ISSN
2307–3489 (Print), ІSSN
2307–6666
(Online)
Наука
та прогрес транспорту. Вісник
Дніпропетровського
національного університету залізничного
транспорту, 2017,
№
2
(68)
НЕТРАДИЦІЙНІ
ВИДИ ТРАНСПОРТУ. МАШИНИ ТА МЕХАНІЗМИ
udc
004.942
s. s.
tyshchenko1, a.
V. krasniuk 2, t.
v. ulchenko3, A.
S. SHCHERBAK 4*
1Dep.
«Higher Mathematics»,
Dnipropetrovsk State Agrarian-Economic
University,
Voroshilov
St., 25, Dnipro,
Ukraine, 49600,
tel. +38 (056)
713 51 86,
e-mail
mozganet@mail.ua, ORCID
0000-0003-4860-4818
2Dep.
«Grafics», Dnipropetrovsk National
University of Railway Transport
named after Academician V. Lazaryan,
Lazaryan St., 2, Dnipro, Ukraine,
49010, tel. +38 (056) 373 15 38,
e-mail krasnyuk@mail.diit.edu.ua,
ORCID 0000-0002-1400-9992
3Dep.
«Grafics», Dnipropetrovsk National
University of Railway Transport
named after Academician V. Lazaryan,
Lazaryan St., 2, Dnipro, Ukraine,
49010, tel. +38 (067) 724 47 22, e-mail ulchenkotv@ya.ru,
ORCID 0000-0003-2354-7765
4Dep.
«Grafics», Dnipropetrovsk National
University of Railway Transport
named after Academician V. Lazaryan,
Lazaryan St., 2, Dnipro, Ukraine,
49010, tel. +38 (056) 373 15 59, e-mail pro-f@ukr.net,
ORCID 0000-0003-1340-0284
DESIGNING OF DEVELOPED
SURFACES OF COMPLEX PARTS
Purpose. The paper focuses on ensuring the
rational choice of parameters of the mating surfaces of parts when
designing process equipment based on the methods of artificial
intelligence. Methodology. The paper considers the
geometric model of a ruled developed surface, the conditions of
existence of such a surface and provides a generalized algorithm for
surface plotting regardless of the type of the working element or the
machine-building product. One of the most common technical surfaces
are the ruled ones, among which a special position is occupied by
developed surfaces (thanks to their differential-parametric
properties): surface tangent plane is n contact along the rectilinear
generator and does not change its position in space when changing the
point of contact; surfaces can be produced by bending sheet metal.
These provisions enable a product manufacturer to save significant
material and energy means, therefore, the development of geometric
models of such surfaces is an important task. Findings. We
analyzed the geometrical model of the developed surface which is
incident to two guides. Experimental studies have shown the
application prospectivity of semi-digger
moldboards on moldboard plows, particularly on the double-deck ones.
Taking into account the operating speed of the plow 2.8 m/s, the
plant residues plowing percentage for plow with semi-digger
moldboards is 98.9%, and with the digger ones – 96.1%.
Originality. According to results: 1) the approaches to
solving the problem of recognition of wear conditions of the tested
interface, depicted by its conceptual model, were elaborated;
2) the corresponding algorithms of the computational
