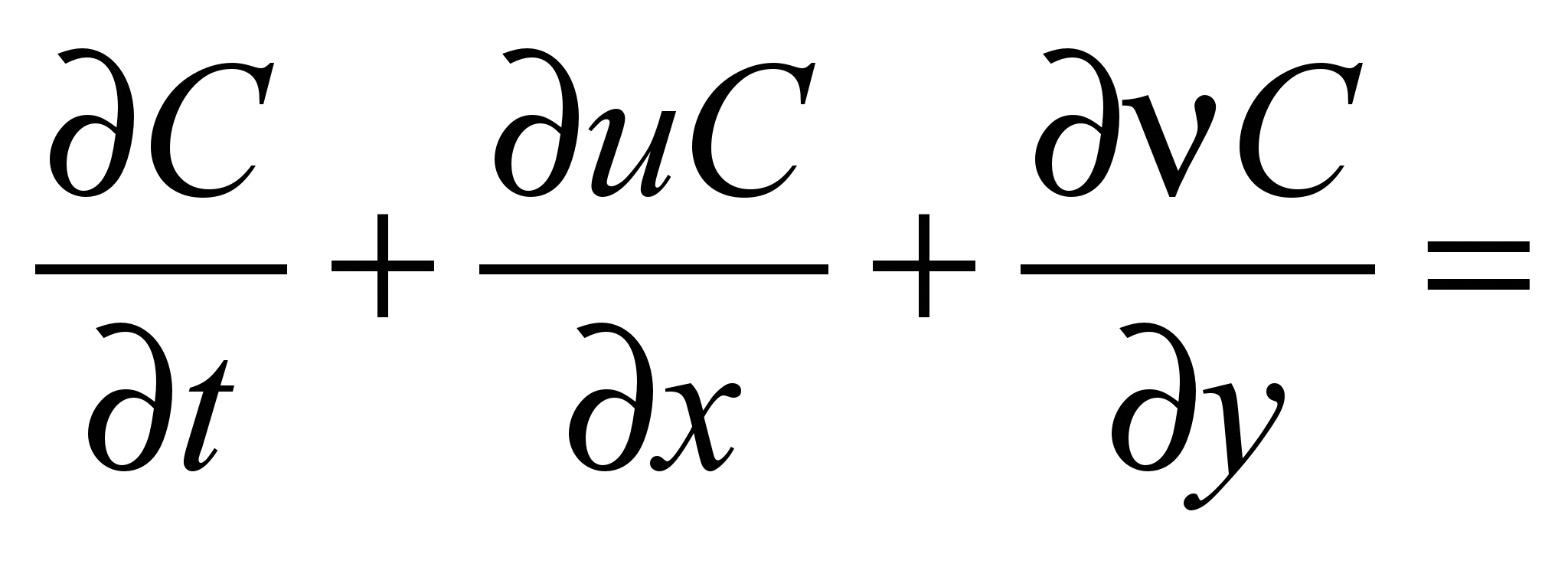
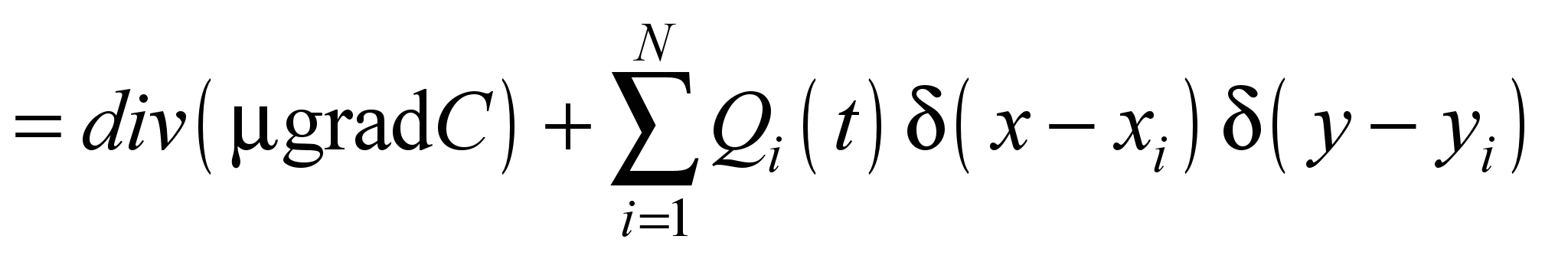 , (4)
, (4)
where С
is mean concentration
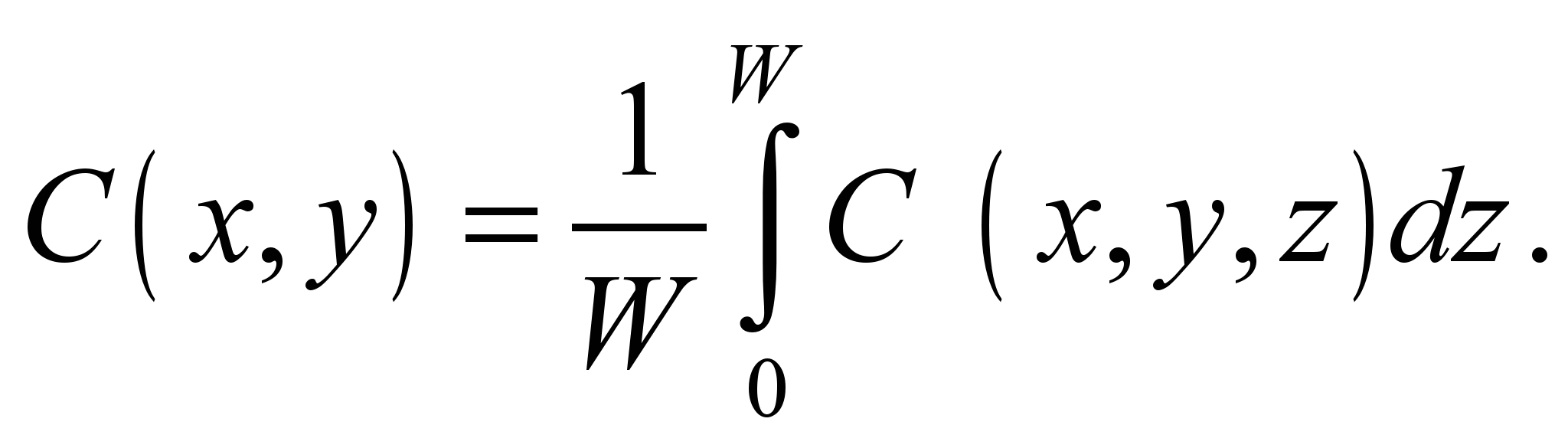
W
is width of the computational region;
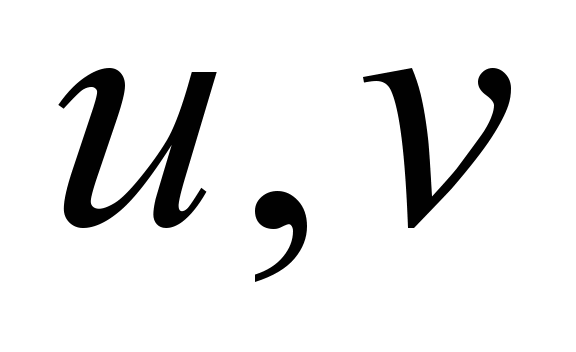 are
the wind velocity components;
are
the wind velocity components;
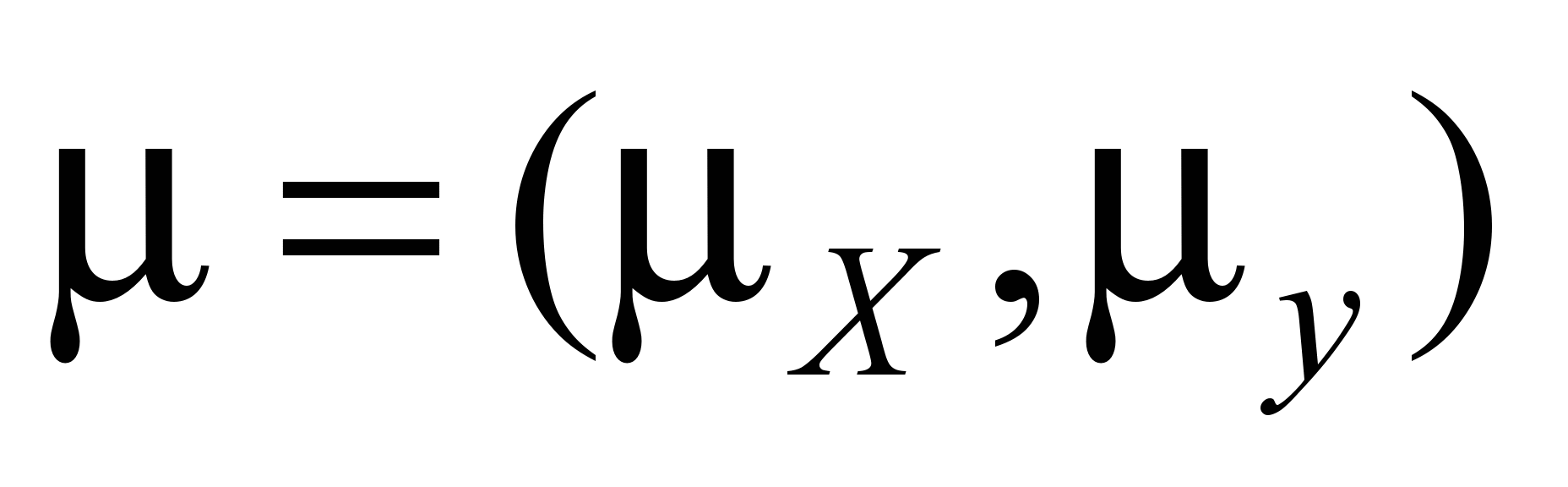 are the diffusion coefficients;
are the diffusion coefficients;
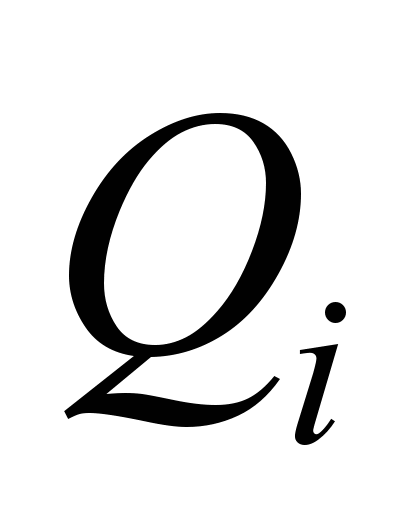 is rate of emission;
is rate of emission;
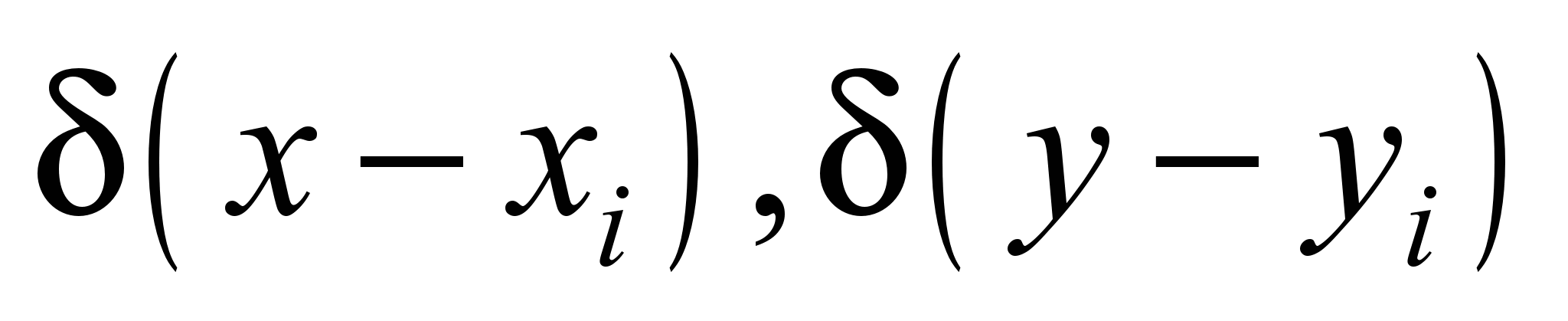 – are Dirac delta function; t is
time.