procedures were built; 3) the mathematical model that determines the
effect of the parameters of the contacting surfaces on their
performance properties – linear wear rate during the normal wear
and tear was developed; 4) for this model the theoretical
prerequisite of use for the random mating study were designated.
Practical value. Currently, these areas produced significant
results which are in line with modern requirements of construction
engineering. The process of parametric model optimization generates a
plurality of desired values of the surface parameters. There are
formed the algorithms for automatic recognition of design features
and operation of interfaces by their images, which are set by a
structured set of formal signs. The recognition result is the
interface designation to a particular group, each of which
corresponds to an individual computational model of quality
parameters normalization.
Keywords: geometry; surfaces; developed surfaces;
model; working elements
Introduction
For a multiple production the
most important among the technological equipment is mechanical
processing equipment characterized by the need of frequent change,
optimal service life is 5-7 years. Analysis of design methods of
technological and mechanical processing equipment showed that at the
early design stages it is very difficult to assess and take into
account the variety of factors affecting the quality of its work.
There is a problem of automated selection of design and process
parameters the mating surfaces to ensure operating purpose of the
product. At the same time, there is no scientific methodological
framework that allows taking into account the design and
technological features of the designed equipment.
One of the
main directions of descriptive geometry
is designing surfaces, linear and two-dimensional contours, which
correspond to different positional, metric, differential conditions.
Currently, these areas received significant results that meet the
modern requirements of design planning.
The works
[10, 11]
present the geometric model
of ruled surfaces with multiparameter sets of lines and special
lines of surfaces, but a large number of parameters and difficult
determination of special lines, such as curvature, make the use of
these models difficult in practice. The
works [12-15]
are devoted to the development of geometric models of tillage
working element surfaces. The disadvantage of these models is that
they are specified for the working element, which reduces the
possibility of their use in the design of other tools. A
common
shortcoming of
these models
is that
they are
presented in
general or
for a
specific working
element.
This leads to the fact that in each case it is necessary to develop
the own algorithm for surface building.
Purpose
The main
directions of the descriptive geometry of surfaces formulated by I.
I. Kotov [7,
8] and including
development of methods for designing linear and two-dimensional
contours, continuous frames in compliance with the set
differential-isometric conditions, generation of contours and
surfaces equations, are still up to date. Furthermore, increasing
requirements for accuracy characteristics,
increase in speed and the need to improve the dynamic
characteristics of surface interactions with the environment made
the surface geometry conditions more complicated. For example, the
transition curves of railways need continuous fourth derivative at
the junctions [4, 18];
bi-dimensional contours must have degree of smoothness at the joint
not lower than the second one [3, 9]
for the surfaces, operating in conditions of high density
environment (working elements of tillage tools, machines and
mechanisms in the car-locomotive facilities of railways, ship
contours, etc.) or of high speeds.
The above
generates an urgent need to develop new methods for continuous
mathematical surface models (MSM), which correspond to a large
number of
differential geometric terms with a given degree of accuracy and
solution of various applied problems on the received MSM.
An important sector of
technology, which is connected with engineering progress, are those
units that are engaged in designing and manufacturing of products,
whose main functional element is the surface, working in conditions
of high speeds or a large density, particularly the tillage elements
and machines. Energy costs thus depend on the geometric properties
of surfaces.
One
of the
most common
technical
surfaces are
the ruled
ones, among
which a
special position
is occupied
by developed
surfaces thanks
to their
differential-parametric
properties:
– surface
tangent plane is n contact along the rectilinear generator and does
not change its position in space when changing the point of contact;
– the
surfaces can be made by bending sheet metal.
These provisions enable a
product manufacturer to save significant material and energy means,
therefore, the development of geometric models of such surfaces is
an important task.
The work purpose is to ensure
the rational choice of parameters of the mating surfaces of parts
when designing process equipment based on the methods of artificial
intelligence.
The study
object is a combination of machining and mechanical processing
equipment, tools and other machine parts, working in conditions of
friction under boundary lubrication and made of general
purpose structural materials.
The paper
considers the geometric model of a ruled developed surface, the
conditions of existence of such a surface and provides a generalized
algorithm for surface plotting regardless of the type of the working
element or the machine-building product [6].
Methodology
We know that
a developable
surface is given by two curves which have the property: if through
any point of the first curve to draw the area tangent to both
curves, this tangent property is kept in
many geometric transformations.