– are Dirac delta function; t is
time.
Initial
and boundary conditions for Eq. 4 are described in [1, 4].
Before
solving Eq. (2) we made it’s physical splitting into the sequence
of three equations. These are the
following equations:
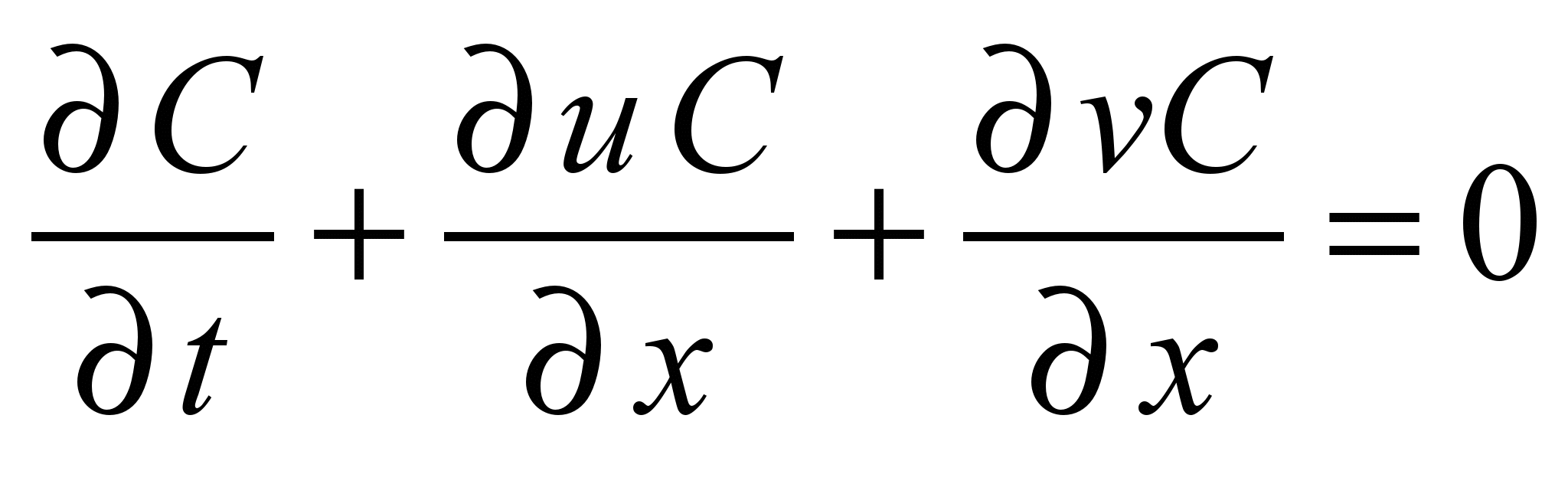 , (5)
, (5)
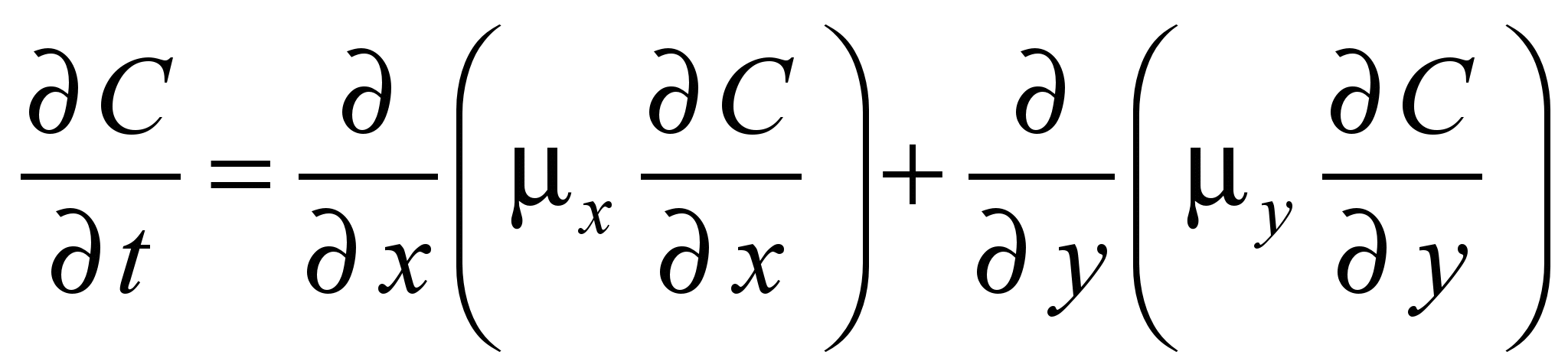 ,
,
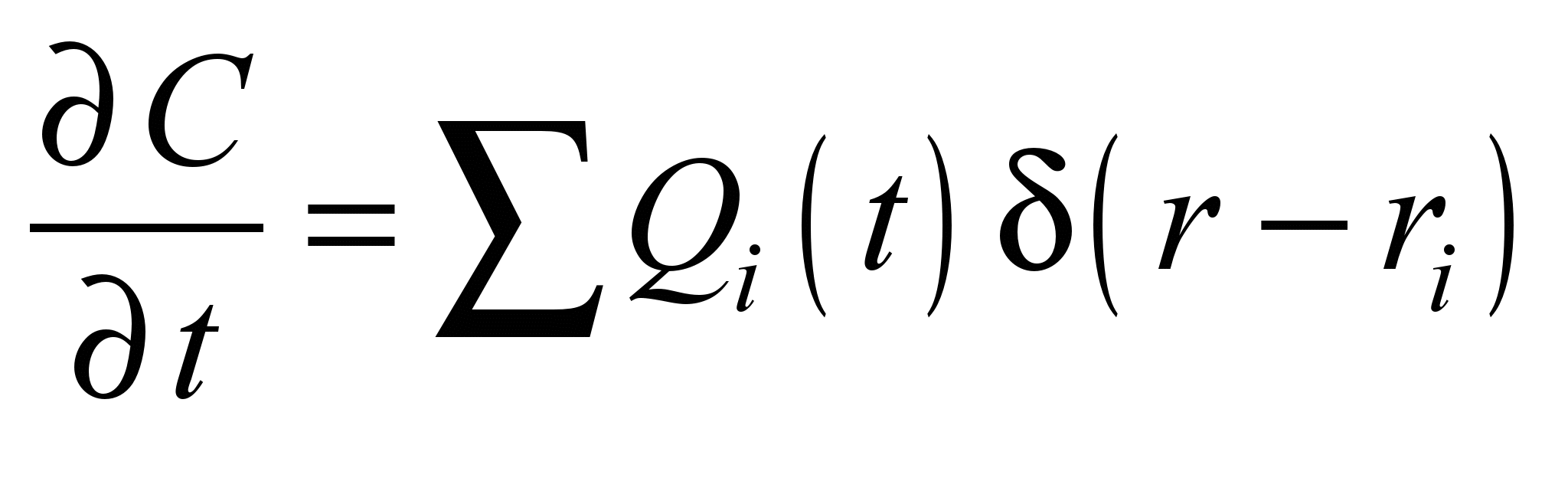 ,
,
where
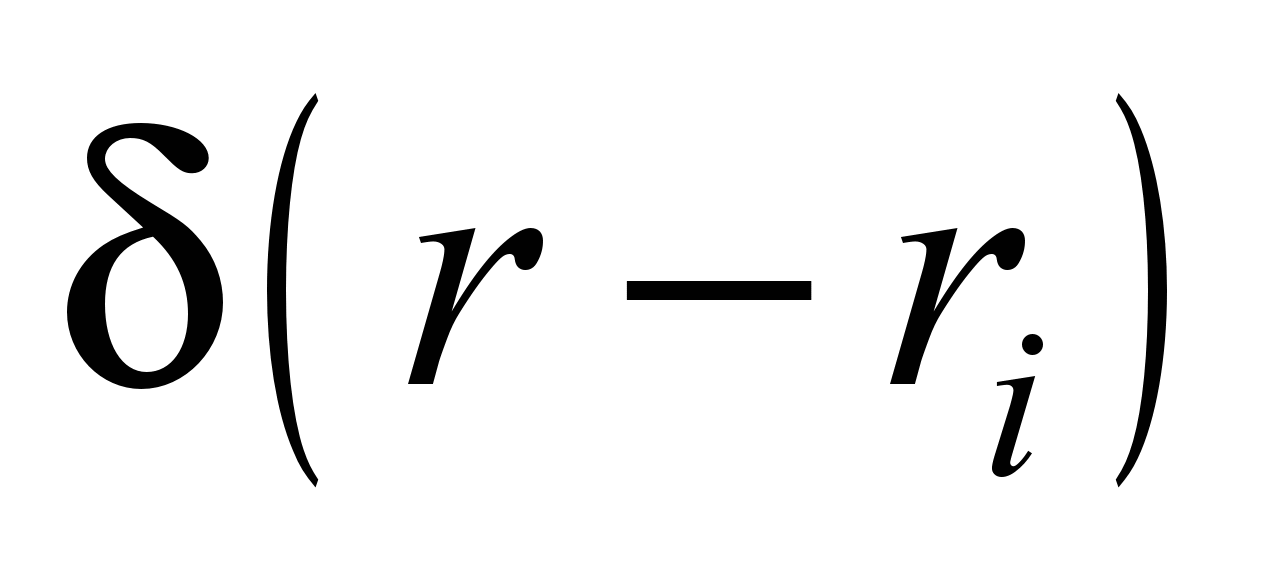 is Dirac delta function;
is Dirac delta function;
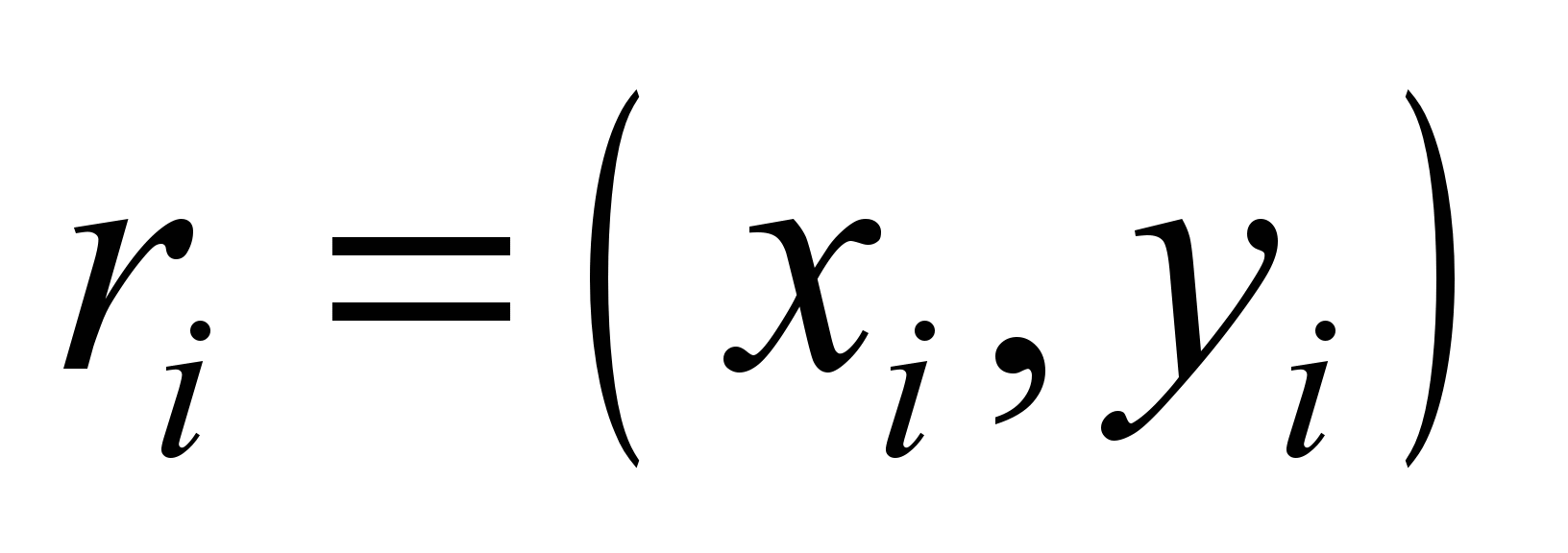 are the coordinates of the point source.
are the coordinates of the point source.
The
first equation in (5) describes pollutant transfer along
trajectories. The second equation in (5) describes the diffusive
dispersion of pollutant. The third equation in (5) describes
concentration change under the action of source
 .
.
To
solve the first and the second equations in (5) the implicit change
– triangle difference scheme was used [1]. To solve the third
equation from (5) Euler method was used [5].
Numerical
integration of difference equations is performed using rectangular
grid. Values of P, C
are determined in the centers of computational cells, values of u,
v are determined at the sides of the
computational cells. For coding difference equations, we used
FORTRAN language.
Findings
Developed
numerical model and code were used to compute CO
concentrations near road which has
barrier at the curb. Numerical simulation was performed for two
scenarios. The first one is scenario where barrier has a form of
vertical plate (Fig. 1).
The second scenario is application of barrier which has
additional «short
wing» at the
top (Fig. 2).
«Body»
of the vehicle is represented as rectangular. Its form and form of
the curb, barrier is represented in numerical model using «markers»
(porosity technique). Outlet opening of the vehicle is a passive
source of emission. It means that we don’t take into account speed
of gases which move from it. Arrow indicates the wind direction.
Results
of numerical simulations are shown in Fig. 3–5. Fig. 3, 4
represent CO concentration
field near road. We can see that application of barrier with «short
wing» allows to
reduce the width of contaminated zone behind the barrier.
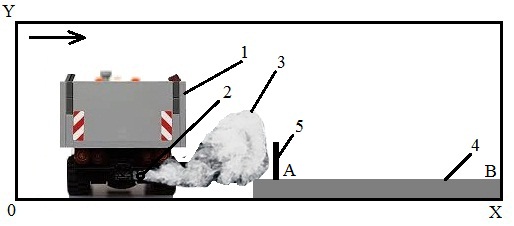
Fig. 1. Sketch of computational region (the first
scenario): 1
– vehicle; 2
– source of emission
(outlet
opening); 3
– plume; 4
– curb; 5
– barrier
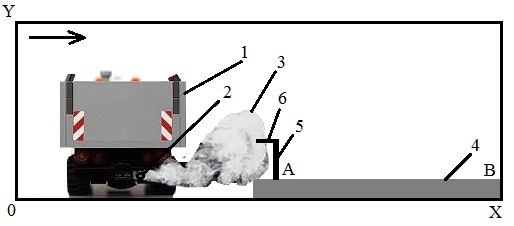
Fig. 2. Sketch of computational region
(the second
scenario):
1
– vehicle; 2
– source of emission (outlet
opening);
3
– plume; 4
– curb; 5
– barrier; 6
– «short wing»
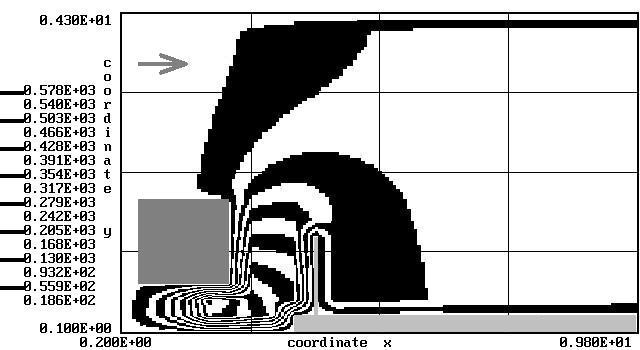
Fig. 3. Computed CO concentration
(barrier
without «wing»)
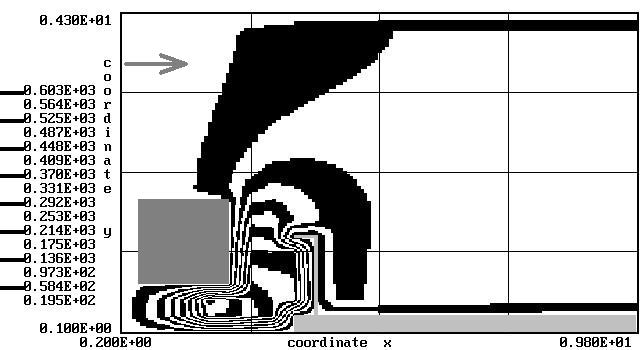
Fig. 4. Computed CO concentration
(barrier
with «short wing»)
In
Table 1 we present computed CO concentration behind barriers at
height h=1,7
m.
Table
1
Computed CO concentration at
height h
=1.7 m
|
Distance
from barrier
|
Concentration
(scenario: no wing)
|
Concentration
(scenario: short wing)
|
|
0.6
m
|
1.01
mg/m3
|
0.94
mg/m3
|
|
1.0 m
|
0.95
mg/m3
|
0.88
mg/m3
|
|
1.4 m
|
0.89
mg/m3
|
0.82
mg/m3
|
|
1.8 m
|
0.85
mg/m3
|
0.78
mg/m3
|
As we can
see from Table 1 application of barrier having «short
wing» allows
reduce CO concentrations near the road.
Worthy
of note that computational time was about 5 sec. for each scenario.
It allows to use the developed numerical model for practical
application when series of computational experiments must be
run.
Originality and
practical value
A
model has been developed to compute concentrations near roads.
Numerical model is based on application of mass transfer equation
and equation of potential flow.
The
peculiarity of the developed model is the use quick calculation of
contaminated zones and account of geometrical form of vehicle, curb,
barriers near the road.
Conclusions
Numerical
model for estimating the level of atmospheric air pollution near
roads is proposed. Proposed numerical model allows to predict level
of pollution with account of geometrical form of vehicle, curb,
barriers near the road, intensity of emission rate. The solution of
the aerodynamic problem is based on the numerical integration of
equation for potential flow. This allows to perform quick
calculation of wind pattern near road using PC which are available
now in Ukraine. To predict toxic gases concentrations near road
convective – diffusive equation is used. Numerical integration of
this equation is performed using implicit difference scheme.
Using the developed numerical model some numerical experiments were
performed to study the influence of barrier form on intensity of
local contamination near road.
Further
improvement of the model should be carried out in the direction of
creating a 3D numerical model.
LIST
OF REFERENCE
LINKS
Беляев,
Н. Н. Моделирование загрязнения
атмосферного воздуха выбросами
автотранспорта на улицах городов :
монография / Н. Н. Беляев, Т. И. Русакова,
П. С. Кириченко. – Днепропетровск :
Акцент ПП, 2014. – 159 с.
Беляев,
Н. Н. Прогноз загрязнения атмосферного
воздуха выбросами автотранспорта с
учетом химической трансформации
вредных веществ / Н. Н. Беляев, Е. С.
Славинская, Р. В. Кириченко // Наука та
прогрес транспорту. – 2017. – № 3 (69). –
С. 15–22. doi:
10.15802/stp2017/104549.
Беляев,
Н. Н. CFD прогнозирование
процесса загрязнения воздушной среды
на улицах / Н. Н. Беляев, Т. И. Русакова
// Екологія і природокористування
: зб. наук. пр. Ін-ту проблем
природокористування та екології НАН
України. – Київ, 2013. – Вип. 17. – С.
188–194.
Марчук,
Г. И. Математическое
моделирование в проблеме окружающей
среды / Г. И. Марчук. –
Москва : Наука, 1982. – 320
с.
Самарский,
А. А. Теория
разностных схем / А. А.
Самарский. – Москва : Наука, 1983. – 616 с.
A
new simplified NO/NO2
conversion model under consideration of direct NO2-emissions
/ I. Düring, W. Bächlin, M. Ketzel, A. Baum, U. Friedrich,
S. Wurzler // Meteorologische Zeitschrift. – 2011. – Vol. 20. –
Iss. 1. – P.
67–73. doi: 10.1127/0941-2948/2011/0491.
Berlov,
O. V. Atmosphere protection in case of
emergency during transportation
of dangerous cargo /
O.