Assume that we have two set
curves:
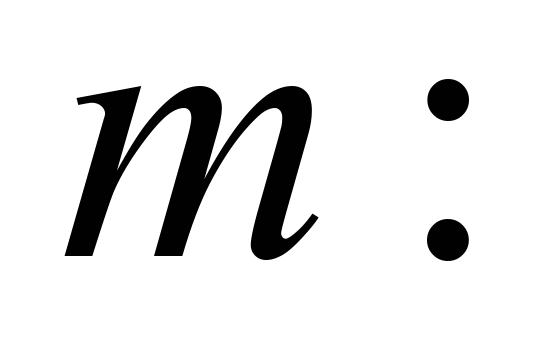
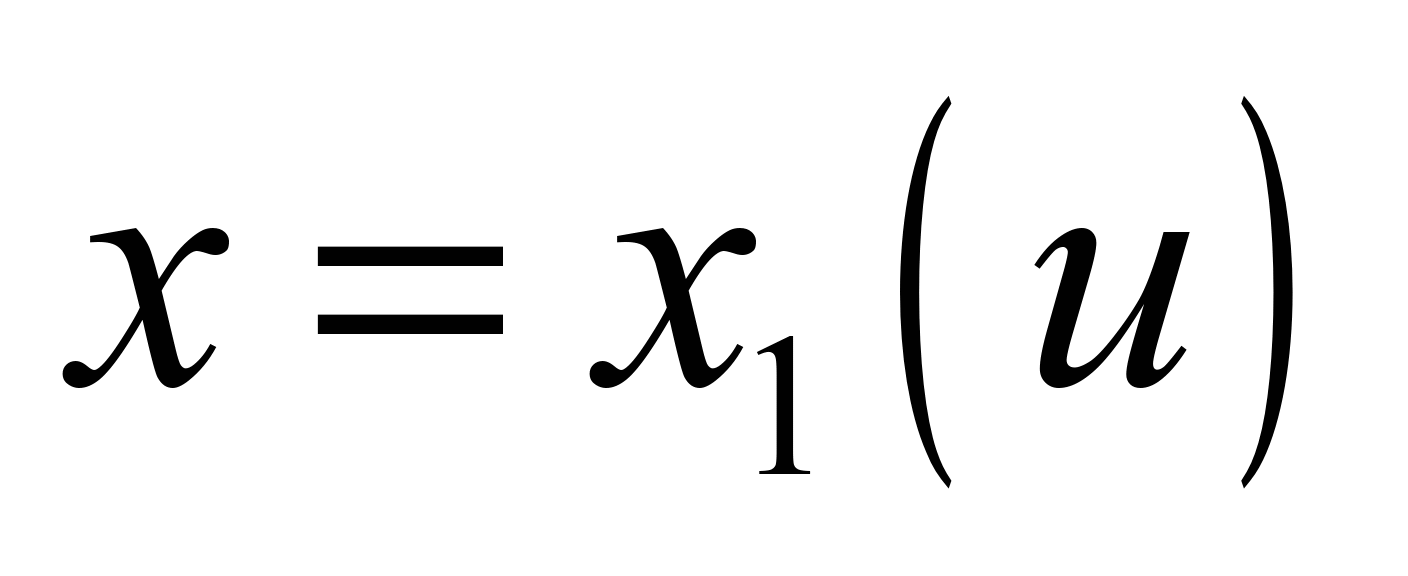 ,
,
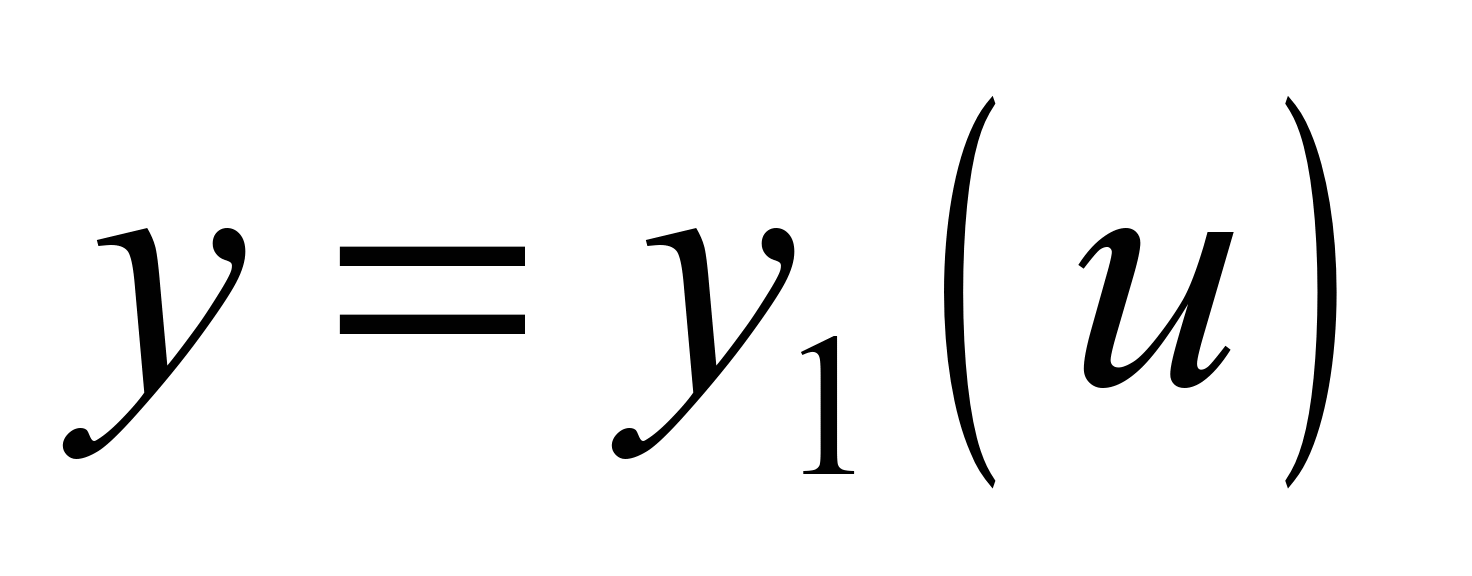 ,
,
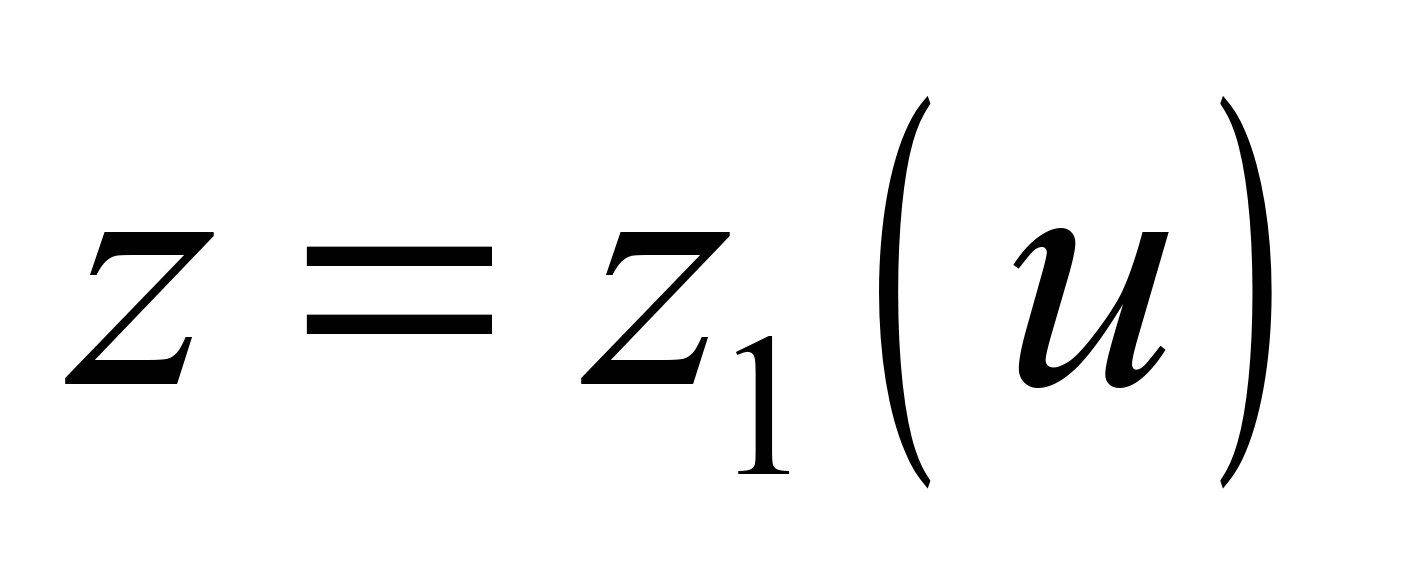 , (1)
, (1)
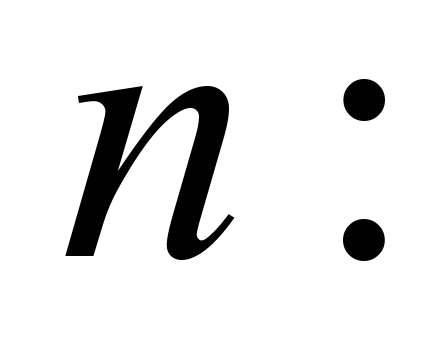
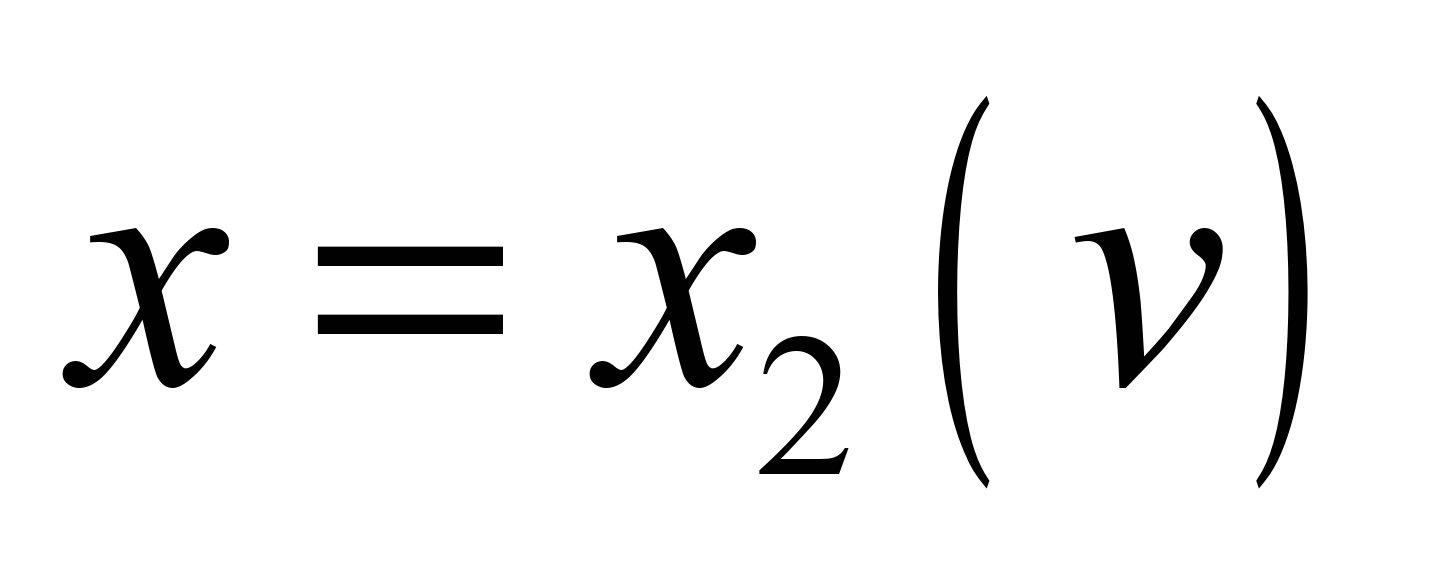 ,
,
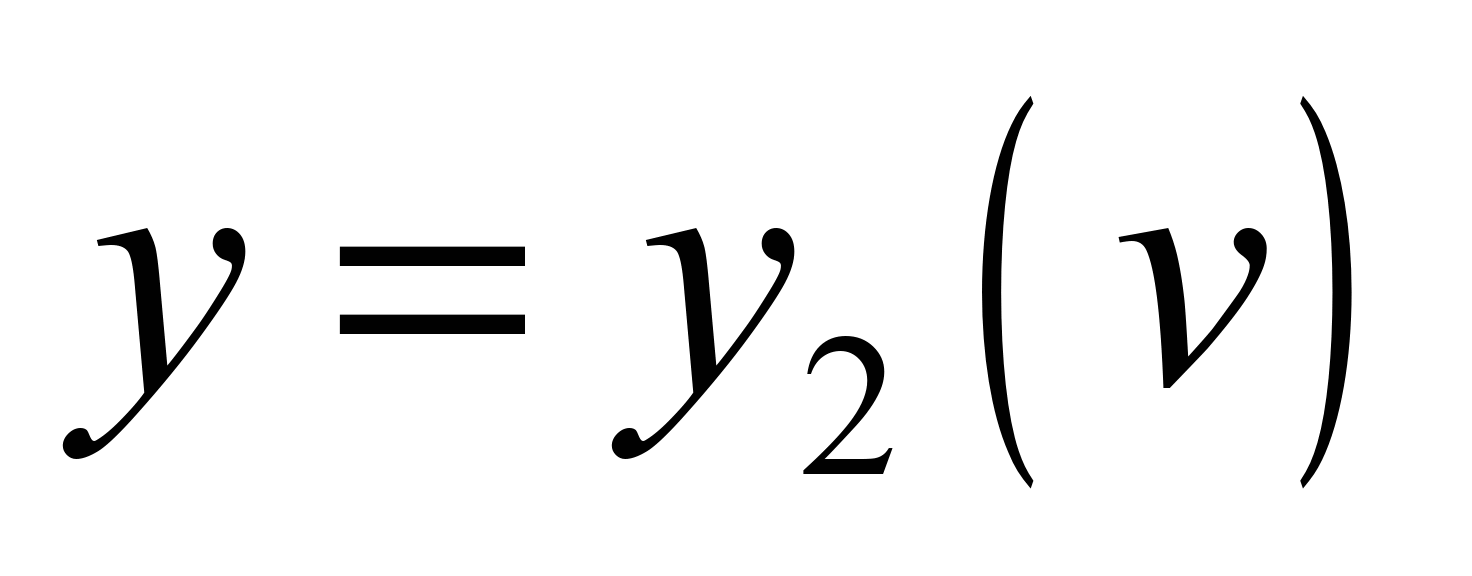 ,
,
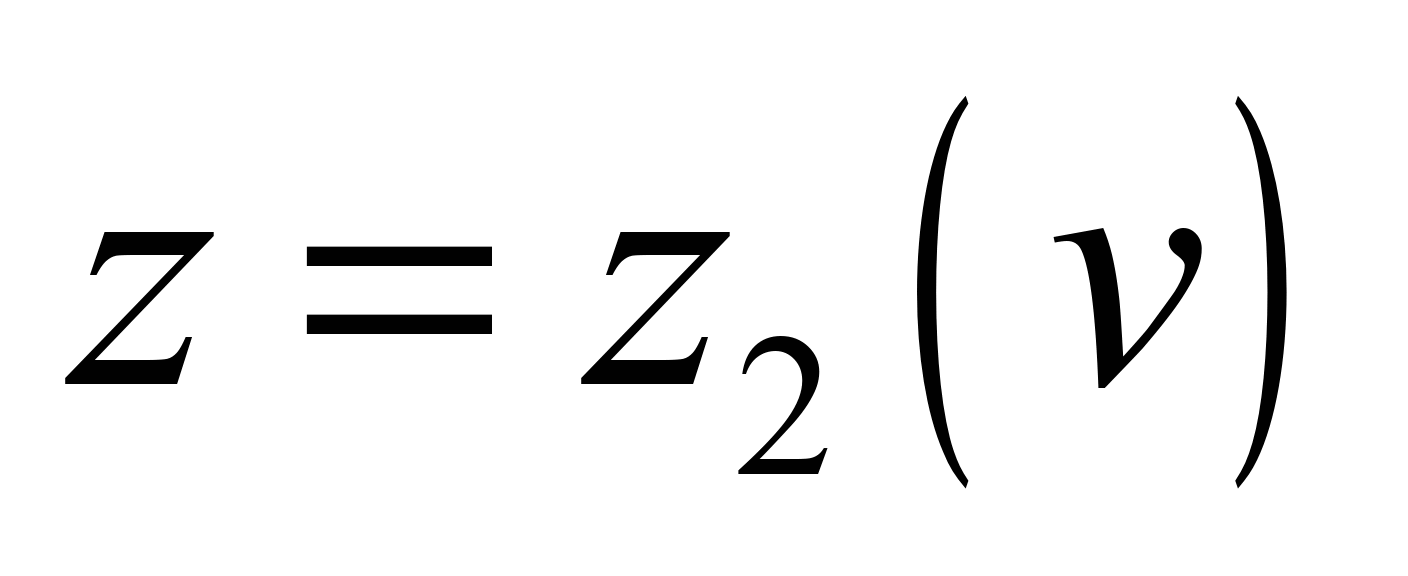 , (2)
, (2)
which
separate a
congruence from
a set
of lines:
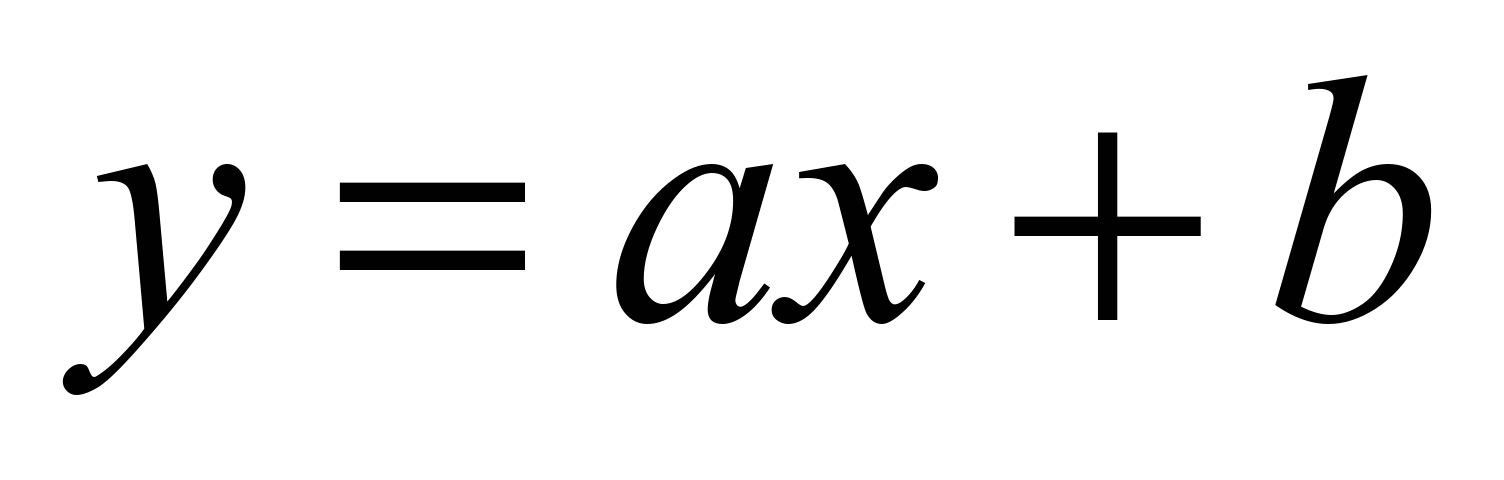 ,
,
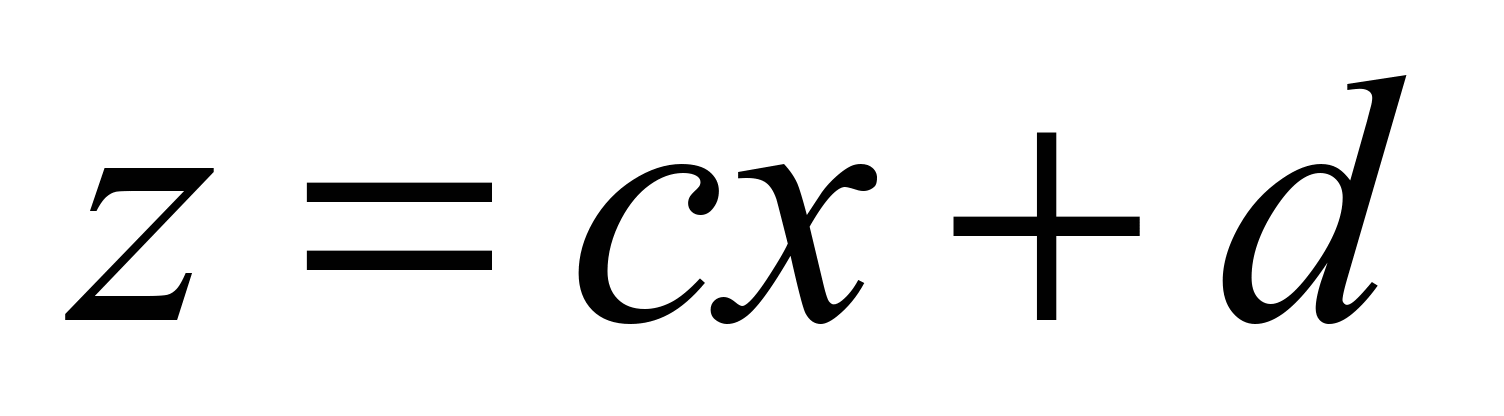 . (3)
. (3)
Herewith the
parameters
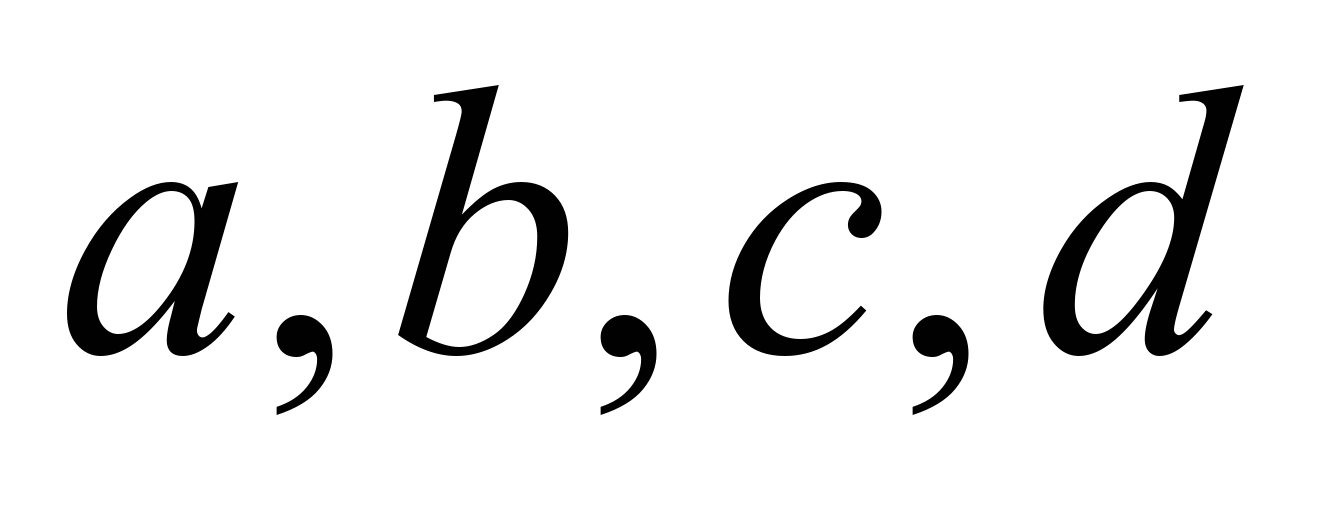 depend on
depend on
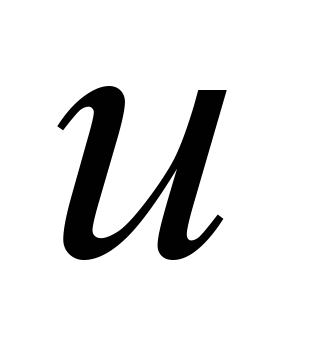 and
and
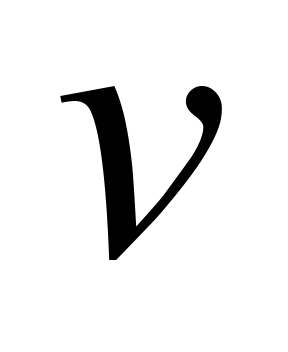 and are determined by the equations (1) and (2), (3), so that,
and are determined by the equations (1) and (2), (3), so that,
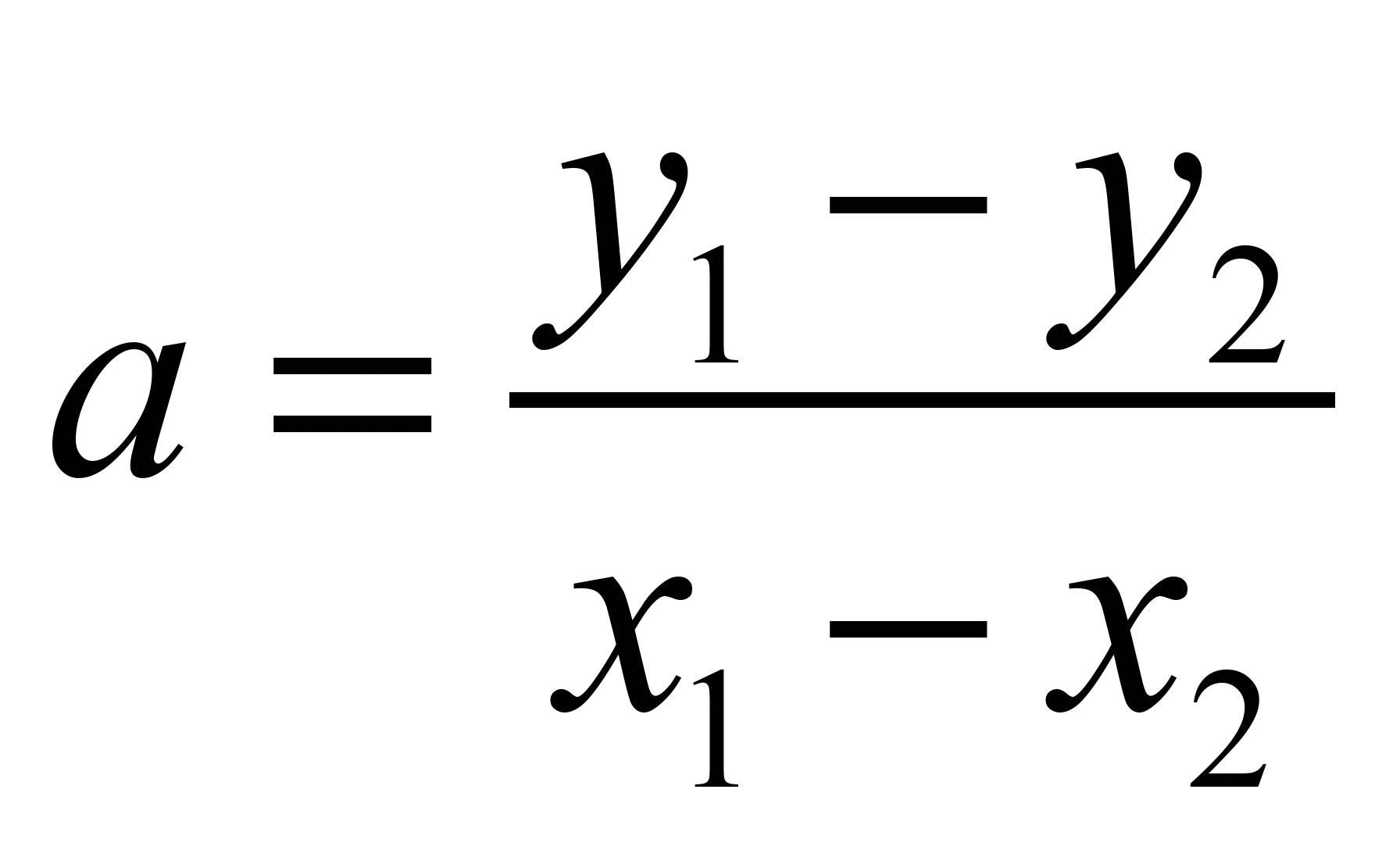 ;
;
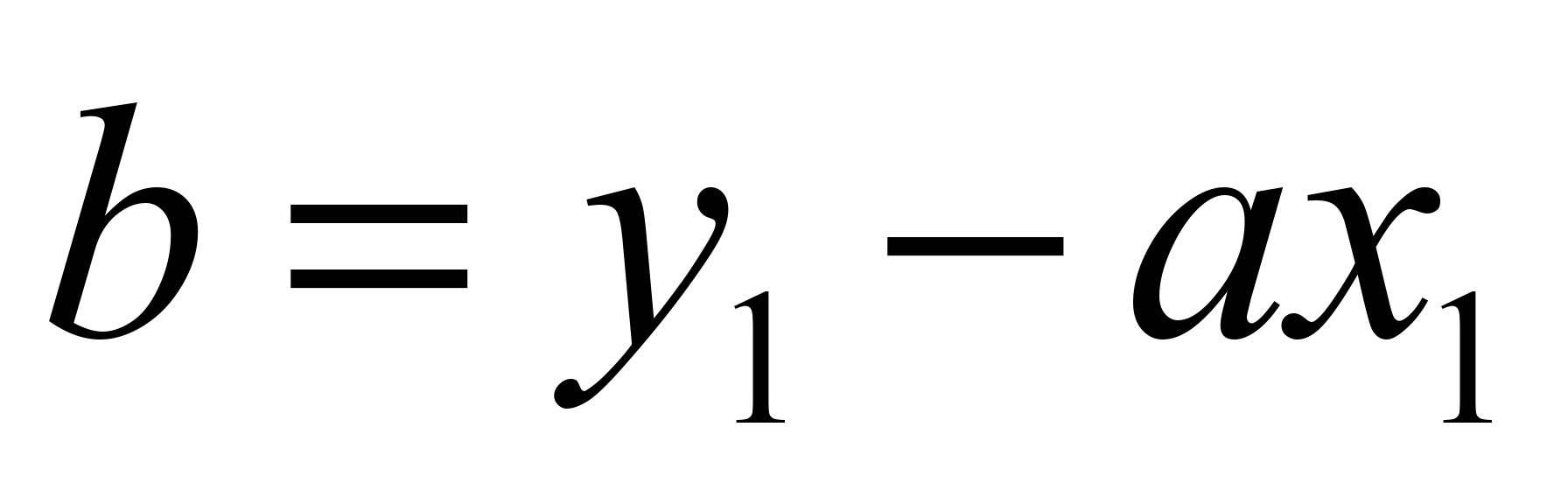 ; (4)
; (4)
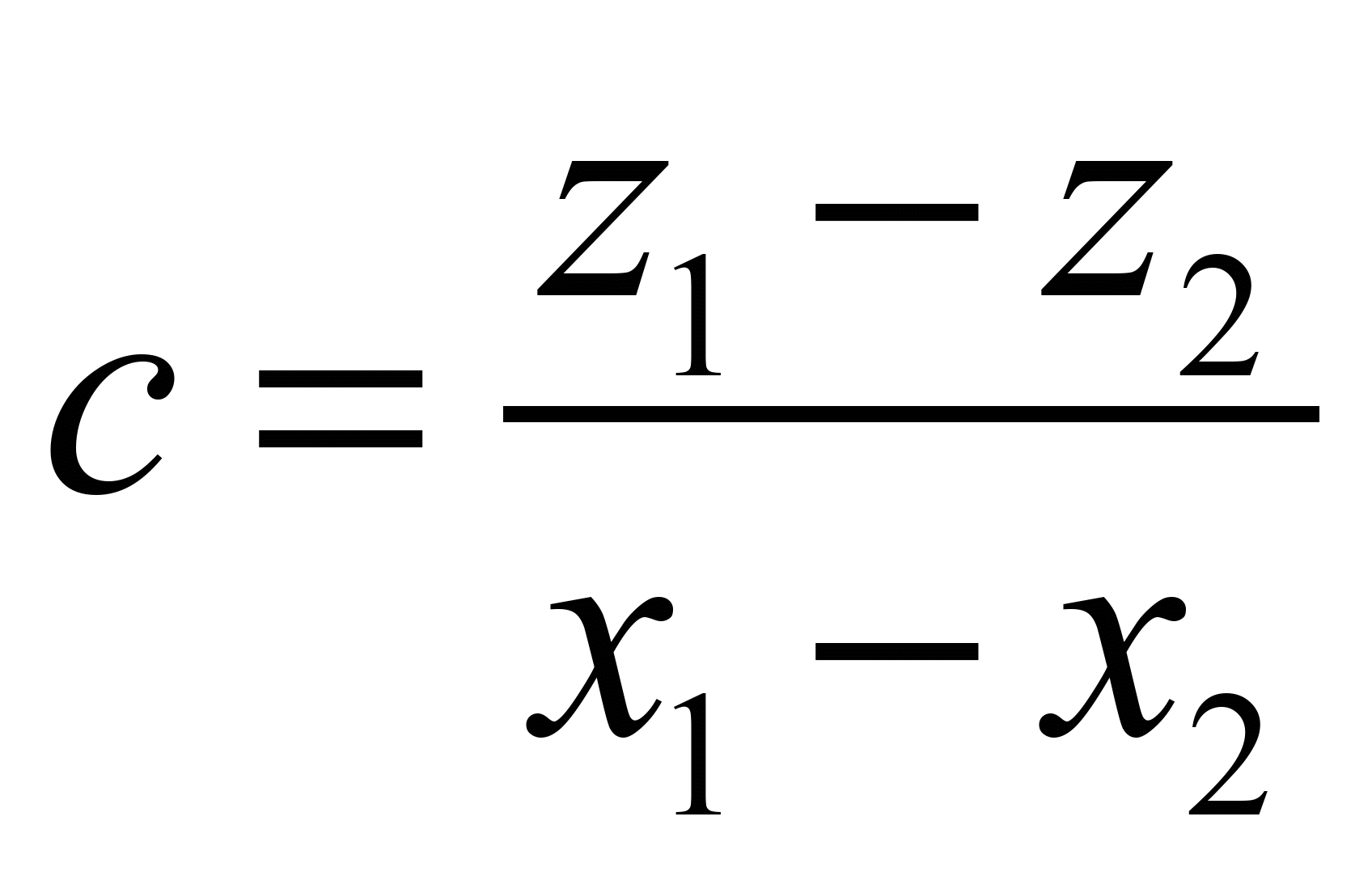 ;
;
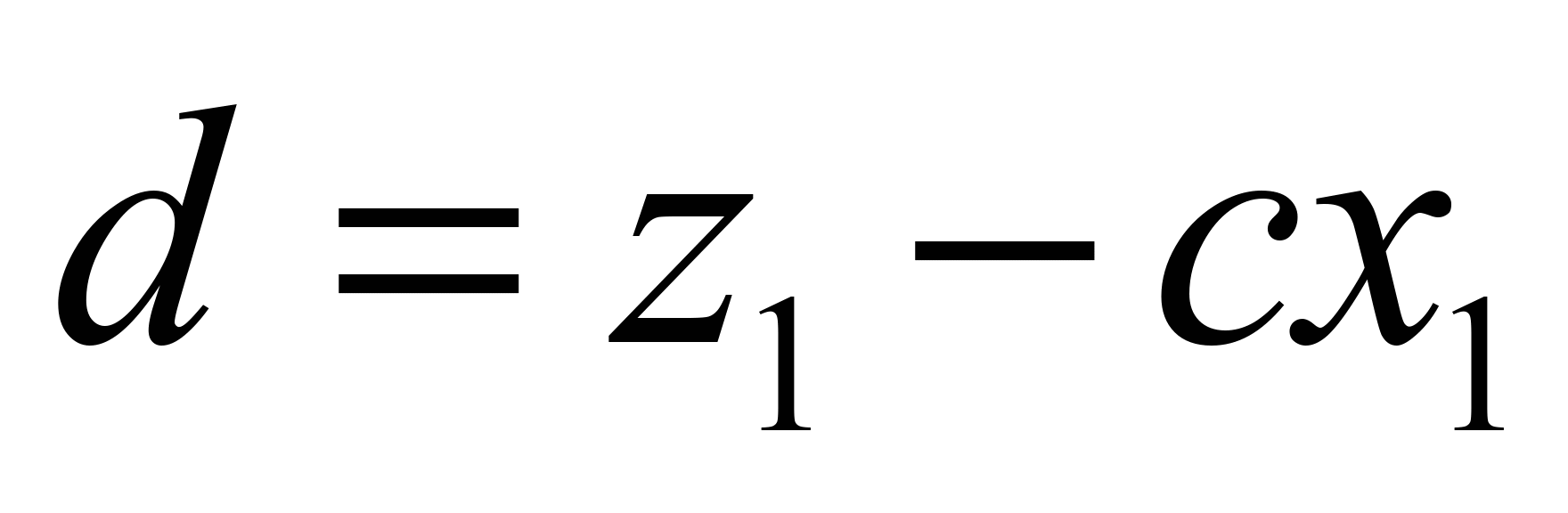 . (5)
. (5)
To
separate a
developable
surface, we
introduce
additional
condition as
compatibility of
equations
defining the
framing of
both curves
with the
standards of
future surface
[1, 2]:
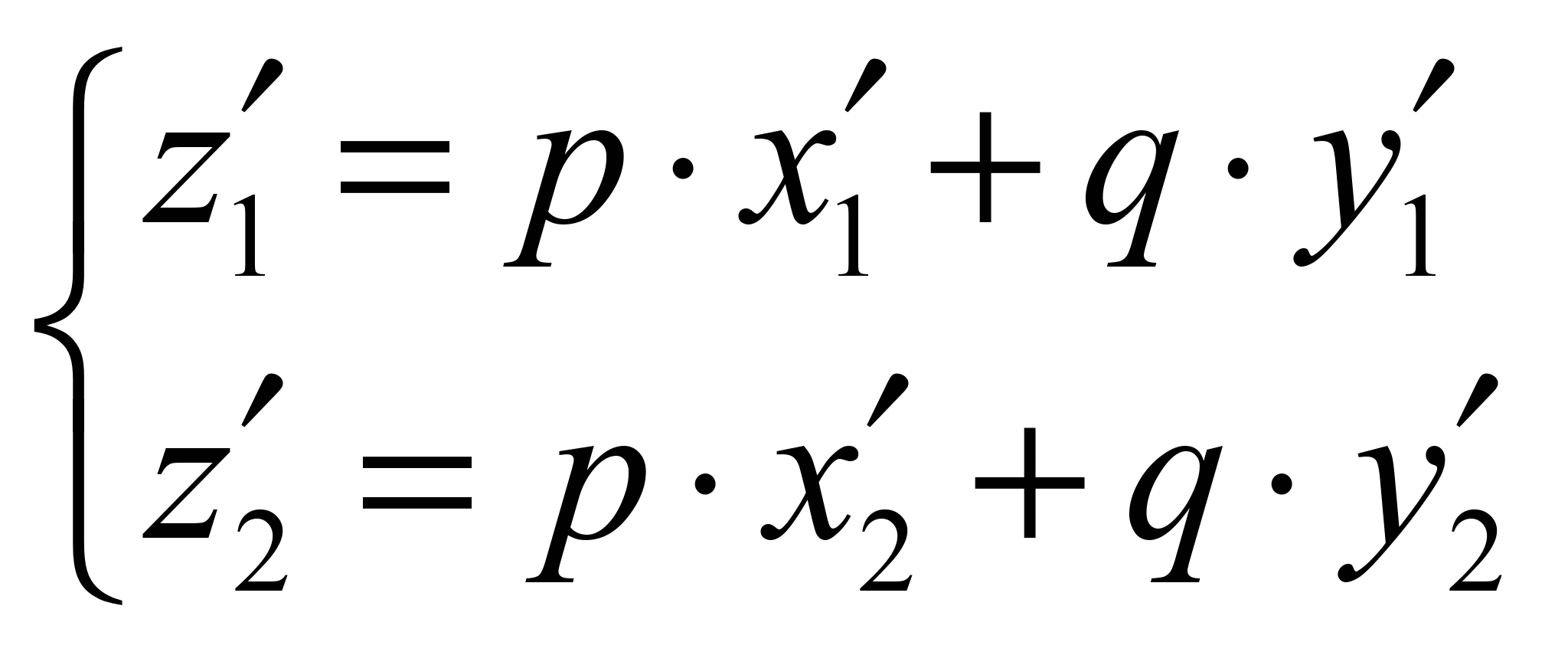 , (6)
, (6)
where
primes indicate
the rates
of the
functions that
define curves
by their
parameters, and
differential
equation of
ruled surface:
 , (7)
, (7)
which is equivalent to the
equation:
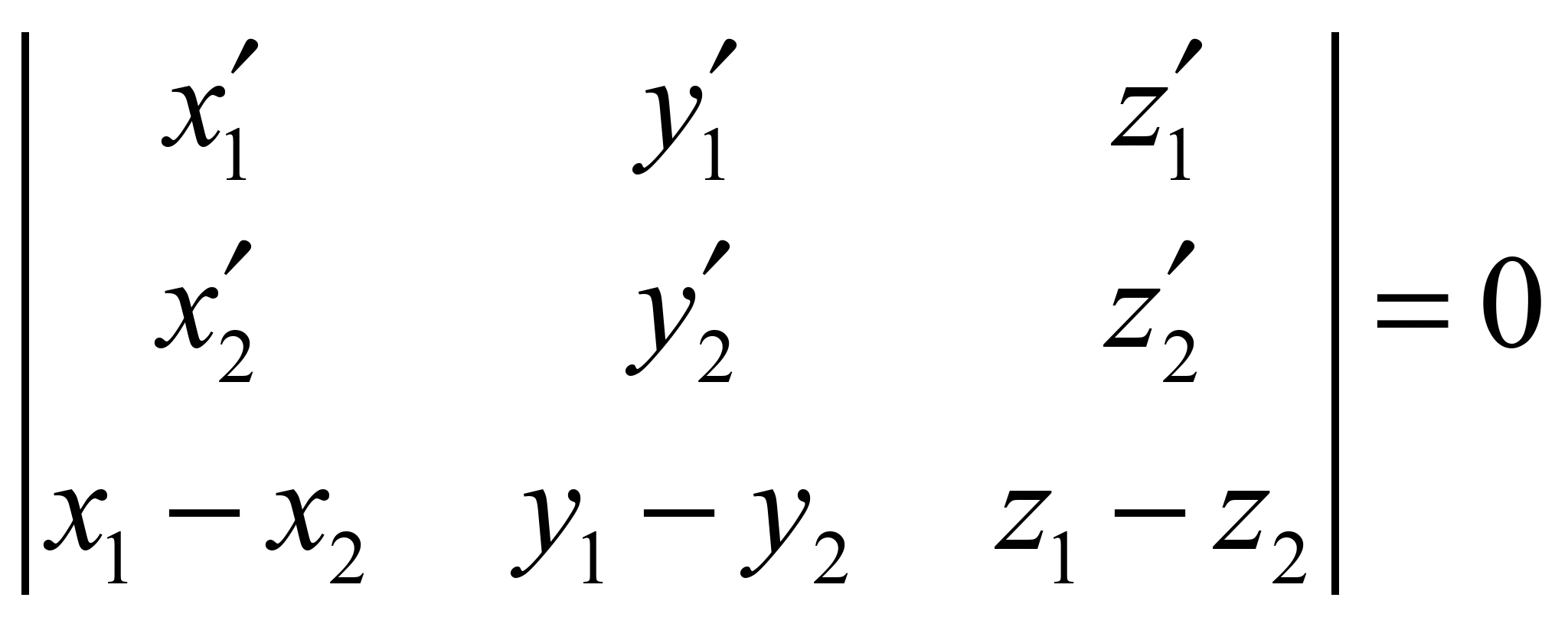 . (8)
. (8)
The equation (6) expresses the
fact that the surface standards at the relevant points of the set
curves (which belong to the same straight line generator) are
parallel that is equivalent to existence of general tangent area to
the surface in these points. Indeed, given (4) and (5), the equation
(8) takes the form:
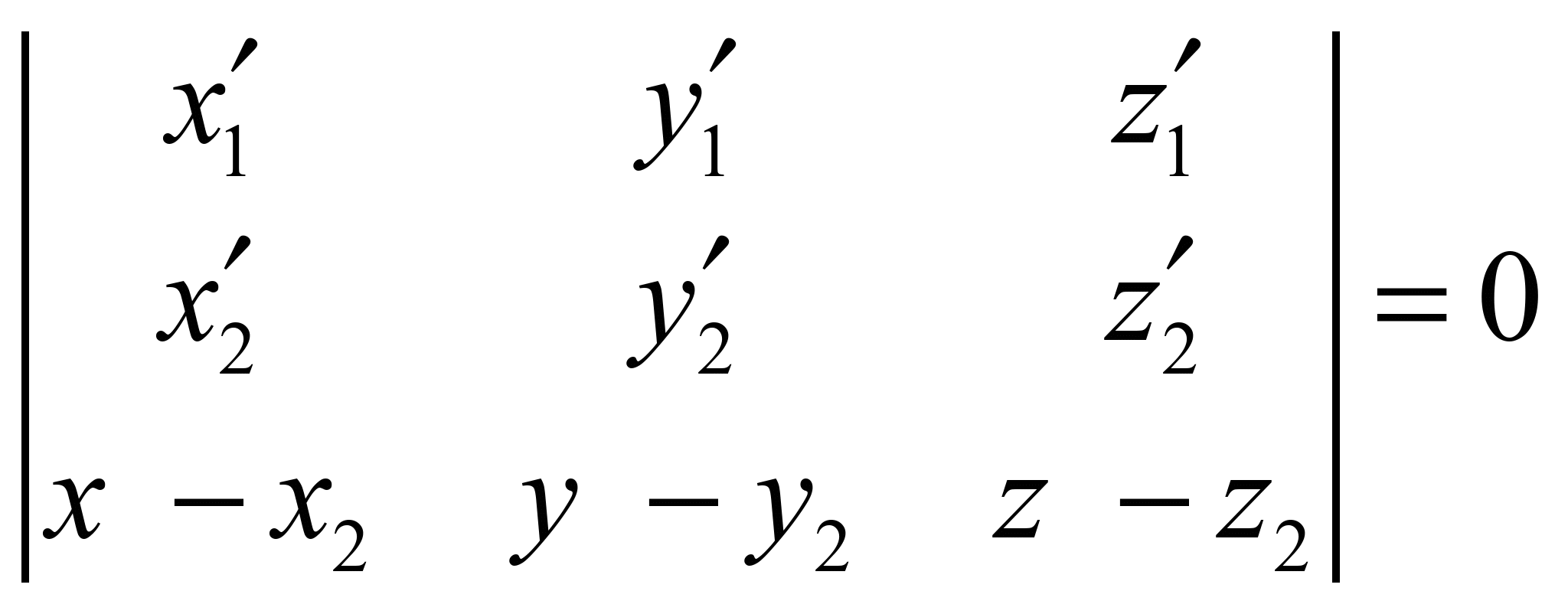 , (9)
, (9)
i.e. vectors tangent to the
curve and generators are coplanar.
Equation
(9) allows
determining the
relationship
between the
parameters
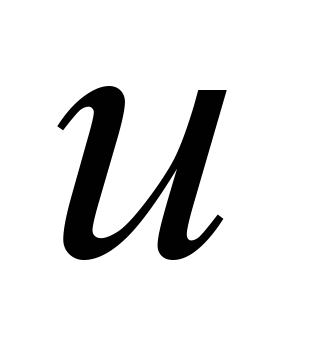 and
and
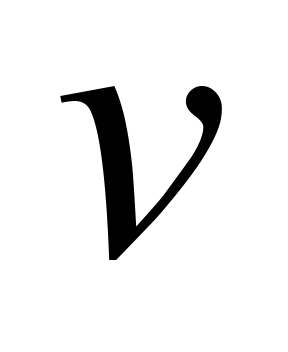 provided the
surface
developability:
provided the
surface
developability:
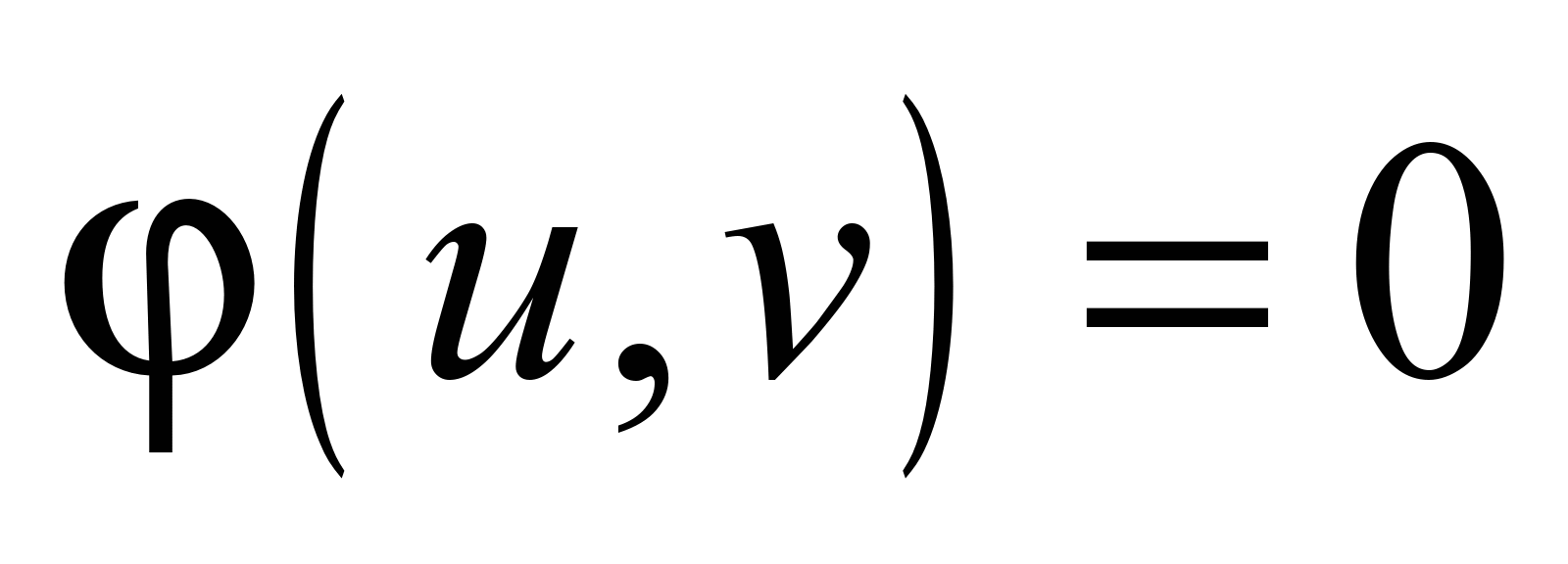 , (10)
, (10)
that
together with (3), (4), (5) gives the
desired surface equation.
If one of
the parameters (for example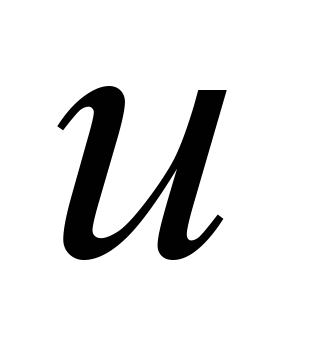 )
can be from (10) expressed clearly through the other parameter,
)
can be from (10) expressed clearly through the other parameter,
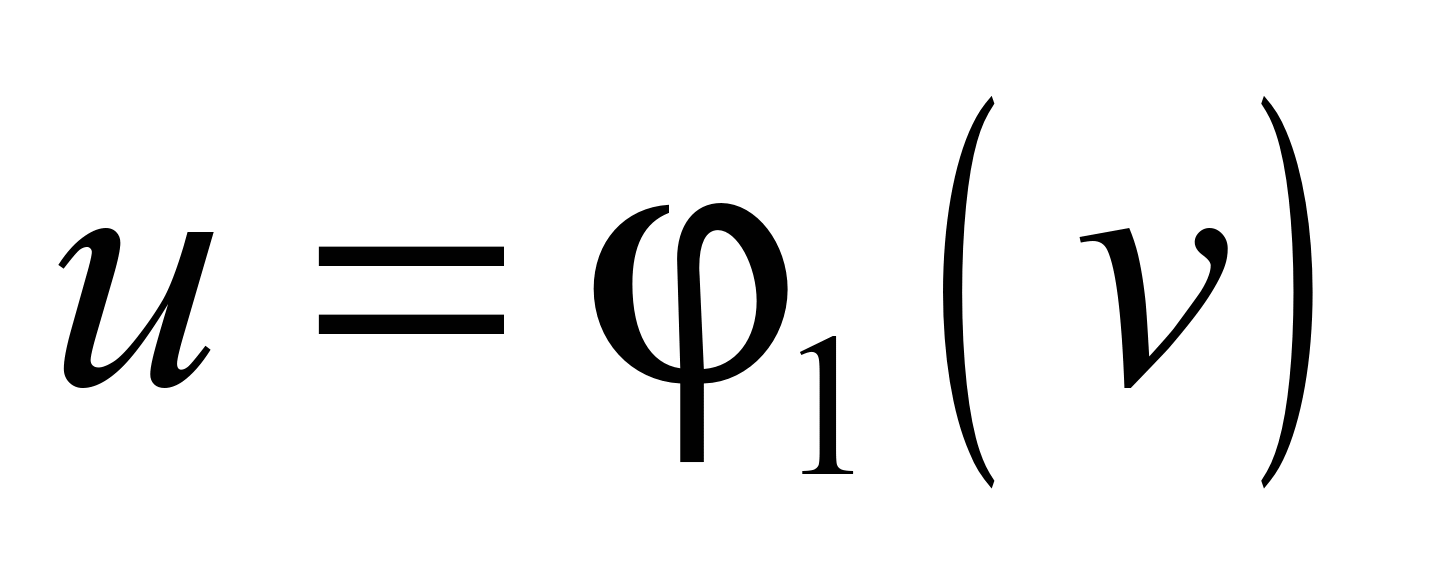 , (11)
, (11)
then with (4), (5) and (11)
surface equation will look like:
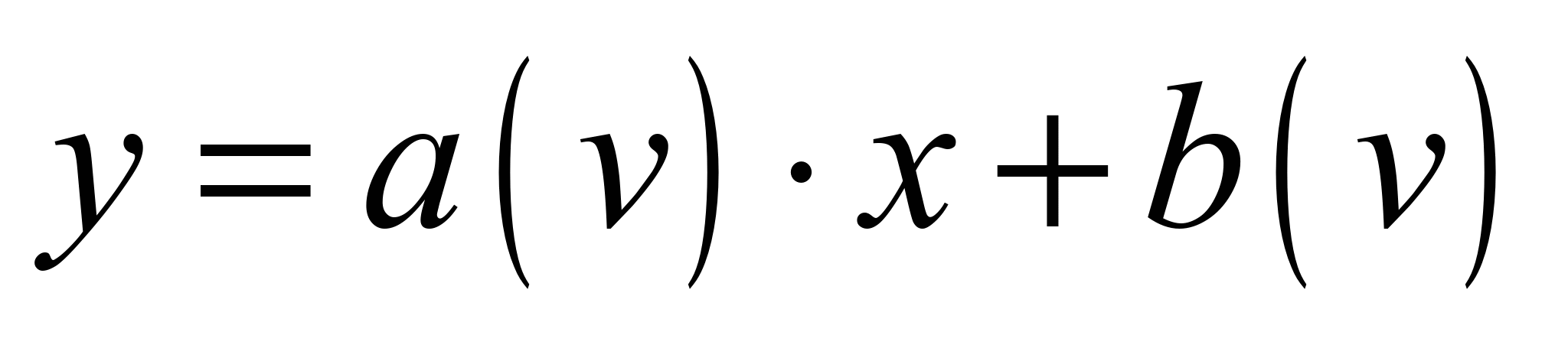 ,
,
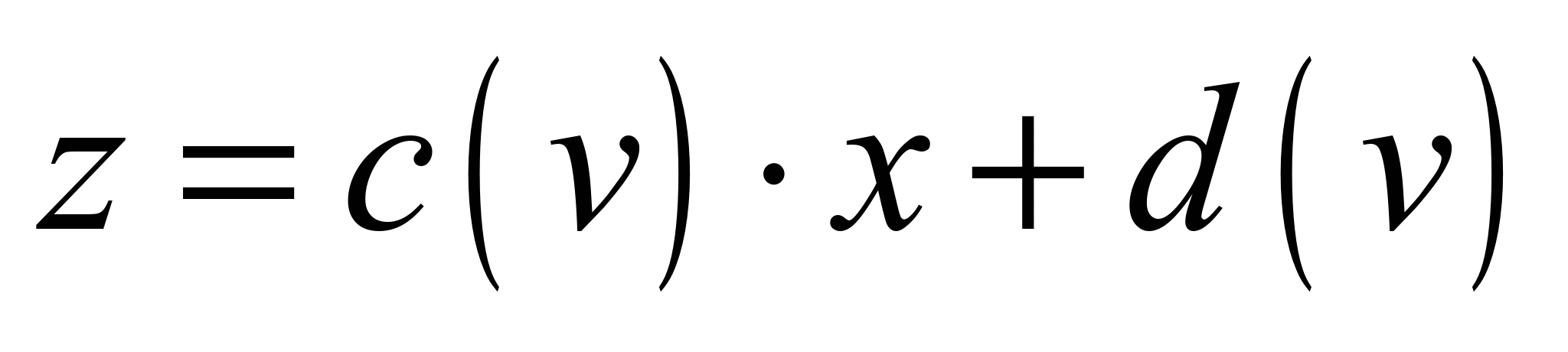 . (12)
. (12)
To find the
edge of regression l, we
differentiate
(12) by
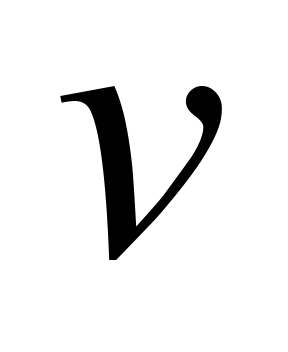 :
:
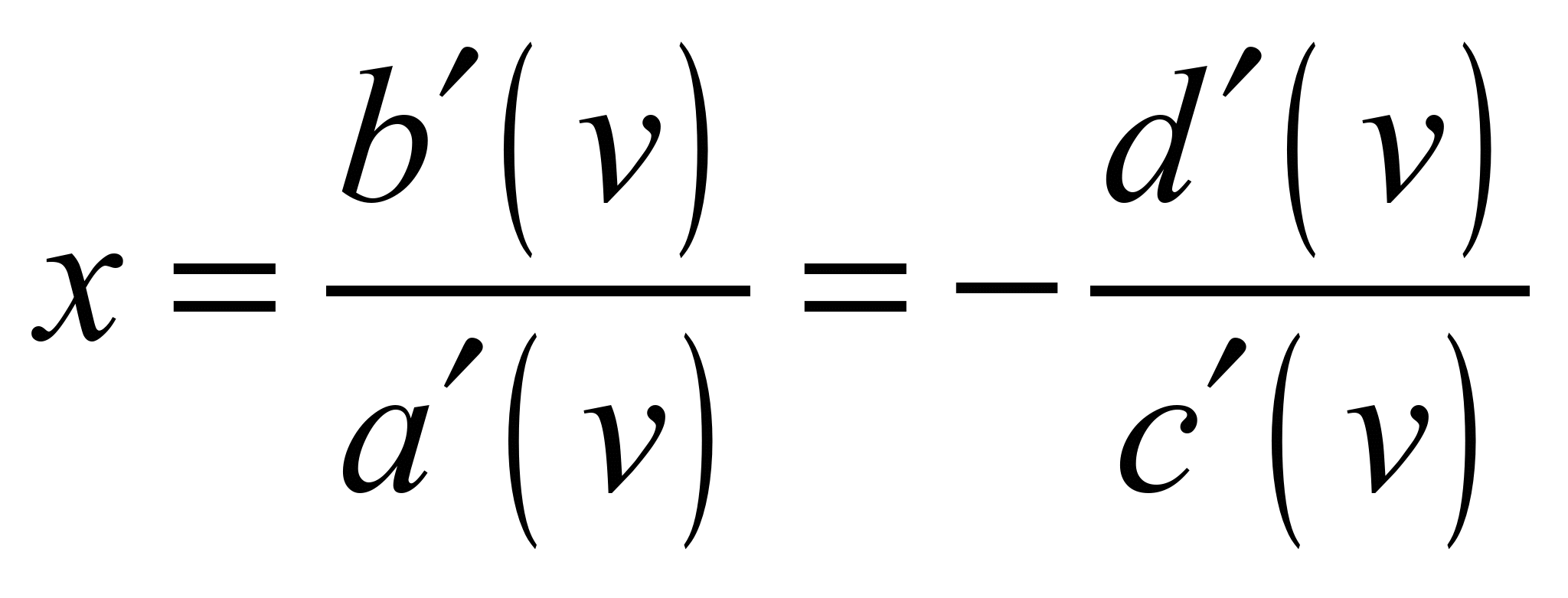 . (13)
. (13)
One of the equations (13)
together with (12) will define l.