V. Berlov // Наука та прогрес
транспорту. – 2016.
– № 1
(61). – С.
48–54.
doi: 10.15802/stp2016/60953.
Nguyen,
T. N. Numerical simulation of wind flow and pollution transport in
urban street canyons / T. N. Nguyen, T. C. Nguyen, V. T. Nguyen //
Advanced Science and Technology Letters. – 2015. – Vol. 120. –
P. 770–777. doi: 10.14257/astl.2015.120.152.
Numerical
simulations and wind tunnel studies of pollutant dispersion in the
urban street canyons with different height arrangements / Ch.-H.
Chang, J.-S. Lin, C.-M. Cheng, Y.-S. Hong //
J. of Marine
Science and technology. – 2013. – Vol. 21, No. 2.
– P. 119–126.
Overman,
H. T. J. Simulation model for NOx
distributions in a street canyon with air purifying pavement:
мaster thesis / H. T. J. Overman ;
University of Twente. – Enschede,
Netherlands, 2009. – 69 р.
М. М. БІЛЯЄВ1*, О. С. СЛАВІНСЬКА2*,
Р. В. КИРИЧЕНКО3*
1*Каф. «Гідравліка
та водопостачання», Дніпропетровський
національний університет залізничного
транспорту
імені академіка В. Лазаряна,
вул. Лазаряна, 2, Дніпро, Україна, 49010,
тел. +38 (056) 273 15 09,
ел. пошта
water.supply.treatment@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0002-1531-7882
2*Каф. «Управління
виробництвом та майном», Національний
транспортний університет, вул. Суворова,
1, Київ,
Україна, 01010,
тел. +38 (044) 280 82
03, ел. пошта
water.supply.treatment@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0001-5163-5645
3*Каф.
«Управління виробництвом та майном»,
Національний транспортний університет,
вул. Суворова, 1, Київ,
Україна, 01010,
тел. +38 (044) 280 82 03, ел. пошта
water.supply.treatment@gmail.com,
ORCID 0000-0001-9918-3895
Чисельне моделювання
розповсюдження забруднення
на міській
вулиці
Мета.
У науковій статті необхідно
вирішити питання щодо розробки 2D
чисельної моделі, яка дозволила б швидко
розрахувати процес забруднення
атмосферного повітря викидами
автотранспорту. Передбачено також
створити чисельну модель, що давала б
можливість прогнозувати рівень
забруднення атмосферного повітря при
використанні захисних бар’єрів біля
дороги. Методика.
Використано розроблену модель, яка
базується на рівнянні нев’язкої рідини
та рівнянні масопереносу. Рівняння для
потенціалу швидкості використовується
для розрахунку поля швидкості повітряного
потоку при експлуатації бар’єрів. При
вирішенні рівняння для потенціалу
швидкості задіяна неявна різницева
схема «умовної апроксимації». Для
чисельного рішення задачі масопереносу
вживається неявна поперемінно-трикутна
різницева схема. Чисельне інтегрування
здійснюється на прямокутній різницевій
сітці. Для формування складної форми
розрахункової області використовуються
маркери, а для моделювання джерела
емісії – модель точкового джерела, яка
формується за допомогою дельта-функції
Дірака. Результати.
Авторами розроблено 2D чисельну модель,
яка враховує основні фізичні фактори,
що впливають на процес розсіювання
шкідливих речовин в атмосфері при
викидах від автотранспорту з урахуванням
розміщення захисних бар’єрів біля
дороги. На основі побудованих чисельних
моделей проведено обчислювальний
експеримент із оцінки рівня забруднення
повітряного середовища на вулиці.
Наукова новизна.
Створено чисельну модель, яка дозволяє
розрахувати 2D аеродинаміку вітрового
потоку в умовах наявності перешкод та
процес масопереносу викидів токсичних
газів від автотраси. Модель дозволяє
враховувати наявність автомобіля на
дорозі, форму захисного бар’єру,
присутність бордюру. Виконано розрахунки
по визначенню зони забруднення, що
формується біля захисного бар’єру,
розташованого біля автомагістралі.
Практична значимість.
Розглянута ефективна чисельна модель,
яка може бути застосована при розробці
заходів із охорони навколишнього
середовища при експлуатації автомобільного
транспорту в місті. Розроблена модель
дозволяє оцінити розміри, форму та
інтенсивність зони забруднення біля
автомагістралі.
Ключові слова: забруднення
атмосфери; міські вулиці; поширення
забруднень; чисельне моделювання
Н. Н. БЕЛЯЕВ1*, О. С. СЛАВИНСКАЯ2*,
Р. В. КИРИЧЕНКО3*
1*Каф.
«Гидравлика и водоснабжение»,
Днепропетровский национальный
университет железнодорожного
транспорта
имени академика В. Лазаряна, ул. Лазаряна,
2, Днипро, Украина, 49010, тел. +38 (056)
273 15
09,
эл. почта water.supply.treatment@gmail.com
, ORCID 0000-0002-1531-7882
2*Каф.
«Управление производством и имуществом»,
Национальный транспортный университет,
ул. Суворова, 1, Киев, Украина, 01010, тел.
+38 (044) 280
82 03,
эл. почта water.supply.treatment@gmail.com, ORCID
0000-0001-5163-5645
3*Каф.
«Управление производством и имуществом»,
Национальный транспортный университет,
ул. Суворова, 1, Киев, Украина, 01010, тел.