Obviously,
not every
two lines
with their
shape and
position in
space will
enable to
plot a developable surface.
In solving
the determinant
(9) there may
be the
following cases
(except the
discussed above,
which leads
to (10)):
– determinant
identically
equals to
zero (curves
are in
the same
area, which
is the
sought surface
regardless of
function
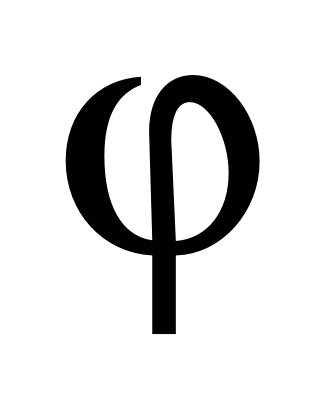 );
);
– as
a result
of the
solution (9)
becomes the
equation of
one parameter
(there is
no developable
surface, there
are separate
generators,
whose number
equals to
the number
of roots
of equations,
where there
is a
common tangent
area by
given curves);
– determinant
(9) is not equal to zero (developable surface does not exist).
Thus, the desired result gives
only the case that leads to (10).
We
consider the
equation (6) and
(9). Minor determinants
 of the
first two
rows of
the determinant
(9) are the
coordinates of
the surface
standard
of the
first two
rows of
the determinant
(9) are the
coordinates of