+38 (044) 280
82 03,
эл. почта water.supply.treatment@gmail.com, ORCID
0000-0001-9918-3895
Численное моделирование
распространения
загрязнения на городской
улице
Цель.
В научной статье необходимо решить
вопрос разработки 2D численной модели,
которая позволила бы быстро рассчитать
процесс загрязнения атмосферного
воздуха выбросами автотранспорта.
Предполагается также создать численную
модель, которая давала б возможность
прогнозировать уровень загрязнения
атмосферного воздуха при использовании
защитных барьеров у дороги. Методика.
Использована разработанная модель,
основанная на уравнении невязкой
жидкости и уравнении массопереноса.
Уравнение для потенциала скорости
используется для расчета поля скорости
воздушного потока при эксплуатации
барьеров. При решении уравнения для
потенциала скорости задействована
неявная разностная схема «условной
аппроксимации». Для численного решения
задачи массопереноса употребляется
неявная попеременно-треугольная
разностная схема. Численное интегрирование
осуществляется на прямоугольной
разностной сетке. Для формирования
сложной формы расчетной области
применяются маркеры. А для моделирования
источника эмиссии – модель точечного
источника, которая моделируется с
помощью дельта-функции Дирака. Результаты.
Авторами разработана 2D численная
модель, которая учитывает основные
физические факторы, влияющие на процесс
рассеивания вредных веществ в атмосфере
при выбросах от автотранспорта с учетом
размещения защитных барьеров у дороги.
На основе построенных численных моделей
проведен вычислительный эксперимент
по оценке уровня загрязнения воздушной
среды на улице. Научная
новизна. Создана
численная модель, которая позволяет
рассчитать 2D аэродинамику ветрового
потока в условиях наличия помех и
процесс массопереноса выбросов токсичных
газов от автотрассы. Модель позволяет
учитывать наличие автомобиля на дороге,
форму защитного барьера, присутствие
бордюра. Выполнены расчеты по определению
зоны загрязнения, формируемой у защитного
барьера, который расположен у
автомагистрали.
Практическая значимость.
Рассмотрена эффективная численная
модель, которая может быть применена
при разработке мероприятий по охране
окружающей среды при эксплуатации
автомобильного транспорта в городе.
Разработанная модель позволяет оценить
размеры, форму и интенсивность зоны
загрязнения у автомагистрали.
Ключевые слова: загрязнение
атмосферы; городские улицы; распространение
загрязнений; численное моделирование
REFERENCES
Biliaiev,
M. M., Rusakova, T. I., & Kirichenko, P. S. (2014).
Modelirovaniye zagryazneniya
atmosfernogo vozduha vybrosami avtotransporta na ulicah gorodov
[Monograph]. Dnipropetrovsk: Aktsent PP.
Biliaiev,
M. M., Slavinska, O. S., &
Kyrychenko, R. V. (2017). Prediction
of atmospheric air pollution by emissions of motor transport taking
into account the chemical transformation of harmful substances.
Science and Transport Progress,
3(69),
15-22. doi:10.15802/stp2017/104549
Biliaiev,
M. M., & Rusakova, T. I. (2013). CFD
prediction of air pollution in the streets.
Ecology and Nature Management,
17,
188-194.
Marchuk,
G. I. (1982). Matematicheskoye
modelirovaniye v probleme okruzhayushchey sredy.
Moscow: Nauka.
Samarskiy,
A. A. (1983). Teoriya raznostnykh
skhem. Moscow: Nauka.
Düring,
I., Bächlin, W., Ketzel, M., Baum, A., Friedrich, U., &
Wurzler, S. (2011). A new simplified NO/NO2
conversion model under consideration of direct NO2-emissions.
Meteorologische Zeitschrift,
20 (1),
67-73. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2011/0491
Berlov,
O. V. (2016). Atmosphere protection in case of emergency during
transportation of dangerous cargo.
Science and Transport Progress,
1(61),
48-54. doi:10.15802/stp2016/60953
Nguyen,
T. N., Nguyen, T. C., & Nguyen, V. T. (2015). Numerical
simulation of wind flow and pollution transport in urban street
canyons. Advanced Science and
Technology Letters, 120,
770-777.
doi:10.14257/astl.2015.120.152
Chang,
C.-H., Lin, J.-S., Cheng, C.-M., & Hong, Y.-S. (2013).
Numerical simulations and wind tunnel studies of pollutant
dispersion in the urban street canyons with different height
arrangements. Journal of Marine
Science and Technology, 21(2),
119-126.
Overman,
H. T. J. (2009). Simulation
model for NOx
distributions in a street canyon with air purifying pavement.
(Master thesis). University Twente, Netherlands.
Prof.
S. A. Pichugov,
Dr. Sc. in Phys.-and-Math. (Ukraine);
Prof. S. Z.
Polishchuk, D. Sc. (Tech.), (Ukraine)
recommended this article to be published
Received:
April 10, 2017
Accessed:
July 21, 2017
doi
10.15802/stp2017/109526 ©
M. M. Biliaiev, O. S. Slavinska, R. V. Kyrychenko,
2017
, (1)
.
, (2)
is «fictitious»
time.
the solution of equation (2) tends to the solution of equation (1).
.(3)
can be easily determined from
each difference equation (3) using explicit formulae of «running
calculation».
As the «initial»
condition for Eq. 2 we may use, for, example, P=0
for
=0.
, (4)
are
the wind velocity components;
are the diffusion coefficients;
is rate of emission;
– are Dirac delta function; t is
time.
, (5)
,
,
is Dirac delta function;
are the coordinates of the point source.
.