the surface
standard
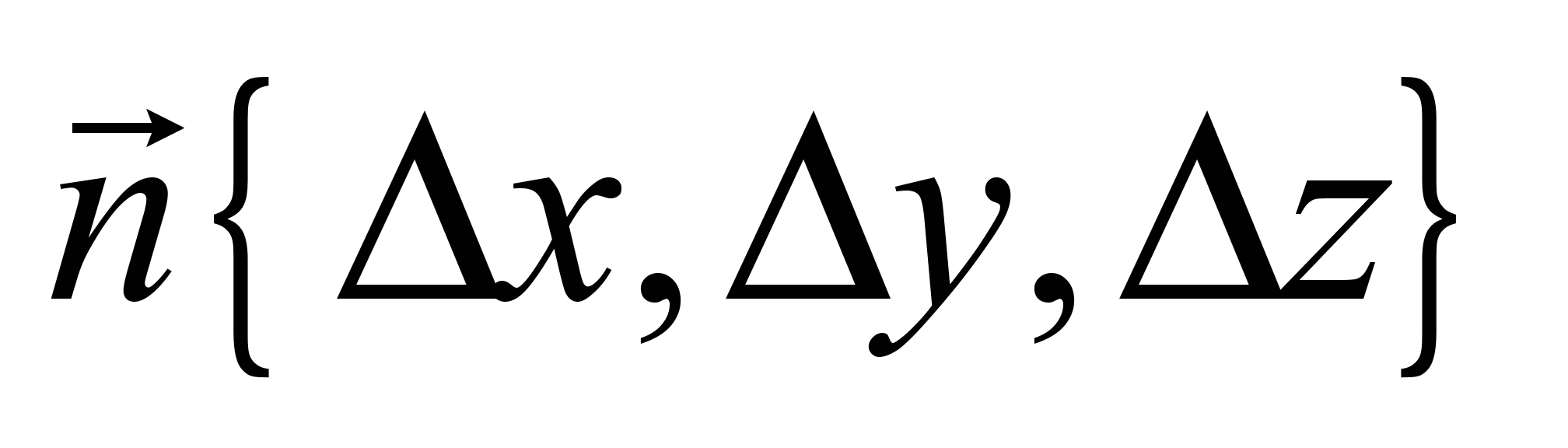 ,
so that
,
so that
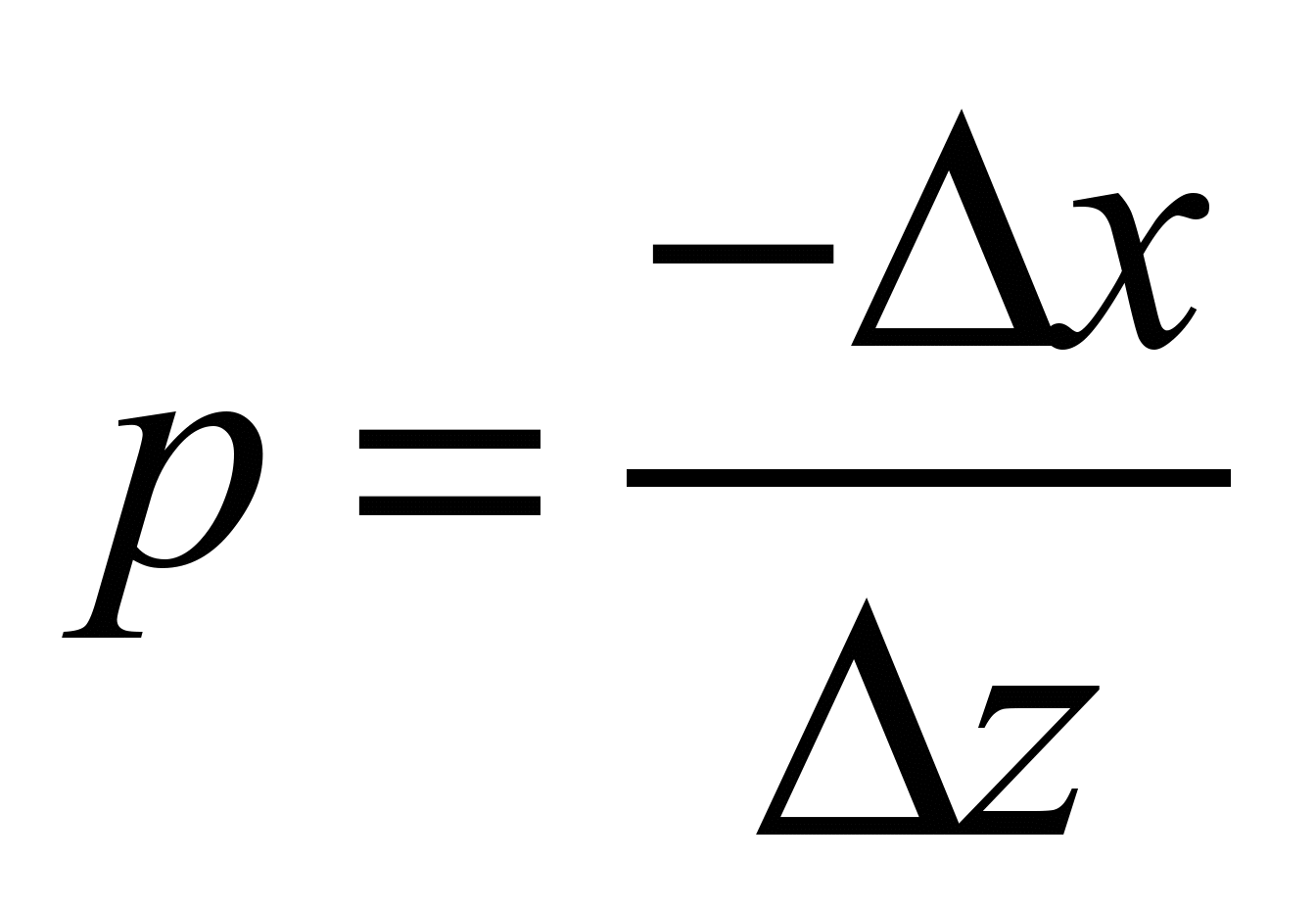 ,
,
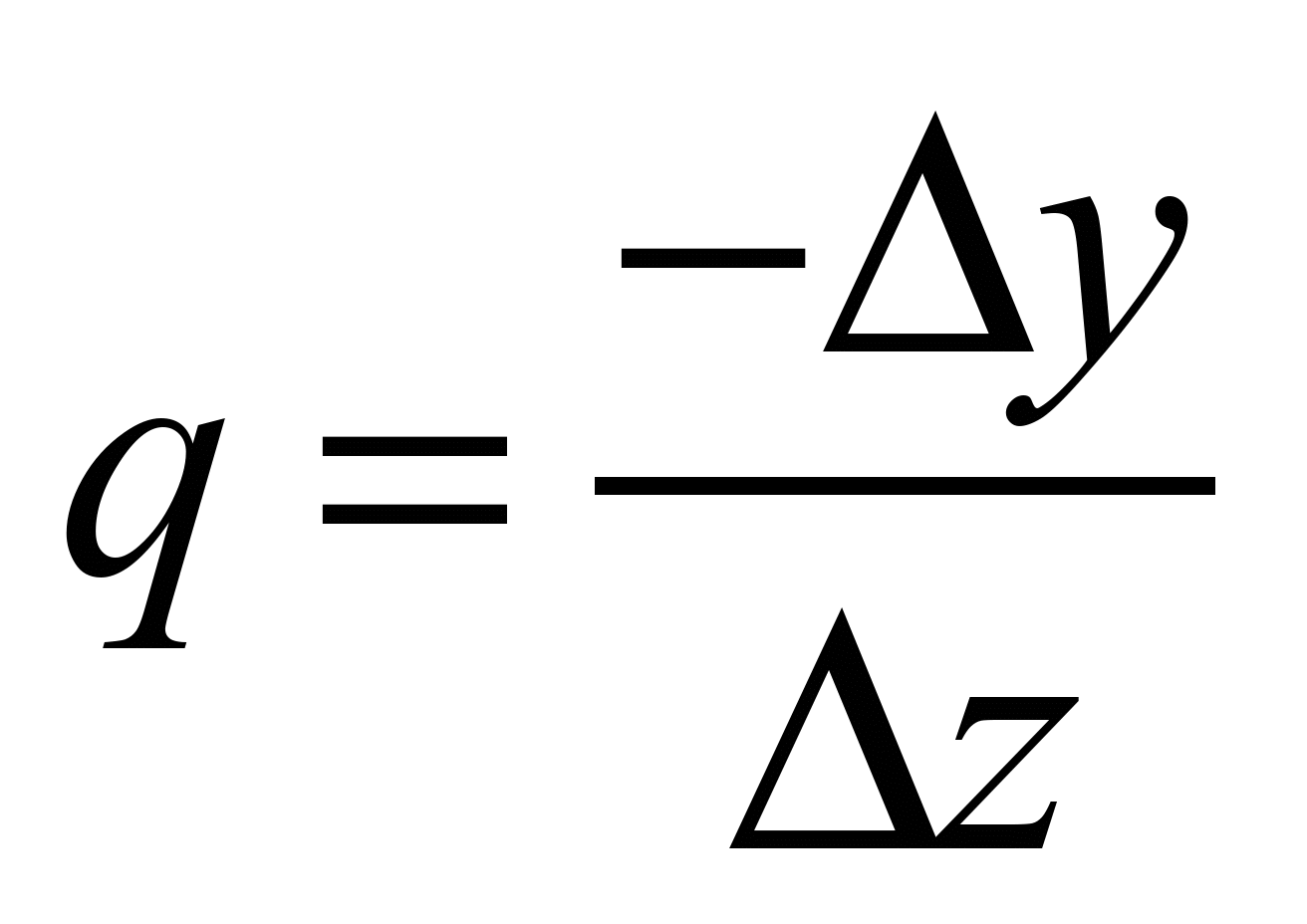 , (14)
, (14)
where
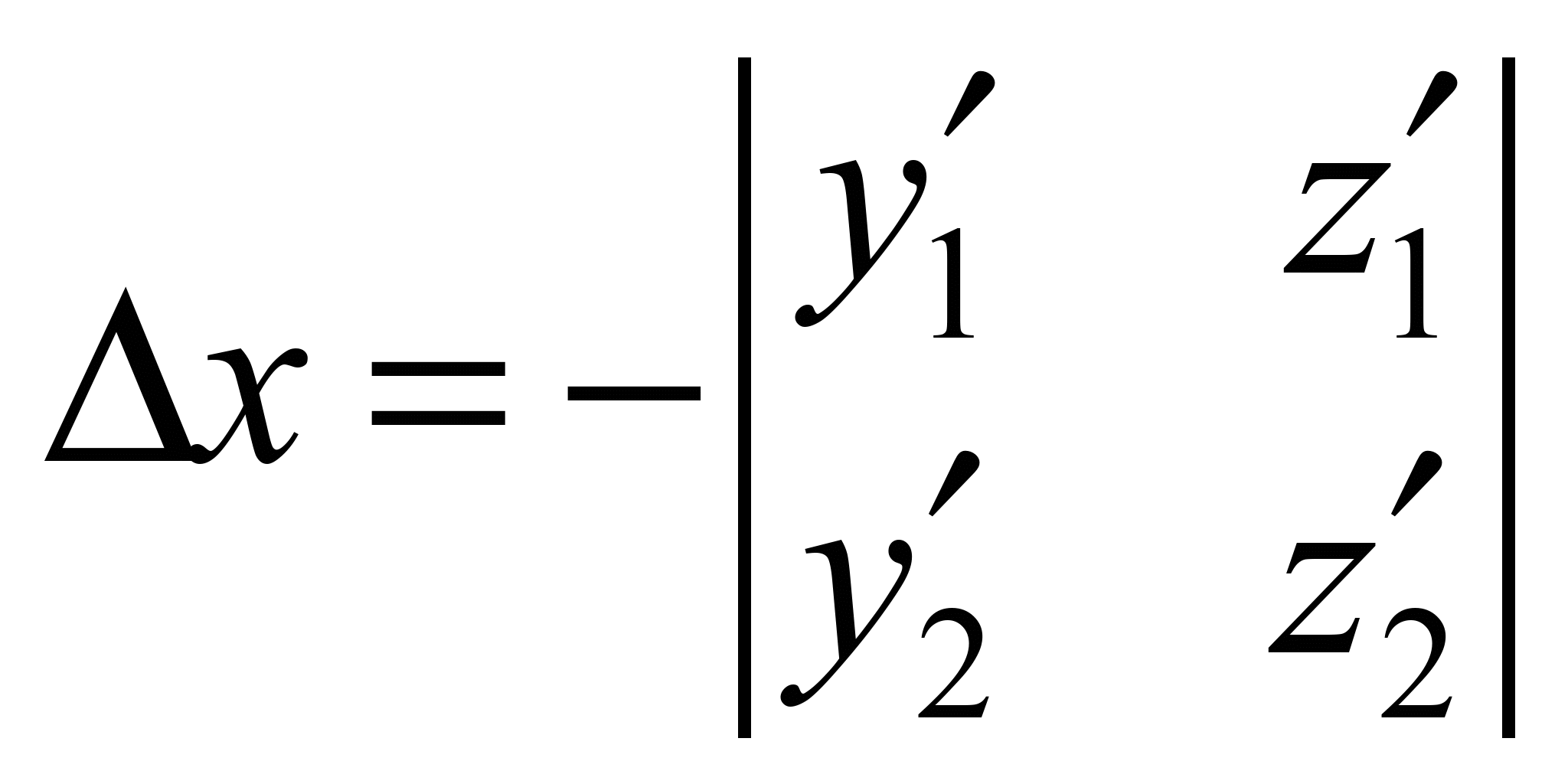 ;
;
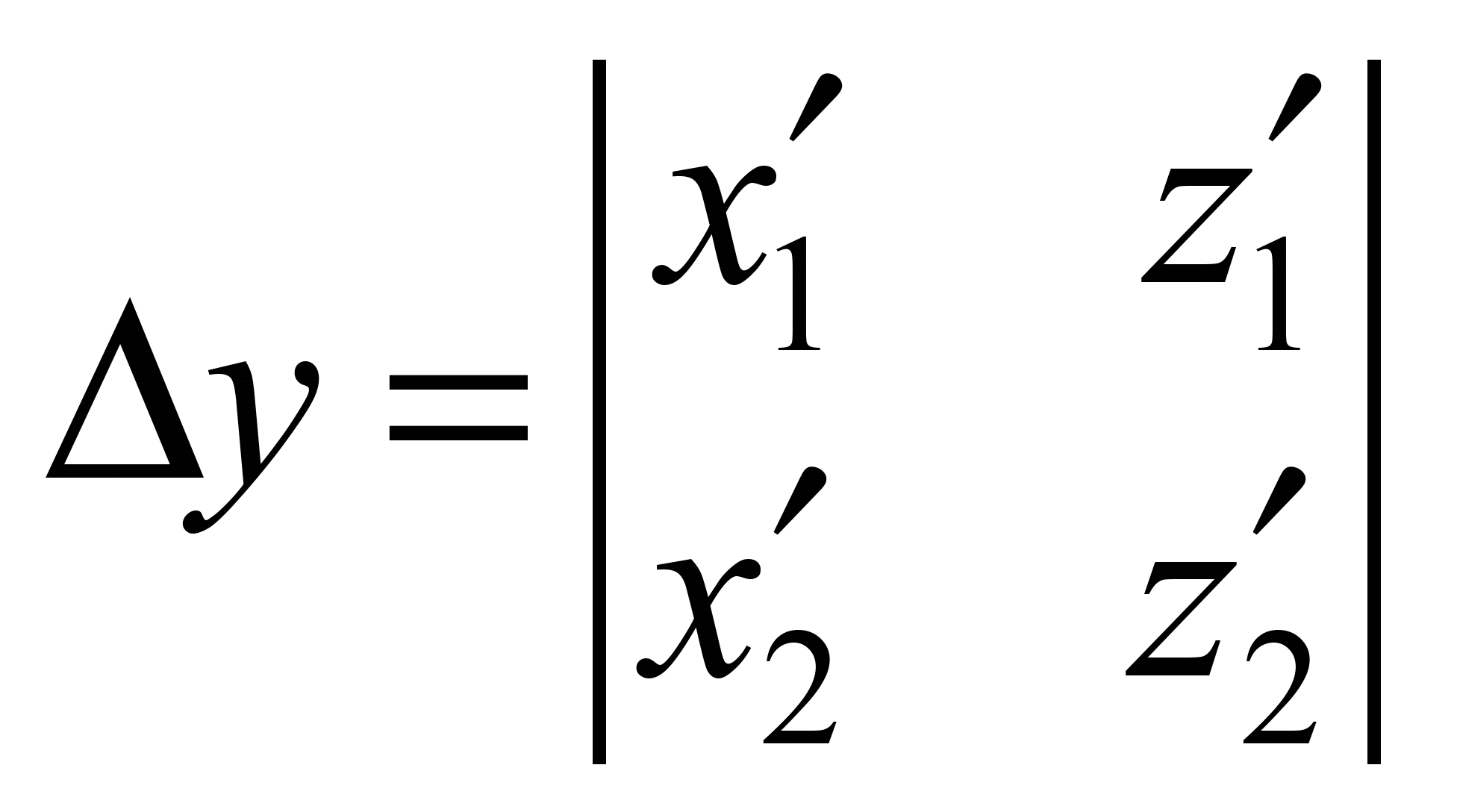 ;
;
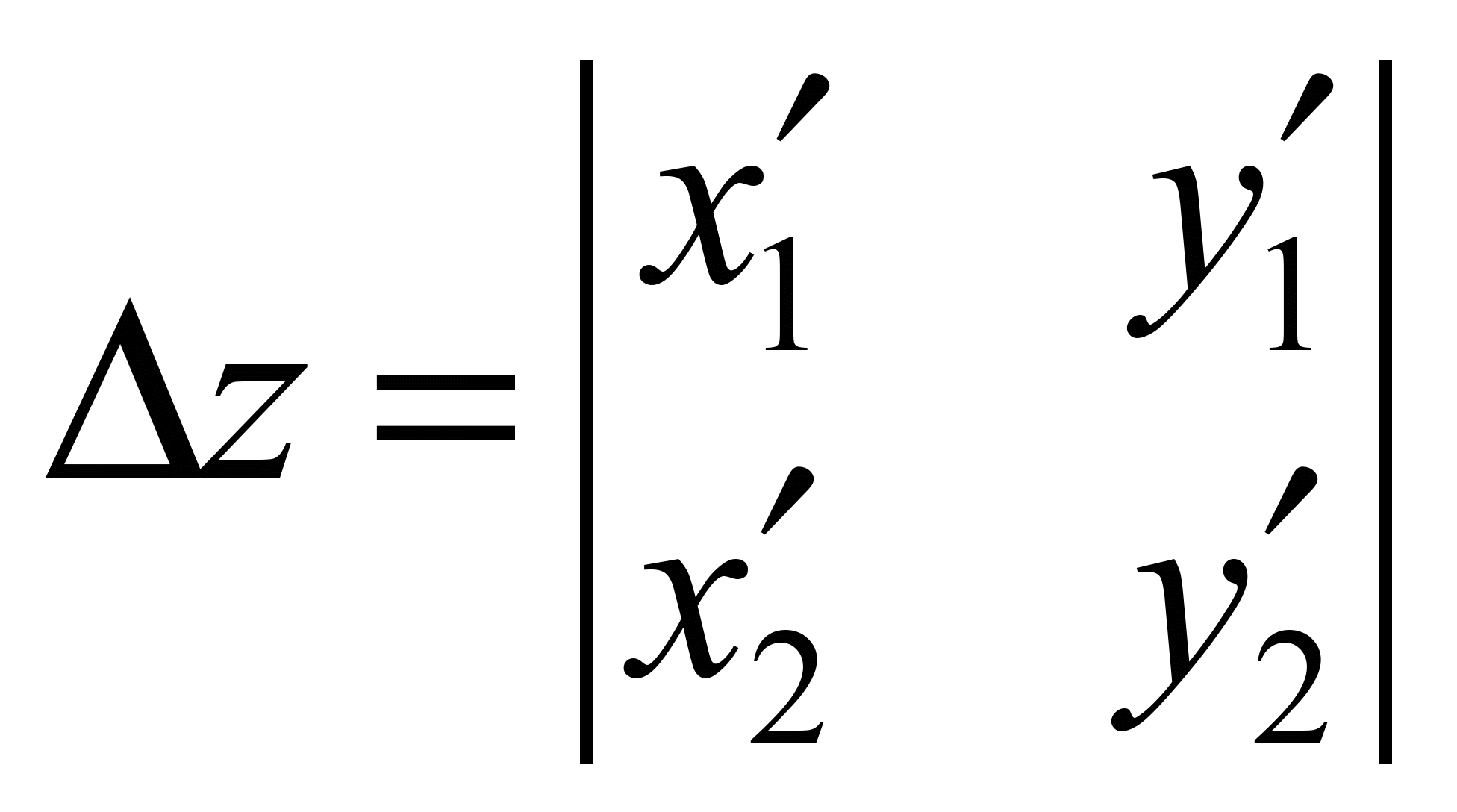 (15)
(15)
Plotting of
the surface is greatly simplified when the guide curves are contour
lines. For example, if
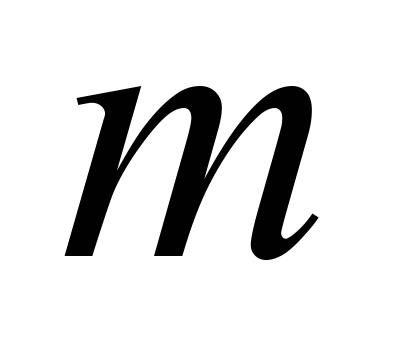 and
and
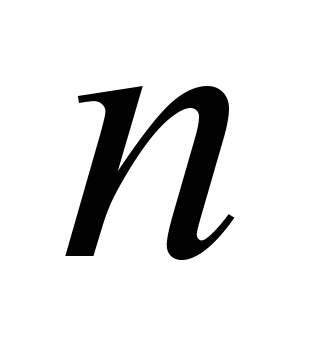 are horizontals, then the condition of a
developable surface is
are horizontals, then the condition of a
developable surface is
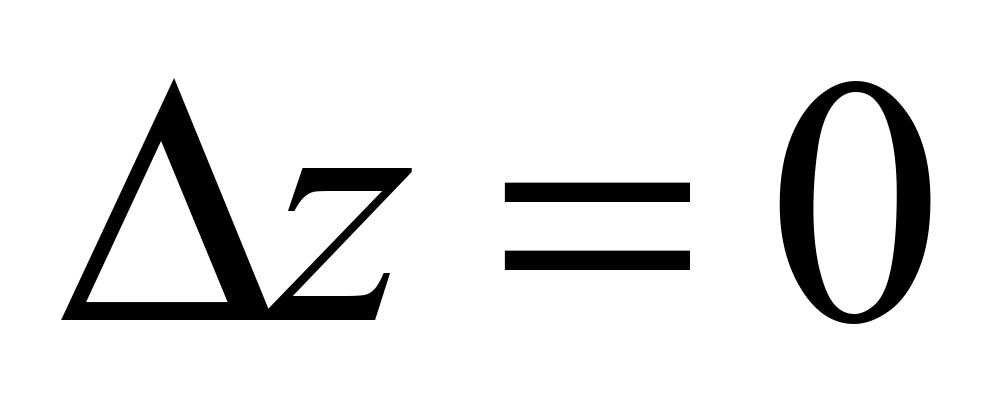 ,
and for the frontals:
,
and for the frontals:
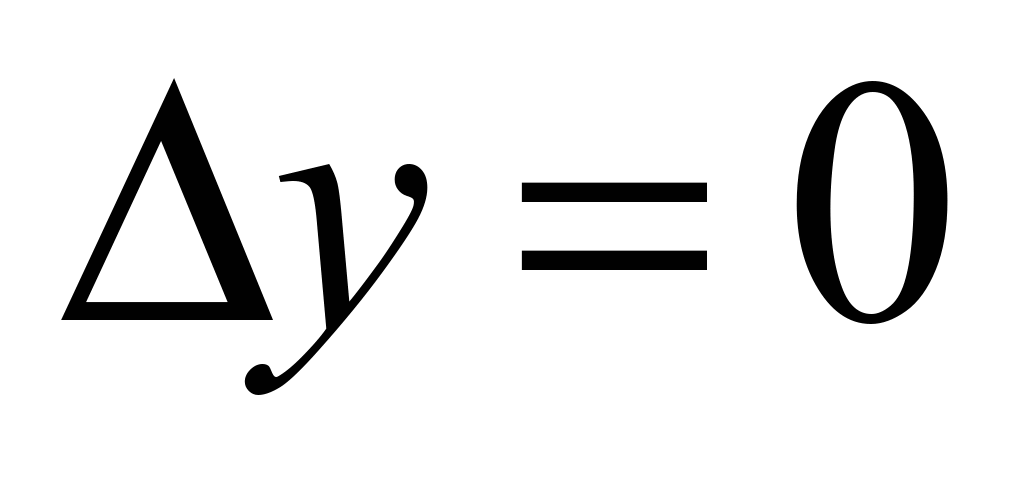 and so on.
and so on.
Algorithm for plotting the
surface.
There are
given
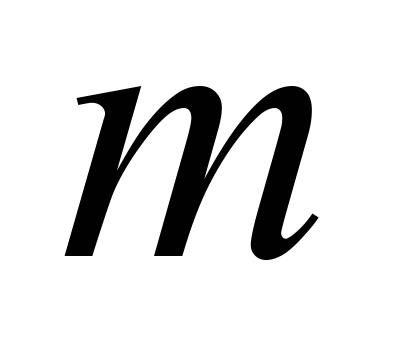 and
and
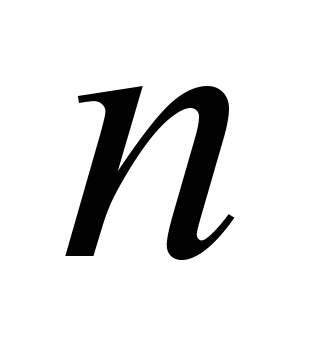 curves
(equation (1) and (2)).
curves
(equation (1) and (2)).
1. We
find the generators
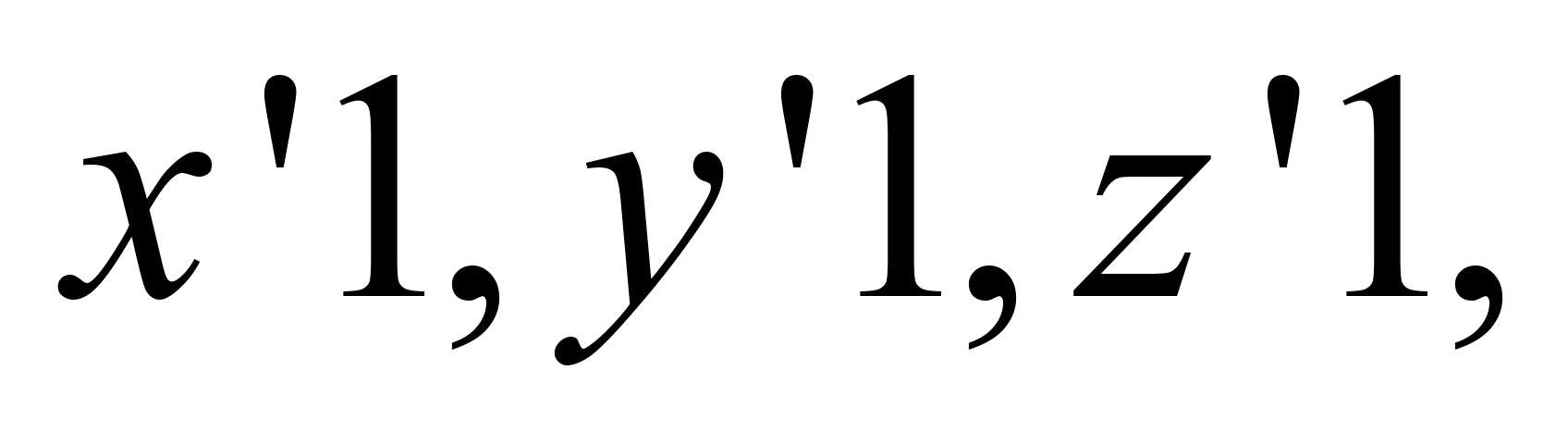
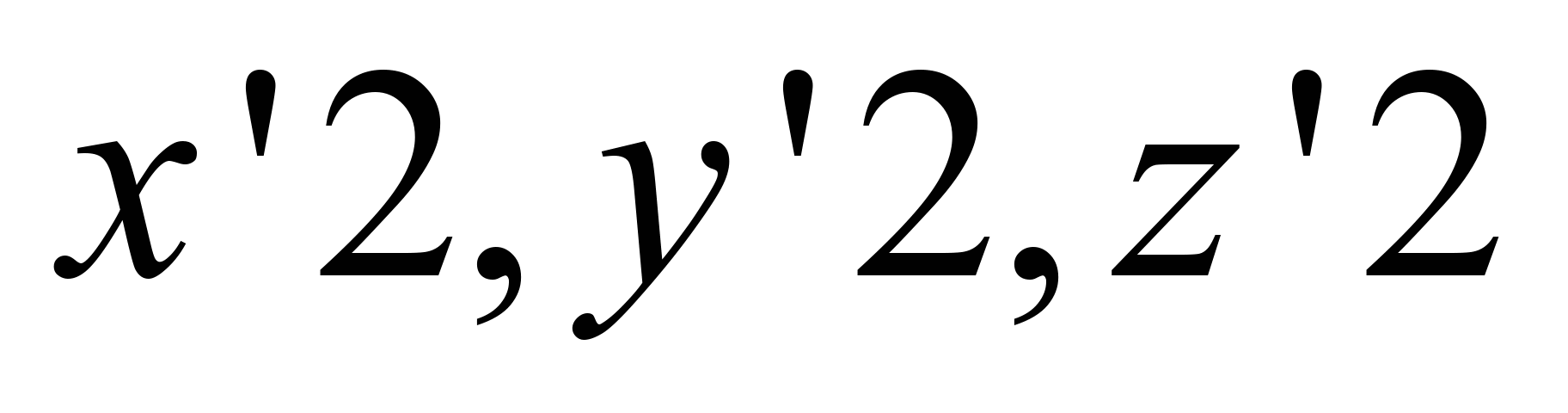 .
.
2. We
add the
determinant (9)
as a
result of
which find
a solution
(10). If the dependence (10) does not
arise from the determinant (9), then the solution does not exist.
3. We
determine the coefficients
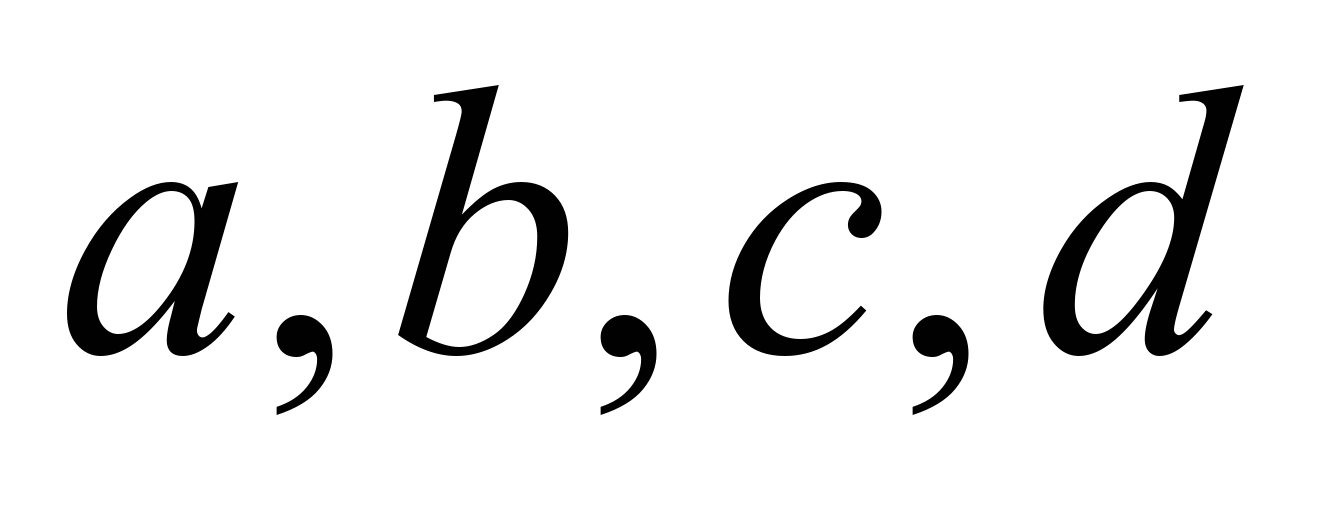 according to (4) and (5).
according to (4) and (5).
4. We
find
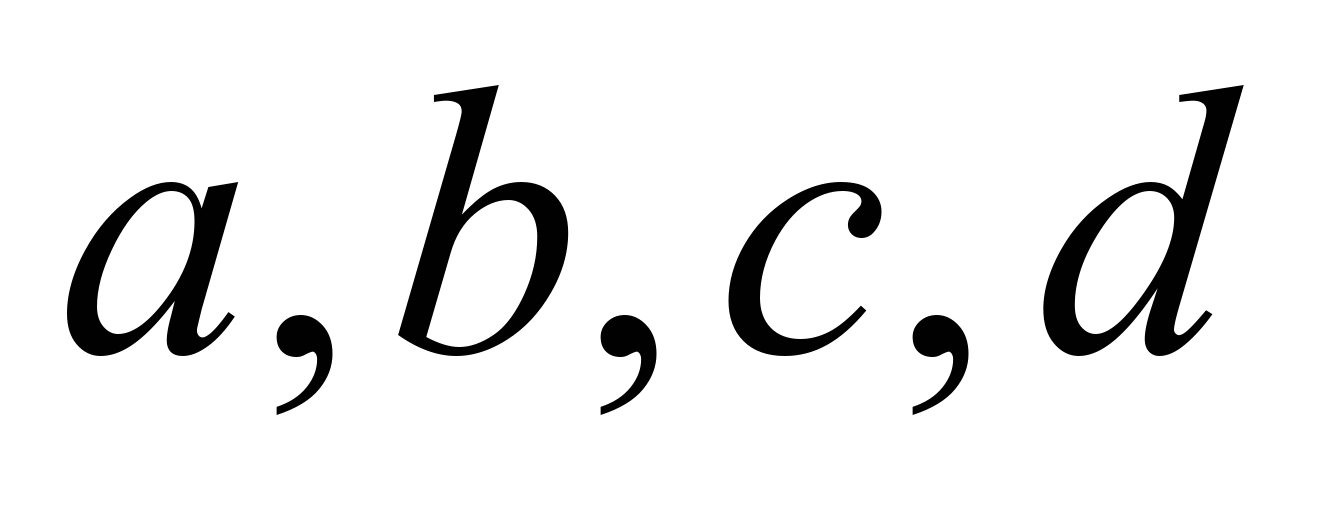 taking into account
(10).
taking into account
(10).
5. We
write the surface equation (3).
The given
model is used for building the semi-digger moldboard of the upper
deck of a double-deck plow PNY-4-40 (Fig. 1), while the lower deck
had digger moldboards. As the guide curves we selected boundary
movement trajectories of soil beds [5,
16, 17].
Findings
The assessment of the operation
quality of the double-deck plow with digger and semi-digger
moldboards of the upper deck was conducted by the following
indicators:
– depth
of plowing
of plant
residues;
– percentage
of plowing
of plant
residues
Experimental
studies have shown the application prospectivity of semi-digger
moldboards on moldboard plows, particularly on the double-deck ones.
Taking into account the operating speed of the plow 2.8 m/s, the
plant residues plowing percentage for plow with semi-digger
moldboards is 98.9%, and with the digger ones – 96.1%, which is
4.3% higher, that is why semi-digger moldboards mounted on the upper
deck of the double-deck plow outweigh the digger moldboards by
agro-technical parameters [19].
Originality
and practical value
1. The
approaches to solving the problem of recognition of wear conditions
of the tested interface, depicted by its conceptual model, were
elaborated; the corresponding algorithms of the computational
procedures were built.
a)
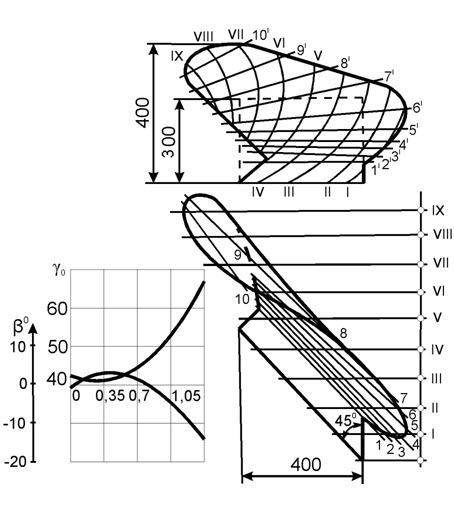
b)
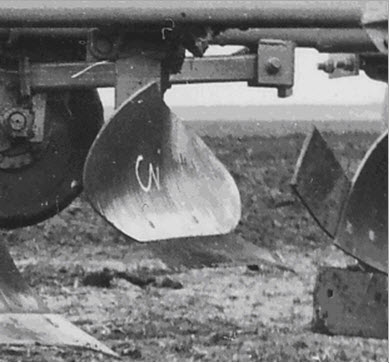
Fig.
1. Semi-digger moldboard of
double-deck plow:
a
–moldboard
drawing;
b
–
general
view
of
semi-digger
moldboard
2. The
mathematical model that determines the effect of the parameters of
the contacting surfaces on their performance properties – linear
wear rate during the normal wear and tear was developed; for this
model the theoretical prerequisite of use for the random mating
study were designated. The process of parametric model optimization
generates a
plurality of desired values of the surface parameters.
3. There
are formed the algorithms for automatic recognition of design
features and operation of interfaces by their images, which are set
by a structured set of formal signs.
The recognition
result
is the interface designation to a particular group, each of which
corresponds to an individual computational model of surface quality
parameters normalization.
Conclusions
1. The
analysed method of putting together the analytic formulas of
specific transformations allows
us to study the converted lines and surfaces using the methods of
analytic geometry.
2. The
designed model of developed surface is expedient to be used for
designing various working elements, including tillage tools.
3. Using
the system, we elaborated the algorithms and compiled the programs
for analytical calculation of line, non-line and equidistant to them
surfaces by given differential geometric terms, which have shown
high efficiency of the system application in solving the above
problems.
4. We
proposed a new equation of patch-wise surface centre without
transitional functions that saves the computing resources and
simplifies the solutions of various geometric and engineering
problems.
LIST OF REFERENCE LINKS
Айзикович,
С.
М.
Внедрение
параболического индентора в неоднородную
полосу, лежащую на упругом основании
/ С. М. Айзикович
,
Ю.
Ч. Ванг, С. С.
Волков
// Соврем.
проблемы механики сплошной среды
: сб. тр. XVII
Междунар.
конф.
(14.10–17.10.2014).
– Ростов-на-Дону
: ЮФУ, 2014. – С. 16–19.
Годес,
А.
Ю.
Напряженно-деформированное
состояние упругой плоскости с дуговой
трещиной между круговым включением и
матрицей
/ А. Ю. Годес, В. В.
Лобода
//
Вісн.
Дніпропетр. ун-ту. Серія: «Механіка».
– Дніпропетровськ, 2013.
–
Вип.
17,
т.
1.
–
С. 3–10.
Голованов,
Н. Н. Геометрическое моделирование /
Н. Н. Голованов. – Москва :
Изд-во физ.-мат. лит., 2002. – 472 с.
Ельфимов,
Г. В. Теория переходных кривых / Г. В.
Ельфимов. – Москва :
Трансжелдориздат, 1948. – 311 с.
Зелёный,
П. В.
Компьютерное моделирование геометрии
движения пахотного агрегата / П. В.
Зелёный, О. К.
Щербакова // Инновац. технологии в
инженер. графике: проблемы и перспективы
: сб. тр. Междунар. науч.-практ. конф., 27
марта 2015 г. – Новосибирск : НГАСУ
(Сибстрин), 2015. – С. 24–26.
Квазилинейные
графические модели пространства / А.
Д. Малый, Ю. Я. Попудняк, Т. В. Ульченко,
Т. В. Старосольская
// Мости та тунелi : теорія, дослідження,
практика. – 2014. – Вип. 5. – С. 51–56.
Котов,
И. И. Методическое пособие по начертательной
геометрии «Алгоритмы конструирования
каркасных поверхностей». – Москва
: Изд-во Моск. авиац. ин-та, 1975.– 63
с.
Котов,
И. И. Начертательная геометрия. Курс
лекций для слушателей ФПК. – Москва
: Изд. Моск. авиац. ин-та, 1973. – 198
с.
Лагута,
В. В. Удосконалення проектування кривих
залізничної колії в плані : автореф.
дис. … канд. техн. наук : 05.22.06 / Лагута
Василь Васильович
; Дніпропетр. держ. техн. ун-т залізн.
трансп. – Дніпропетровськ, 2002. – 18 с.
Найдыш,
В. М. Конструирование поверхностей из
многопараметрических множеств линий
и поверхностей / В. М.
Найдыш // Науч. тр. Укр. с.-х. акад. – Киев,
1980. – Вып. 234. – С. 141–144.
Найдыш,
В. М. Конструирование поверхностей,
проходящих через их специальные линии
/ В. М. Найдыш // Изв. высш.
учеб. завед. Серия: Авиационная
техника. – 1981. – № 2. –
С. 88–90.
Тищенко,
С. С. Геометрическая адаптация
поверхностей почвообрабатывающих
рабочих органов к выполняемому процессу
/ С. С. Тищенко // Вісн. Харк. нац. техн.
ун-ту сіл. госп-ва ім. П. Василенка. –
Харків, 2007. – Вип. 59, т. 1. – С. 110–114.
Тищенко,
С. С. Геометрическая модель адаптивной
поверхности почвообрабатывающего
рабочего органа инцидентной двум
кривым / С. С. Тищенко // Сб. науч. раб.
Крым. гос. ун-та. – Симферополь, 2005. –
Вып. 84. – С. 242–247.
Тищенко,
С. С. Конструирование
поверхности окучника для пропашных
культур по абсолютным траекториям
движения почвы /
С. С. Тищенко, В. В. Карась // Вісн.
Дніпропетр. держ. агроуніверситету. –
2006. – № 1. – С. 27–30.
Трухина,
В. Д. Применение вычислительной техники
при проектировании лемешно-отвальных
поверхностей : учеб.
пособие / В. Д. Трухина ; М-во высш. и
сред. спец. образования РСФСР, Алт.
политехн. ин-т им. И. И.
Ползунова. – Барнаул, 1989. – 82 с.
Brown,
L. D. A
semiparametric multivariate partially linear model: A difference
approach / L.
D. Brown,
M. Levine,
L.
Wang // J.
of Statistical Planning and Inference.
– 2016. – Vol. 178.
– P.
99–111. 10.1016/j.jspi.2016.06.005.
One-to-one
nonlinear transformation the space with identity plane / A. D.
Malyi, T. V. Ulchenko, A. S. Shcherbak [et al.] // Наука та
прогрес транспорту.
– 2016. – № 3 (63). – С. 181–190.
doi:
10.15802/stp2016/74768.
Watson,
D. F. Computing the n-dimensional Delaunay tessellation with
application to Voronoi polytopes / D. F. Watson // The
Computer Journal. – 1981. – Nо.
2. – Р. 167–172.
Xu,
Х. A spatial autoregressive model with a
nonlinear transformation of the dependent variable / Х.
Xu, L. Lee // Journal of Econometrics. –
2015. – Vol.
186. – Iss.
1. – P. 1–18. doi:
10.1016/j.jeconom.2014.12.005.
С. С. Тищенко1, А. В. краснюк2,
Т. В. УЛЬЧЕНКО3, А. С. Щербак4*
1Каф.
«Вища математика», Дніпропетровський
державний аграрно-економічний
університет,
вул. Ворошилова, 25,
Дніпро, Україна, 49600, тел. +38
(056) 713 51 86, ел. пошта
mozganet@mail.ua,
ORCID 0000-0003-4860-4818
2Каф.
«Графіка», Дніпропетровський національний
університет залізничного транспорту
імені академіка В. Лазаряна, вул.
Лазаряна, 2, Дніпро, Україна, 49010,
тел.
+38 (056) 373 15 38, ел. пошта
krasnyuk@mail.diit.edu.ua, ORCID 0000-0002-1400-9992
3Каф.
«Графіка», Дніпропетровський національний
університет залізничного транспорту
імені академіка В. Лазаряна, вул.
Лазаряна, 2, Дніпро, Україна, 49010, тел.
+38 (067) 724 47
22,
ел. пошта ulchenkotv@ya.ru, ORCID
0000-0003-2354-7765
4*Каф.
«Графіка», Дніпропетровський національний
університет залізничного транспорту
імені академіка В. Лазаряна, вул.
Лазаряна, 2, Дніпро, Україна, 49010, тел.
+38 (056) 373 15
59,
ел. пошта pro-f@ukr.net, ORCID 0000-0003-1340-0284
ПРОЕКТУВАННЯ РОЗГОРТНИХ
ПОВЕРХОНЬ
ДЕТАЛЕЙ СКЛАДНОЇ ФОРМИ
Мета. У
статті необхідно розглянути забезпечення
раціонального вибору параметрів
поверхонь, що сполучаються, та оброблюваних
деталей при проектуванні технологічного
обладнання на основі методів штучного
інтелекту. Методика.
В роботі розглядається геометрична
модель лінійчатої розгортної поверхні,
умови існування такої поверхні та
приводиться узагальнений алгоритм
побудови поверхні, незалежно від типу
робочого органу або машинобудівного
виробу. Одними з найбільш поширених у
техніці поверхнями є лінійчаті, серед
яких особливе положення займають
розгортні (завдяки своїм
диференціально-параметричним
властивостям): дотична площина контактує
з поверхнею вздовж всієї прямолінійної
твірної та не змінює свого положення
у просторі при зміні точки дотику;
поверхні можуть виготовлятись методом
згину металевого листа. Ці положення
дозволяють при виготовленні виробів
заощаджувати значні матеріальні та
енергетичні кошти, тому розробка
геометричних моделей таких поверхонь
є важливою задачею. Результати.
Авторами розглянуто геометричну модель
розгортної поверхні, яка інцидентна
двом напрямним. Експериментальні
дослідження показали перспективність
застосування напівгвинтових полиць
на поличних плугах, зокрема, на двоярусних.
Приймаючи до уваги робочу швидкість
руху плугу 2,8 м∕с, відсоток заорювання
рослинних решток для плугу з напівгвинтовими
полицями складає 98,9 %, а з культурними
– 96,1 %. Наукова новизна.
За результатами експерименту: 1) вироблені
підходи до вирішення задачі
розпізнавання умов зношування
досліджуваного сполучення, зображеного
його концептуальною моделлю; 2)
побудовані відповідні алгоритми
обчислювальних процедур; 3) розроблено
математичну модель, яка визначає вплив
параметрів контактуючих поверхонь на
їх експлуатаційну властивість – лінійну
інтенсивність зношування в період
нормального зносу; 4) для даної моделі
позначені теоретичні передумови
застосування в дослідженні довільного
сполучення. Практична
значимість. На даний
час у цих напрямках отримані серйозні
результати, які стоять на рівні сучасних
вимог конструкторського проектування.
В процесі параметричної оптимізації
моделі формується безліч шуканих
значень параметрів поверхонь. Сформовані
алгоритми автоматичного розпізнавання
особливостей конструкції та експлуатації
сполучень за їх зображеннями, що
задається структурованими сукупностями
формалізованих ознак. Результатом
розпізнавання є віднесення сполучення
до певної групи, кожній з множин яких
відповідає індивідуальна розрахункова
модель нормування параметрів якості.
Ключові слова: геометрія;
поверхні; розгортні поверхні; модель;
робочі органи
С. С. Тищенко1, А. В. краснюк2,
Т. В. УЛЬЧЕНКО3, А. С. Щербак4*
1Каф.
«Высшая математика», Днепропетровский
государственный
аграрно-экономический
университет, ул. Ворошилова, 25, Днипро,
Украина, 49600, тел. +38 (056)
713 51 86, эл. почта mozganet@mail.ua,
ORCID 0000-0003-4860-4818
2Каф.
«Графика», Днепропетровский национальный
университет
железнодорожного транспорта
имени академика
В. Лазаряна, ул.
Лазаряна, 2, Днипро, Украина, 49010,
тел.
+38 (056) 373 15
38, эл. почта krasnyuk@mail.diit.edu.ua,
ORCID 0000-0002-1400-9992
3Каф.
«Графика», Днепропетровский национальный
университет
железнодорожного транспорта
имени академика
В. Лазаряна, ул.
Лазаряна, 2, Днипро, Украина, 49010,
тел.
+38 (067) 724 47
22, эл. почта ulchenkotv@ya.ru,
ORCID
0000-0003-2354-7765
4Каф.
«Графика», Днепропетровский
национальный университет
железнодорожного
транспорта имени академика
В. Лазаряна,
ул. Лазаряна, 2, Днипро, Украина, 49010,
тел.
+38 (056) 373 15
59, эл. почта pro-f@ukr.net,
ORCID 0000-0003-1340-0284
ПРОЕКТИРОВАНИЕ РАЗВЕРНУТЫХ
ПОВЕРХНОСТЕЙ ДЕТАЛЕЙ
СЛОЖНОЙ ФОРМЫ
Цель. В
статье необходимо рассмотреть обеспечение
рационального выбора параметров
сопрягаемых поверхностей обрабатываемых
деталей при проектировании технологического
оборудования на основе методов
искусственного интеллекта. Методика.
В работе рассматривается геометрическая
модель линейчатой развернутой
поверхности, условия существования
такой поверхности и приводится обобщенный
алгоритм построения поверхности,
независимо от типа рабочего органа или
машиностроительного изделия. Одними
из наиболее распространенных в технике
поверхностей являются линейчатые,
среди которых особое положение
занимают развернутые (благодаря
своим дифференциально-параметрическим
свойствам):
касательная плоскость соприкасается
с поверхностью
вдоль всей прямолинейной образующей
и не меняет своего положения в пространстве
при изменении точки соприкосновения;
поверхности могут изготавливаться
методом сгиба металлического листа.
Эти положения позволяют при изготовлении
изделий экономить значительные
материальные и энергетические средства,
поэтому разработка геометрических
моделей таких поверхностей является
важной задачей. Результаты.
Авторами рассмотрена геометрическая
модель развернутой поверхности, которая
инцидентна двум направляющим.
Экспериментальные исследования показали
перспективность применения полувинтовых
полок на полочных плугах, в частности,
на двухъярусных.
Принимая во внимание рабочую скорость
движения плуга 2.8 м/с, процент запахивания
растительных остатков для плуга с
полувинтовыми полками составляет 98,9
%, а с культурными – 96,1%. Научная
новизна. По результатам
эксперимента: 1) выработаны
подходы к решению задачи распознавания
условий изнашивания исследуемого
сопряжения, изображаемого его
концептуальной моделью; 2) построены
соответствующие алгоритмы вычислительных
процедур; 3) разработана
математическая модель, определяющая
влияние параметров контактирующих
поверхностей на их эксплуатационное
свойство – линейную интенсивность
изнашивания в период нормального
износа; 4) для
данной модели обозначены теоретические
предпосылки применения к исследованию
произвольного сопряжения. Практическая
значимость. В настоящее
время по этим направлениям получены
серьезные результаты, которые находятся
на уровне современных требований
конструкторского проектирования. В
процессе параметрической оптимизации
модели формируется множество искомых
значений параметров поверхностей.
Сформированы алгоритмы автоматического
распознавания особенностей конструкции
и эксплуатации сочетаний по их
изображениям, которые задаются
структурированными совокупностями
формализованных признаков. Результатом
распознавания является отношение
сопряжения к определенной группе,
каждой из множества которых соответствует
индивидуальная расчетная модель
нормирования параметров качества.
Ключевые слова: геометрия;
поверхности; развернутые поверхности;
модель; рабочие органы
REFERENCES
Ayzikovich, S. M., Vang, Y. C., &
Volkov, S. S. (2014). Vnedreniye
parabolicheskogo indentora v neodnorodnuyu polosu, lezhashchuyu na
uprugom osnovanii. Proceedings of the
XVII International Conference on Sovremennye problemy mekhaniki
sploshnoy sredy, October 14-17, 2014, Rostov-on-Don.
16-19.
Rostov-on-Don:
Southern Federal University.
Godes,
A. Y., & Loboda, V. V. (2013). Napryazhenno-deformirovannoye
sostoyanie uprugoy ploskosti s dugovoy treshchinoy mezhdu krugovym
vklyucheniem i matritsey. Bulletin of
Dnipropetrovsk University, Series Mechanics, 17
(1), 3-10.
Golovanov,
N. N. (2002). Geometricheskoye
modelirovanyie. Moscow: FIZMATLIT.
Yelfimov,
G. V. (1948). Teoriya perekhodnykh
krivykh. Moscow: Transzheldorizdat.
Zelenyy,
P. V., & Shcherbakova, O. K. (2015). Kompyuternoye
modelirovaniye geometrii dvizheniya pakhotnogo agregata.
Proceedings of the International
Conference on Innovatsionnyye tekhnologii v inzhenernoy grafike:
problemy i perspektivy, March 27, 2015, Novosibirsk.
24-26. Novosibirsk: NGASU (Sibstrin).
Malyi,
А. D., Popudniak, Y. Y., Ulchenko, Т. V., & Starosol’ska Т.
V. (2014). Quasilinear
graphic models of space. Bridges
and Tunnels: Theory, Research, Practice,
5,
51–56.
Kotov,
I. I. (1975). Algoritmy
konstruirovaniya karkasnykh poverkhnostey: Metodicheskoye posobiye
po nachertatelnoy geometrii. Moscow:
MAI.
Kotov,
I. I. (1973). Nachertatelnaya
geometriya: Kurs lektsiy dlya slushateley FPK.
Moscow: MAI.
Laguta,
V. V. (2002). Improvement of designing
of the railway curves in a plan. (PhD
thesis). Available from Dnipropetrovsk National University of
Railway Transport named after Academician V. Lazaryan,
Dnipropetrovsk.
Naydysh,
V. M. (1980). Konstruirovaniye poverkhnostey iz
mnogoparametricheskikh mnozhestv liniy i poverkhnostey. Nauchnyye
trudy Ukrainskoy selskokhozyaystvennoy akademii,
234,
141-144.
Naydysh,
V. M. (1981). Konstruirovaniye poverkhnostey, prokhodyashchikh
cherez ikh spetsialnyye linii. Izvestiya
vysshikh uchebnykh zavedenii:
Aviatsionnaya Tekhnika,
2,
88-90.
Tishchenko,
S. S. (2007). Geometricheskaya adaptatsiya poverkhnostey
pochvoobrabatyvayushchikh rabochikh organov k vypolnyaemomu
protsessu. Visnyk Kharkivskoho
natsionalnoho tekhnichnoho universytetu silskoho hospodarstva im.
P. Vasylenka, 59(1),
110-114.
Tishchenko,
S. S. (2005). Geometricheskaya model adaptivnoy poverkhnosti
pochvoobrabatyvayushchego rabochego organa intsidentnoy dvum
krivym. Sbornik nauchnykh rabot
Krymskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta,
84,
242-247.
Tishchenko,
S. S., & Karas, V. V. (2006). Konstruirovaniye poverkhnosti
okuchnika dlya propashnykh kultur po absolyutnym traektoriyam
dvizheniya pochvy. News of
Dnipropetrovsk State Agrarian and Economic University,
1,
27-30.
Trukhina,
V. D. (1989). Primeneniye
vychislitelnoy tekhniki pri proyektirovanii lemeshnootvalnykh
poverkhnostey. Barnaul: API.
Brown,
L. D., Levine, M., & Wang, L. (2016). A semiparametric
multivariate partially linear model: A difference approach. Journal
of Statistical Planning and Inference,
178, 99-111.
doi:10.1016/j.jspi.2016.06.005
Malyi,
A. D., Ulchenko, T. V., Shcherbak, A. S., Popudniak, Y. Y., &
Starosolskaya, T. V. (2016). One-to-one nonlinear transformation
the space with identity plane. Science
and Transport Progress, 3(63),
181-190. doi:
10.15802/stp2016/74768
Watson,
D. F. (1981). Computing the n-dimensional Delaunay tessellation
with application to Voronoi polytopes. The
Computer Journal, 24(2),
167-172. doi:
10.1093/comjnl/24.2.167
Xu,
X., & Lee, L. (2015). A spatial autoregressive model with a
nonlinear transformation of the dependent variable. Journal
of Econometrics, 186(1),
1-18. doi: 10.1016/j. jeconom.2014.12.005
Prof. M. V. Shchpyrko, D.
Sc. (Tech.), (Ukraine); Prof. V. D. Petrenko, D. Sc. (Tech.)
recommended this article to be published)
Accessed:
Dec. 14,
2016
Received:
March 23,
2017
,
,
, (1)
,
,
, (2)
,
. (3)
depend on
and
and are determined by the equations (1) and (2), (3), so that,
;
; (4)
;
. (5)
, (6)
, (7)
. (8)
, (9)
and
provided the
surface
developability:
, (10)
)
can be from (10) expressed clearly through the other parameter,
, (11)
,
. (12)
:
. (13)
);
of the
first two
rows of
the determinant
(9) are the
coordinates of
the surface
standard
,
so that
,
, (14)
;
;
(15)
and
are horizontals, then the condition of a
developable surface is
,
and for the frontals:
and so on.
and
curves
(equation (1) and (2)).
.
according to (4) and (5).
taking into account
(10).